Experimental study on migration and deposition of particles under alternating dynamic and static loads
-
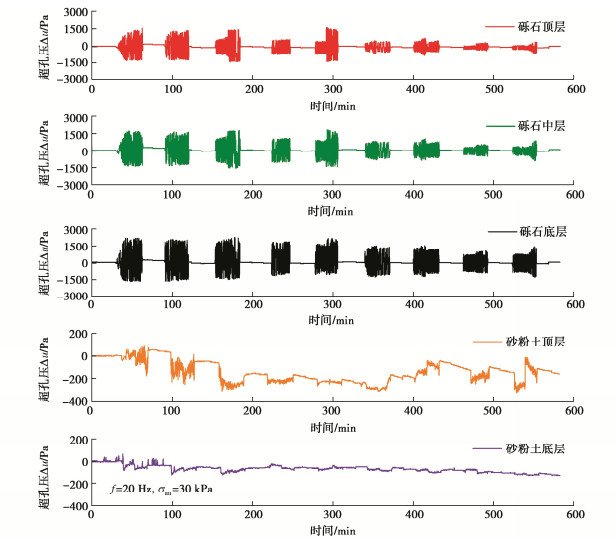
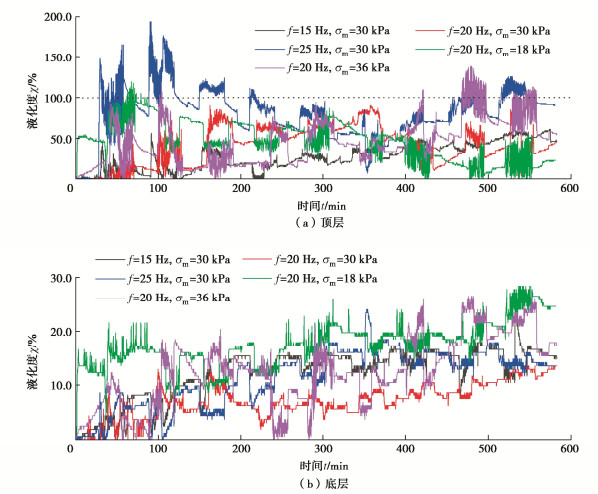
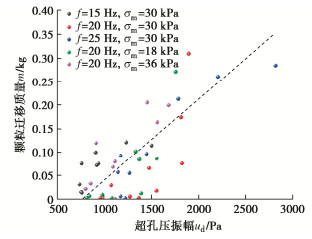
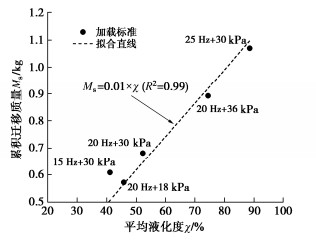
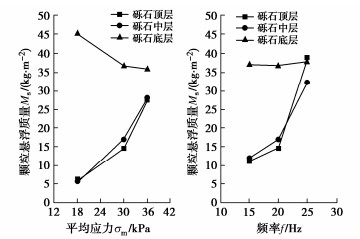
摘要: 悬浮颗粒在路基中迁移和沉积运动规律研究对揭示翻浆冒泥病害孕育、发展与致灾机制具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。通过开展动-静组合荷载下分层砾石-砂粉土柱翻浆试验,探究了动荷载加载强度、静荷载间歇时长、以及动静组合加载重复次数等对颗粒迁移和沉积行为的影响规律,并结合试样动水力响应特征分析了诱发颗粒迁移的驱动机制。试验结果表明:颗粒在动水力作用下发生悬浮迁移而在静荷载段受重力作用发生沉降,从而造成砾石层内泥浆浊度呈现波动型增长特征。随动静组合加载重复次数增加,每一个重复周期内的颗粒悬浮增量趋于降低,且悬浮颗粒逐渐堵塞砾石孔隙并在一定程度上抑制翻浆发展。提高动载频率和动应力会进一步降低砂粉土表层的内部稳定性,但相比于增大平均动应力,提高加载频率对增大颗粒迁移量和竖向迁移距离更加显著。Abstract: The study on the migration and deposition of suspended particles in subgrade is important to reveal the generation and disaster-causing mechanism of mud pumping. The effects of magnitude of dynamic loads, intermittent duration of static loads and repetition number of alternating dynamic and static loads on the migration and deposition of particles are studied by carrying out the mud pumping tests on the layered gravel-sandy silt column. According to the hydrodynamic response characteristics of specimens, the driving mechanism of particle migration is analyzed. The test results show that the suspended particles migrate upward under hydrodynamic force and settle under gravity during the interval of static loads, which results in the fluctuating growth of slurry turbidity in the gravel layer. The particle suspension increment tends to decrease with the increasing repetition of alternating dynamic and static loads, and these particles gradually clog gravel pores and inhibit mud pumping to a certain extent. Increasing the dynamic frequency and stress can further reduce the internal stability of the sandy silt surface layer. However, compared with increasing the dynamic stress, increasing the loading frequency is more beneficial to increase the particle migration mass and vertical migration distance.
-
Keywords:
- mud pumping /
- laboratory test /
- particle migration /
- excess pore pressure
-
0. 引言
当前中国隧道建设方兴未艾,工程中出现了不少多洞近距离并行设置的情况。隧道建设期间,相邻隧道净距较小时,将存在明显的相互影响,降低围岩稳定性。多洞并行隧道围岩稳定性及失稳破坏机理问题,亟需从理论计算分析等方面开展深入研究,以促进围岩稳定性评价及加固方案制定等工作。
对于隧道围岩稳定性课题,岩土塑性极限分析上限法可用于探究极限状态下隧道临界荷载与围岩潜在破坏模式[1-9]。在并行隧道方面,谢骏等[10]构建了双洞并行圆形隧道的破坏模式,获得了稳定性系数上限解;吕绍文[11]应用平移破坏模式推导了双洞平行隧道内部支护力上限解表达式;Osman[12]提出了双洞并行隧道连续变形破坏模式;Yamamoto等[13]采用刚性滑块上限法和极限分析上、下限有限元法研究了双洞圆形隧道稳定性;Sahoo等[14]应用极限分析上限有限元法分析了双洞并行隧道的稳定性;Zhang等[15]和Yang等[16]采用刚体平动运动单元上限法评价了多参数影响下的并行双洞椭圆和圆形隧道稳定性,获得了围岩滑移线网破坏模式。
隧道围岩稳定性评价可分为强度折减法[17]获得安全系数和荷载增加法对应的稳定系数。上述研究多采用荷载增加法,考虑了隧道内部支护力[10-12]、地表超载[13, 16]和围岩自重[14-15]等因素的影响。对于双洞并行隧道围岩稳定性的文献报道,还包括应用计算分析[18]和模型试验[19]等研究手段。
由于铁路、公路及市政交通廊道的空间限制,工程中出现了三洞并行小净距隧道[20-23], 甚至四洞并行的情况[24]。此时,小净距条件下相邻隧道相互影响集中体现在中夹岩区域的稳定性,净间距对围岩潜在破坏模式的影响较之并行双洞的情况更加显著,需开展定量分析研究。
本文针对多洞隧道围岩稳定性问题,考虑自重作用下并行等间距毛洞隧道的简化模型,利用刚体平动运动单元上限法[9, 25]开展系统分析,探讨多洞净间距S、隧道埋深H及围岩强度等综合参数对稳定性的影响规律,并绘制稳定系数Ncr图表,以期从定量角度揭示围岩滑移线网破坏模式的演化过程,为多洞并行隧道设计、施工和加固方案的制定等问题提供数据支撑。
1. 刚体平动运动单元上限法
刚体平动运动单元上限法[9, 25](简称UB-RTME)属岩土破坏塑性极限分析上限理论范畴。采用“刚体平动三角形单元+速度间断线”的方式离散计算域,设置节点坐标与单元速度作为优化变量,通过极限状态虚功率平衡和内部耗散能最小化获取目标函数的表达式,同时满足速度间断线塑性流动约束、网格形态控制约束以及模型速度约束,建立非线性规划求解极限荷载的上限解。
非线性规划运算亦是搜索极限状态滑移线网的过程,须以多次的网格更新实现。主要包括无效单元合并与剔除、有效单元再次加密以及网格继承与修正等三类网格更新策略。计算流程如图 1。
2. 多洞并行隧道围岩稳定性模型
2.1 问题描述
多洞并行隧道工程修建过程中,一般各单洞开挖面相互错开,属于三维空间的施工力学问题。为便于从保守角度分析围岩稳定性与破坏机理,这里作如下简化:
(1)不计施工过程,稳定性分析模型简化为平面应变问题,且多洞并行隧道按等间距设置。
(2)圆形隧道直径均为D,相邻隧道净间距均为S,地表水平且埋深均为H。
(3)围岩为均质连续的莫尔-库仑材料,强度指标为内摩擦角ϕ和黏聚力c。
(4)不考虑地下水及衬砌支护作用。
(5)按重度增加法评价围岩失稳临界状态。
如图 2,经概化的模型旨在探究围岩自重作用下的自承性能及多洞隧道潜在破坏模式的规律,以净间距S增加趋势反映中夹岩至单个隧道独立承载的演变过程,计算分析采用基于网格更新的刚体平动运动单元上限法。
2.2 运动单元上限法计算模型
如图 2(a),考虑模型对称性,对部分区域进行建模分析,建立多洞并行隧道围岩稳定性上限分析与计算模型如图 2(b)所示。图中未显示三角形网格,模型水平和竖向尺寸分别为D/2+S/2和H+D+L,其中L确定了下部范围,其值随H值变化以消除边界效应。地表(边界6)为水平自由地表,边界1,3,5均为模型对称轴,将其水平速度设为0;模型底部(边界4)水平和竖向速度均设为0。
仅考虑围岩自重荷载,按重度增加法施加体力约束为
ne∑i=1Aivi=−1,Ai>0 (i=1,⋯,ne)。 (1) 式中:γcr=nd∑i=1Pd,i=cnd∑i=1ξ″i为三角形刚体单元i的面积,其数值恒大于零,γcr=nd∑i=1Pd,i=cnd∑i=1ξ″i为单元i的竖向速度分量,γcr=nd∑i=1Pd,i=cnd∑i=1ξ″i为模型单元总数。
依极限分析上限定理,将模型所有速度间断线耗散能之和最小化,获得运动单元上限法对应的非线性规划目标函数,也就是临界重度γcr:
γcr=nd∑i=1Pd,i=cnd∑i=1ξ″i。 (2) 为方便分析,借鉴文献[14]的定义,令稳定系数Ncr=γcrH/c,即临界重度γcr和隧道埋深H乘积与黏聚力c的比值,它是内摩擦角ϕ、埋深比H/D和净距比S/D的函数,具体求解时,Ncr还可表示为
Ncr=γcrH/γcrHcc=Hnd∑i=1ξ″i。 (3) 式(2),(3)中:Pd,i为第i条速度间断线上耗散能;nd为速度间断线总数;ξi′′和ξi′为第i条速度间断线的过程变量,其表达式和约束条件为
Δxi=x′i−x″i, Δyi=y′i−y″i , (4a) ξ′i=Δxiuy,i+Δyivy,i−Δxiuz,i−Δyivz,i , (4b) ξ″i=(−Δyiuy,i+Δxivy,i+Δyiuz,i−Δxivz,i)/tanϕ , (4c) ξ″i+ξ′i≥0 , ξ″i−ξ′i≥0 。 (4d) 式中:(x′i, y′i)为第i条间断线的第一端点坐标,(x″i, y″i)为第二端点坐标; i=1,⋯,nd。于是,以第一端点指向第二端点为正方向,顺时针和逆时针一侧的两个刚性单元对应的速度分量分别为(uy, i, vy, i)和(uz, i, vz, i),。
式(4)满足了速度间断线上的相关联流动约束:Δvi=|Δui|tanϕ。须知,所有间断线均施加该约束。
求解运动单元上限分析模型(见图 2(b))对应的非线性规划问题时,还需施加边界速度和几何约束:
u1,i=0 , x1,j=0 , D/2≤y1,j≤D/2+H (i=1,⋯,n1; j=1,⋯,n1+1) , (5a) u3,i=0 ,x3,j=0 , −D/2−L≤y3,j≤−D/2 (i=1,⋯,n3, j=1,⋯,n3+1) , (5b) u4,i=0 , v4,i=0 , 0≤x4,j≤D/2+S/2 , y4,j=−D/2−L (i=1,⋯,n4 , j=1,⋯,n4+1) , (5c) u5,i=0 , x5,j=D/2+S/2 , −D/2−L≤y5,j≤D/2+H (i=1,⋯,n5 , j=1,⋯,n5+1) , (5d) 0⩽x6,j⩽D/D22+S/D/D22+S22, y6,j=D/D22+H (j=1,⋯,n6+1) , (5e) 4(x2,j/)D2+4(y2,j/D)2=1 (j=1,⋯,n2+1) 。 (5f) 式中:u1,i为边界1第i条边一侧单元的水平向速度,n1表示边界1上施加约束的单元边总数;而x1,j和y1,j为边界1上第j个节点的坐标,式(5b)~(5f)同此命名。式(5a)~(5f)中的几何约束即限定边界上的单元节点坐标只能于相应边界上移动。如式(5f)圆方程限制隧道轮廓(边界2)上的节点只能在圆周上移动。除地表和隧道圆周轮廓上自由外,其余边界速度约束见式(5a)~(5d)。
多洞并行隧道围岩稳定性计算在既有程序基础上,设置式(1),(5)对应的速度和几何边界条件即可开展后续计算[20]。
3. 多洞并行隧道围岩稳定系数Ncr
3.1 稳定系数Ncr变化规律
采用刚体平动运动单元上限法开展了2000余组参数条件下的多洞并行等间距隧道围岩稳定性计算,获得稳定系数Ncr与内摩擦角ϕ、埋深比H/D和净间距比S/D的关系曲线如图 3所示。选取的计算参数ϕ取值5°~30°,H/D取值2~10;S/D取值依从于H/D的变化,即不断增大S/D值依次计算直至相邻隧道的相互影响消失。此外,当接近单洞独立破坏状态时,S/D取值间隔适当减小。
图 3(a)~3(i)分别为H/D=2~10对应的稳定系数Ncr曲线图。总体上看,随着隧道埋深比H/D的增大,相邻隧道相互影响的净间距比S/D范围变大,这与埋深增加上覆围岩荷载增大有关。净间距比S/D与稳定系数Ncr的关系可分述如下:①当S/D较小时(如S/D= 0.25),无论H/D和ϕ如何变化,Ncr值总是接近于0。这缘于中夹岩很窄,上覆岩层主要以自重荷载的形式作用于其上,从而围岩整体稳定性变差。②当S/D增大达到单洞隧道独自破坏的转化间距比Str/D时,Ncr增加至最大值且等于相同条件下单洞隧道围岩稳定系数Ncr(single),此时S/D继续增加,而Ncr值将不再变化。③当S/D小于Str/D时,Ncr值随着S/D增加而逐渐增大,且较之S/D=0.25的情况,H/D和ϕ对Ncr的影响逐渐增大。还可发现,S/D较小时Ncr值增加不明显,而S/D接近Str/D时,Ncr变化的差异同样很小。例如:取H/D=3、ϕ=30°,当S/D=2.875时,Ncr=14.103;而S/D=Str/D=4时,Ncr=14.194,相比前者仅增加了0.65%。④较之其它因素,内摩擦角ϕ增大引起Ncr迅速增大,同时随着S/D的增加,Ncr快速增至单洞条件下对应的稳定系数Ncr(Single)。
3.2 发挥系数ηcr变化规律
定义发挥系数ηcr为多洞稳定系数Ncr与单洞稳定系数Ncr(Single)之比,即ηcr=Ncr/NcrNcr(Single)Ncr(Single),于是ηcr可反映不同净距比S/D条件下多洞与单洞稳定性之间的关联规律。绘制ϕ为10°,20°,30°对应的发挥系数ηcr曲线如图 4所示。可看出,当S/D比较小时,ηcr值接近0,而随着S/D的增加,ηcr值逐渐增长直至最大值1。当隧道埋深比H/D增大时,ηcr随S/D增加的趋势变缓,达到单洞破坏对应的转化间距比Str/D增加。对比图 4(a)~4(c)可知,内摩擦角ϕ较大时,ηcr值随S/D的增加更快地达到最大值1。
3.3 转化间距比Str/D变化规律
上文提到,当多洞并行等间距隧道的净间距S增大到转换间距Str时,从失稳破坏角度可认为相邻隧道间的相互影响消失。因此,有必要进一步探究转换间距比Str/D的影响因素。将转换间距比Str/D与埋深比H/D的关系曲线绘制见图 5。可看出,除内摩擦角ϕ=30°的情况外,Str/D与埋深比H/D的增长基本呈线性关系,且ϕ值越小Str/D增长的比率越大,这与较小内摩擦角引起围岩较大扰动范围的一般规律相符。转换间距比Str/D与围岩内摩擦角ϕ以及埋深比H/D均直接相关,差异在于前者负相关而后者为正相关。多洞存在相互影响时,较大埋深比H/D提供了较大的自重荷载,易诱发围岩失稳破坏。
4. 多洞并行隧道围岩潜在破坏模式
4.1 典型破坏模式特征分析
除稳定系数Ncr外,运动单元上限法对应的非线性规划运算,还可得到多洞并行隧道围岩潜在失稳破坏模式。为分析典型破坏特征及网格密度的影响规律,绘制ϕ=15°,H/D=3,S/D=3对应的滑移线网破坏模式展开讨论(图 6)。
图 6(a)所示滑移线网破坏模式左右边界均为对称轴,上部和下部整体区域以简略形式显示。可看出,相邻隧道中夹岩区域的破坏表现为两簇滑移线网。从隧道周边散发,两簇滑移线于相邻隧道对称轴处交于一点。滑移线网范围内围岩破坏呈速度均不相等状态,即间断线两侧速度不连续。需说明的是,尽管模型网格划分为三角形刚体单元,后处理时筛除了无效速度间断线,因此滑移线网破坏模式更多地显示为由很多相邻三角形构成的四边形块体体系。
为揭示滑移线网速度场的规律,将破坏模式对应的速度间断线(滑移线)相对速度矢量闭合图绘制如图 6(b)。同时,定义隧道上方整体下沉区域的竖向速度为v0,图 6(b)竖轴表示为无量纲竖向速度比v/v0,横轴为水平速度比u/v0;于是竖轴0到1的连线即为v0,竖轴0到网状交叉任一点的连线为对应刚体单元的绝对速度;图 6(b)中网状速度矢量任意线段为对应速度间断线的相对速度。由图可知,隧道上方整体区域下沉速度为v0时,滑移线网破坏区内部速度最大值超过4v0,推测内摩擦角ϕ越大该趋势越明显,即围岩承载能力更好。
通常围岩破坏范围被速度间断线分割为多区域,其中塑性区可等效为密集的滑移线网形态。为探讨滑移网密度对稳定系数Ncr上限解的影响,将ϕ=15°,H/D=3,S/D=3时,稀疏网格对应的滑移线网破坏模式和速度矢量闭合图绘制如图 6(c),6(d),密集网格对应的绘制如图 6(e),6(f)。
对比可知,滑移线网稀疏时,速度间断线沿着两个交叉方向构成的滑移线变得棱角感突出,而速度矢量闭合图也更加稀疏曲折。然而,相同v0条件下,滑移网破坏区内部速度矢量值更大,如最大内部速度超过5v0,由此引起间断线总耗散能增大,这是稀疏网格(图 6(c))对应稳定系数Ncr=5.680,大于常规网格(图 6(a))对应Ncr=5.34的原因之一。依上限定理,较小的稳定系数上限解为较优解;说明网格密度增加,不仅破坏模式的刻画更为精细,同时还提高了Ncr上限解精度。
同样地,对常规网格(图 6(a))进一步加密获得滑移线网破坏模式和速度矢量图绘制如图 6(e),6(f)。可以发现,网格越密集滑移线网和速度矢量变得更加圆顺。此时,密集网格对应的稳定系数Ncr =5.316较之常规网格对应的5.34,并未带来计算精度的显著提升。然而,密集网格对应速度间断线总数nd=438,接近常规网格nd=149的3倍。考虑到运动单元上限分析对应的非线性规划的运算负担,速度间断线和单元数目的增加将带来运算效率的降低。因此,本文2000余组工况计算,均参考了图 6(a)对应的常规网格密度。
4.2 破坏模式演化规律
为反映相邻隧道净间距比S/D对破坏模式的影响规律,选取ϕ=15°,H/D=3条件下,不同S/D (0.25~5.0)对应的滑移网破坏模式绘制如图 7所示。为便于后续的定量分析,定义多洞并行隧道整体下沉区高度为Hc,具体见图 7(d)标示。
由图 7(a)知,当净间距很小(如S/D=0.25),上方围岩整体下沉引起隧道两侧岩柱产生小范围楔形破坏。当S/D逐渐增加至1.0,2.0,3.0(图 7(b)~7(d)),隧道两侧的楔形网状破坏范围逐渐扩展,大约在隧道上下中心线处开始交叉。滑移线网的扩展带来了速度间断线总数和长度的增长,引起破坏区域耗散能增加,对应于稳定系数Ncr的增大(由0.593增至5.340)。
由图 7(e)知,当S/D增加至4.0时,滑移网破坏范围进一步向外侧扩展,特别是上方于中心线处交叉范围更大,此时Ncr=6.535,与S/D=5.0单洞隧道独自破坏对应的Ncr=6.870相差不大(图 7(f))。说明由多洞相互影响破坏至单洞单独破坏的转换净间距比Str/D处于4.0~5.0。还可看出,单洞独自破坏时,破坏模式外侧产生了延伸到地表的贯通破坏面,且水平方向的扩展范围较小。
多洞并行隧道间夹岩破坏呈内部为滑移线网的楔形形状,这里将楔形体上下边线称之为主要破坏面。于是,选取典型参数绘制多洞并行隧道主要破坏面演化规律如图 8所示。
图 8(a)为S/D=2.75,H/D=3.0时,不同内摩擦角ϕ对应的主要破坏面。可看出ϕ由5°增大至30°,上下两条破坏面位置不断上移,上方破坏面的起点从隧道顶部上移趋势更显著,同时两条主要破坏面合围的楔形区面积也随之增长。
图 8(b)为S/D=2.5,ϕ=20°时,不同埋深比H/D对应的主要破坏面。可看出,H/D由2增大至10,上下两条破坏面位置不断下移,不过下移趋势逐渐微弱;特别对于H/D≥5的情况,相对应的主要破坏面几乎重合。说明隧道埋深增加到一定值后,上方整体下沉区以荷载形式施加于中夹岩区域,破坏形态不再演化。
由上可知,围岩内摩擦角和隧道埋深变化将引起破坏面位置及上方整体下沉区高度Hc的改变。于是,定义无量纲参数Hc/D为整体下沉区高度比。绘制ϕ为10°,20°,30°对应的Hc/D曲线如图 9,以此分析Hc/D的变化规律。可以发现,当S/D较小时,Hc/D接近隧道埋深比H/D;随着S/D的增大,Hc/D值逐渐减小,且曲线的斜率变化也逐渐增大。对比图 9(a)~9(c)可知,内摩擦角ϕ增大,Hc/D值的变化幅度更大,相同S/D对应的下沉区高度Hc更小,这与破坏面规律分析中结果一致,即摩擦角对破坏面的影响显著,ϕ的增大会引起破坏面的上移。
5. 对比分析与讨论
5.1 多洞与双洞并行隧道围岩稳定系数Ncr对比
关于多洞并行隧道围岩稳定性分析的研究报道较少,这里选取双洞并行隧道已有数据展开对比分析[13-15]。其中Sahoo和Yamamoto数据源于变形单元上限有限元分析,Zhang和本文数据来自运动单元上限分析。选取ϕ=10°、H/D=5对应的Ncr与S/D变化曲线绘制如图 10。可以看出,Yamamoto等[13]、Sahoo等[14]和Zhang等[15]分别给出的双洞并行隧道稳定系数上限解Ncr随S/D变化曲线的趋势和数值吻合较好。其中以Zhang等[15]运动单元上限解数值稍小,为严格上限理论框架下的较优解。
如3.1节所述,本文多洞并行隧道围岩稳定系数Ncr上限解随S/D的增加快速增长直至达到固定值Ncr(Single)。如图 10,当S/D增大至超过转化间距比Str/D时,多洞与双洞并行隧道围岩稳定系数Ncr值趋同,均对应于单洞隧道独自破坏而无相互影响的情况。此时,本文Ncr上限解较之已有文献结果稍小,数值吻合良好,可印证运动单元上限分析结果的可靠性。
从图 10还看出,当相邻隧道净距比S/D不断减小时,多洞与双洞并行隧道对应的稳定系数Ncr的差异稳步增大,且多洞条件对应的Ncr数值急速下降,反映出多洞围岩稳定性依赖于相邻隧道中夹岩承载性能,这缘于上方围岩难于产生成拱效应,因此稳定性较之相同条件的双洞并行隧道显著降低。
5.2 多洞与双洞并行隧道围岩潜在破坏模式对比
选取ϕ=30°,S/D=2.0,H/D=3.0条件下多洞并行隧道围岩破坏模式绘制如图 11,图中以实线表示滑移线网破坏模式并显示整个隧道。将相同条件下Zhang等[15]给出的双洞并行隧道围岩滑移网破坏模式以虚线形式叠加显示。
由图 11看出,在内侧区域(相邻隧道中夹岩区域),多洞并行隧道围岩滑移线网破坏特征与双洞并行隧道的情况较为吻合,而后者于外侧滑移线网状破坏区向上方发生显著偏移,且增加了一条斜向延伸的贯通滑动面。这体现了与多洞并行隧道围岩破坏模式最大的差异,成为解释多洞并行隧道围岩稳定系数Ncr小于双洞Ncr(Dual)的主要原因,即后者外侧增加了向上破坏面并进一步减小上方围岩整体下沉范围。实质上,净间距较小时,多洞并行隧道围岩破坏机理为相邻隧道中夹岩的破坏,可以此进行双洞、三洞等并行隧道中夹岩稳定性评估。
6. 结论
采用刚体平动运动单元上限法研究了多洞并行等间距隧道围岩稳定性及潜在破坏模式,得到3点结论。
(1)多洞并行隧道净距比S/D对稳定系数Ncr和破坏模式影响显著。当S/D小于转换间距比Str/D时,随着S/D的减小,Ncr数值和滑移线网破坏范围逐渐减小。当S/D数值很小时,各参数影响下的Ncr均趋近于0,体现为隧道上方围岩全部发生整体下沉式失稳。当S/D大于Str/D时,多洞并行隧道对应的Ncr和破坏模式与相同条件下的单洞隧道吻合良好。
(2)多洞和双洞并行隧道破坏模式形态和范围差异明显,相同条件下前者围岩稳定更差。当S/D小于Str/D时,多洞隧道对应的Ncr小于双洞隧道Ncr(Dual),此时多洞隧道滑移线网破坏模式特征与双洞隧道的内侧区域类似,但未产生双洞隧道外侧斜向上延伸的剪切带;体现出多洞隧道破坏主要为相邻隧道间的中夹岩破坏的特点。
(3)本文多洞并行隧道围岩稳定系数和破坏模式的分析结果基于莫尔库仑屈服准则,对于其它屈服准则,如霍克布朗屈服准则的影响与差异所在,需要进一步研究。
-
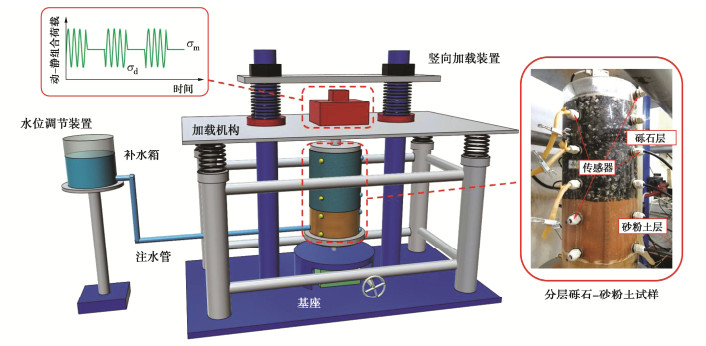
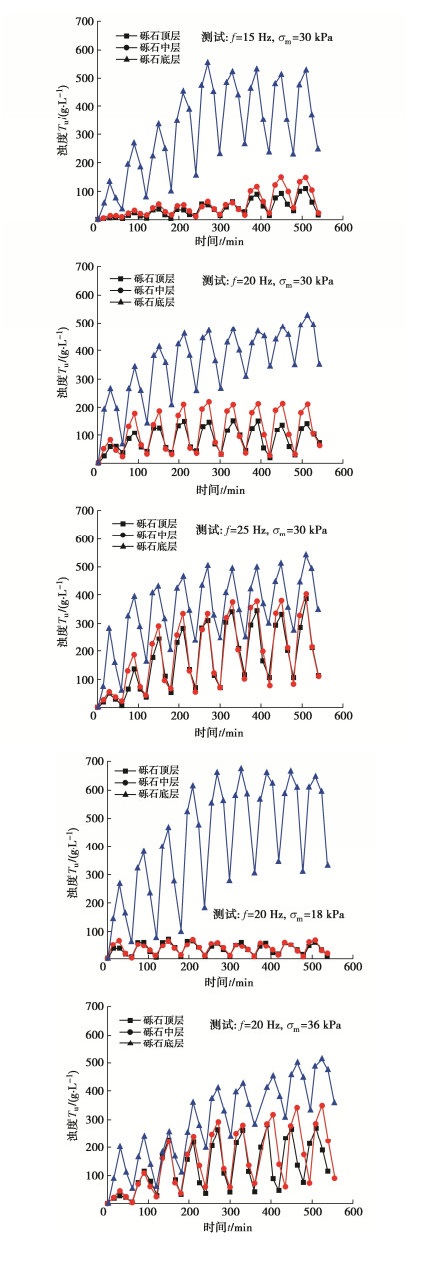
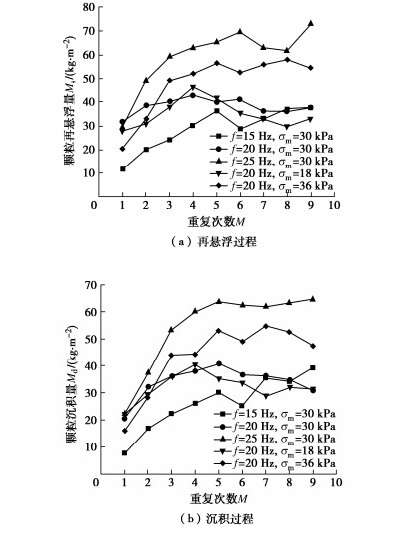
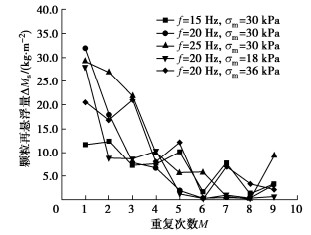
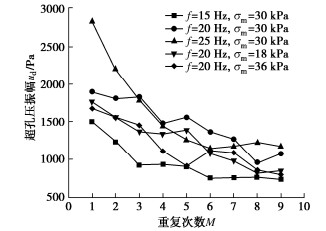
表 1 动静组合加载试验方案
Table 1 Test schemes of combined dynamic and static loads
试验序号 加载频率f/Hz 平均动应力σm/kPa 动应力幅值σd/kPa 动静组合加载重复次数M 动荷载单次循环次数N /103 静荷载单次间歇时长t/min 1 15 30 5.0 9 27 30 2 20 30 36 30 3 25 30 45 30 4 20 18 36 30 5 20 36 36 30 -
[1] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 李小鹏出席国新办"权威部门话开局"新闻发布会, 强调: 奋力加快建设交通强国努力当好中国现代化的开路先锋[EB/OL]. 2023-02-24. https://www.mot.gov.cn/jiaotongyaowen/202302/t20230224_3763233.html. Ministry of Transport of the People's Republic of China. Li Xiaopeng attended the press conference of the "authority department speech opening" of the state information office and stressed: strive to speed up the construction of transportation power and strive to be the pioneer of china's modernization. [EB/OL]. 2023-02-24. https://www.mot.gov.cn/jiaotongyaowen/202302/t20230224_3763233.html. ) (in Chinese)
[2] 张军辉, 彭俊辉, 郑健龙. 路基土动态回弹模量预估进展与展望[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2020.01.001 ZHANG Junhui, PENG Junhui, ZHENG Jianlong. Progress and prospect of the prediction model of the resilient modulus of subgrade soils[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(1): 1-13. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2020.01.001
[3] 彭惠, 马巍, 穆彦虎, 等. 青藏公路普通填土路基长期变形特征与路基病害调查分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(7): 2049-2056. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201507037.htm PENG Hui, MA Wei, MU Yanhu, et al. Analysis of disease investigation and long-term deformation characteristics of common fill embankment of the Qinghai-Tibet Highway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(7): 2049-2056. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201507037.htm
[4] NGUYEN T T, INDRARATNA B, KELLY R. Mud pumping under railtracks: mechanisms, assessments and solutions[J]. Australian Geomechanics, 2019, 54(4): 59-80.
[5] 杨新安, 高艳灵. 沪宁铁路翻浆冒泥病害的地质雷达检测[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(1): 116-119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.01.022 YANG Xinan, GAO Yanling. GPR inspection for Shanghai-nanjing railway trackbed[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(1): 116-119. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.01.022
[6] MNEINA A, SHALABY A. Relating gradation parameters to mechanical and drainage performance of unbound granular materials[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2020, 23(6): 100315. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2999576606
[7] 边学成, 李书豪, 万章博, 等. 路基注浆对高速铁路轨道-路基体系动力特性的影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(4): 294-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ202204038.htm BIAN Xuecheng, LI Shuhao, WAN Zhangbo, et al. Influence of injection remediation on dynamic behaviors of a high-speed railway track-subgrade system[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(4): 294-302. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ202204038.htm
[8] KERMANI B, XIAO M, STOFFELS S M, et al. Reduction of subgrade fines migration into subbase of flexible pavement using geotextile[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2018, 46(4): 377-383. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2018.03.006
[9] INDRARATNA B, BABAR SAJJAD M, NGO T, et al. Improved performance of ballasted tracks at transition zones: a review of experimental and modelling approaches[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2019, 21: 100260. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2019.100260
[10] HAYASHI S, SHAHU J T. Mud pumping problem in tunnels on erosive soil deposits[J]. Géotechnique, 2000, 50(4): 393-408. doi: 10.1680/geot.2000.50.4.393
[11] BEDRIKOVETSKY P, CARUSO N. Analytical model for fines migration during water injection[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2014, 101(2): 161-189. doi: 10.1007/s11242-013-0238-7
[12] WANK J R, GEORGE S M, WEIMER A W. Vibro-fluidization of fine boron nitride powder at low pressure[J]. Powder Technology, 2001, 121(2/3): 195-204.
[13] MAWATARI Y, KOIDE T, TATEMOTO Y, et al. Effect of particle diameter on fluidization under vibration[J]. Powder Technology, 2002, 123(1): 69-74. doi: 10.1016/S0032-5910(01)00432-6
[14] 周健, 杨永香, 刘洋, 等. 循环荷载下砂土液化特性颗粒流数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(4): 1083-1088. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.04.039 ZHOU Jian, YANG Yongxiang, LIU Yang, et al. Numerical modeling of sand liquefaction behavior under cyclic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(4): 1083-1088. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.04.039
[15] ZHOU L F, WANG J W, GE W, et al. Quantifying growth and breakage of agglomerates in fluid-particle flow using discrete particle method[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 26(5): 914-921. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2017.05.018
[16] ZHOU K, HOU J, SUN Q C, et al. A study on particle suspension flow and permeability impairment in porous media using LBM-DEM-IMB simulation method[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2018, 124(3): 681-698. doi: 10.1007/s11242-018-1089-z
[17] ALOBAIDI I, HOARE D. Factors affecting the pumping of fines at the subgrade subbase interface of highway pavements: a laboratory study[J]. Geosynthetics International, 1994, 1(2): 221-259. doi: 10.1680/gein.1.0010
[18] KERMANI B, XIAO M, STOFFELS S M, et al. Measuring the migration of subgrade fine particles into subbase using scaled accelerated flexible pavement testing–a laboratory study[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2019, 20(1): 36-57. doi: 10.1080/14680629.2017.1374995
[19] 蔡袁强, 严舒豪, 曹志刚, 等. 交通荷载下粉质黏土路基翻浆冒泥机理试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1742-1748. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY202105022.htm CAI Yuanqiang, YAN Shuhao, CAO Zhigang, et al. Experiments to investigate mechanism of mud pumping of road base on silty clay soil under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1742-1748. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY202105022.htm
[20] 韩博文, 蔡国庆, 李舰, 等. 有砟轨道路基翻浆冒泥模型试验系统的研发与应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(8): 1406-1415. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202208005 HAN Bowen, CAI Guoqing, LI Jian, et al. Development and application of model test system for mud pumping in ballasted track subgrade[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(8): 1406-1415. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202208005
[21] 白冰, 张鹏远, 宋晓明, 等. 渗透作用下多孔介质中悬浮颗粒的迁移过程研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(10): 1786-1793. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201510006 BAI Bing, ZHANG Pengyuan, SONG Xiaoming, et al. Transport processes of suspended particles in saturated porous media by column seepage tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(10): 1786-1793. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201510006
[22] 张升, 高峰, 陈琪磊, 等. 砂-粉土混合料在列车荷载作用下细颗粒迁移机制试验[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(5): 1591-1598. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202005016.htm ZHANG Sheng, GAO Feng, CHEN Qilei, et al. Experimental study of fine particles migration mechanism of sand-silt mixtures under train load[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(5): 1591-1598. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202005016.htm
[23] ZHANG S, GAO F, HE X Z, et al. Experimental study of particle migration under cyclic loading: effects of load frequency and load magnitude[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2021, 16(2): 367-380. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-01137-x
[24] GAO F, HE X Z, ZHANG S. Pumping effect of rainfall-induced excess pore pressure on particle migration[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2021, 31: 100669. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100669
[25] GAO F, ZHANG S, HE X Z, et al. Experimental study on migration behavior of sandy silt under cyclic load[J]. ASCE-Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2022, 148(5): 06022003. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002796
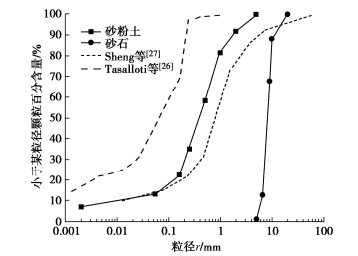
[26] Standard Test Methods for Particle-Size Distribution (Gradation) of Soils Using Sieve Analysis: ASTM D6913/D6913M-17[S]. 2017.
[27] TASALLOTI A, MARSHALL A M, HERON C M, et al. Geocellular railway drainage systems: physical and numerical modelling[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2020, 22: 100299. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2019.100299
[28] SHENG D, ZHANG S, NIU F, et al. A potential new frost heave mechanism in high-speed railway embankments[J]. Géotechnique, 2014, 64(2): 144-154. doi: 10.1680/geot.13.P.042
[29] BIAN X C, LI W, HU J, et al. Geodynamics of high-speed railway[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2018, 17: 69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2018.09.007
[30] LAWRENCE M, BULLOCK R, LIU Z M. China's High-Speed Rail Development[M]. Washington D C: World Bank, 2019.
[31] TERZAGHI K V. The Shearing resistance of saturated soils and the angle between the planes of shear[C]//Proceedings of the 1th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Cambridge, 1936: 54-56.
[32] MCDOUGAL W G, TSAI Y T, LIU P L F, et al. Wave-induced pore water pressure accumulation in marine soils[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, 1989, 111(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1115/1.3257133
[33] BRAY J D, SANCIO R B. Assessment of the liquefaction susceptibility of fine-grained soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2006, 132(9): 1165-1177. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2006)132:9(1165)
[34] LI J E, ZHANG J H, ZHANG A S, et al. Evaluation on deformation behavior of granular base material during repeated load triaxial testing by discrete-element method[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 22(11): 1-11.
[35] WINTERWERP J C, DE BOER G J, GREEUW G, et al. Mud-induced wave damping and wave-induced liquefaction[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2012, 64: 102-112. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2012.01.005
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 夏晶晶,贺姣姣. 基于直剪试验土石混合体路基的稳定性问题研究. 山西建筑. 2025(01): 125-128+172 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨忠平,李勇华,李诗琪,刘浩宇,高宇豪. 不同含石率土石混合体水力侵蚀分异特征及机制. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(01): 133-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 段国勇,徐广超,罗文庆,李森. 酸碱环境下泥岩土石混合体剪切特性研究. 水利水电技术(中英文). 2024(02): 148-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 梁越,何慧汝,许彬,张鑫强,冉裕星. 基于透明土的水力梯度对渗流侵蚀影响试验研究. 河海大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(05): 60-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-
其他相关附件




 下载:
下载: