Stability of stepped sliding of bedding rock slopes with discontinuous joints
-
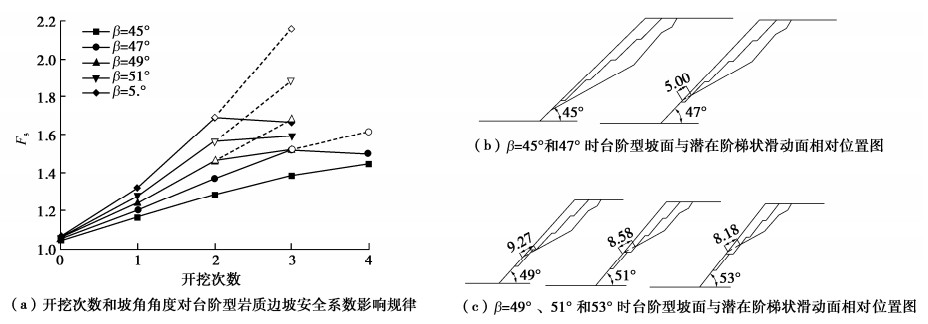
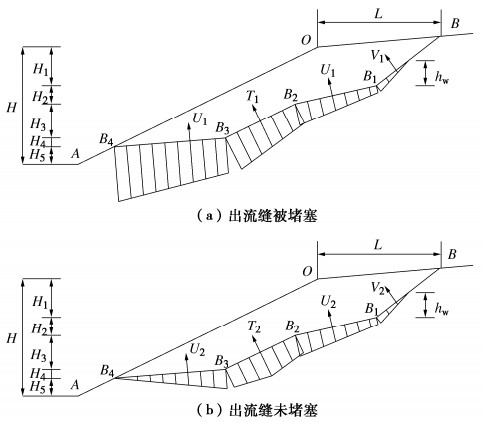
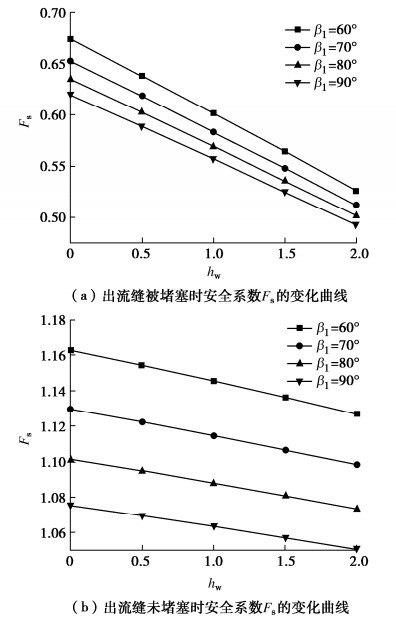
摘要: 阶梯状滑动顺层岩质滑坡在工程中较为常见,其岩桥和节理特性对阶梯状滑动面的形成至关重要。考虑岩桥和节理面之间强度参数弱化特性,构建阶梯状滑动顺层边坡稳定性分析模型。研究表明:与平面型滑动对比验证了分析模型的准确性。裂隙连通率kY、基本摩擦角φb、粗糙度系数JRC和弱化系数Kc对安全系数Fs影响显著。岩桥倾角β3越大,Fs减小越显著,边坡越不稳定。台阶法中开挖次数和坡角角度对边坡稳定性影响显著,通过算例分析验证了该方法与极限平衡解差异率在1%以内。某些情况下当开挖使节理面出露时,Fs显著降低(如β=53°时降低了22.8%),易诱发滑坡的发生。同时,随着拉裂缝倾角β1和充水高度hw的增大,Fs显著降低,出流缝被堵塞时水力效应更为显著,此时边坡最不稳定。Abstract: The bedding rock landslides with stepped sliding surface are common in engineering, and the characteristics of rock bridges and joints are very important to the formation of stepped sliding surface. The weakening characteristics of the strength parameters of rock bridges and joints are considered. The models for stability of stepped sliding of bedding slopes are established. The results show that the accuracy of the model is verified by comparing with the planar failure model. In addition, the fracture connectivity rate kY, basic friction angle φb, roughness coefficient JRC and weakening coefficient Kc have significant influences on Fs. In this mode, the greater β3 is, the more significant the reduction of Fs is, and the more unstable the slope is. In addition, the excavation times and slope angle have significant influences on the slope stability. The difference rate between the proposed method and the limit equilibrium solution is less than 1%. In some cases, when the joint surfaces are exposed by excavation, Fs is significantly reduced (the reduction of 22.8% when β=53°), which easily leads to the occurrence of landslides. Meanwhile, with an increase in angle β1 of tensile cracks and height hw of water, Fs significantly decreases. The water pressure is more significant when the outlets are blocked, and the rock slope is most unstable.
-
0. 引言
土工格室等三维材料由于具有较为优良的工程性质而被较广泛的应用于双向增强复合地基中,深入分析格室体的变形情况可以得知复合地基的工作状况,从而得出桩土应力比等重要参数。在实际工程中,土工格室不仅受到来自路堤的竖向压力、桩与土的支持力,其上下表面还会与垫层材料发生摩擦,因此分析起来较为复杂,而目前的分析方法仍存在相应的局限性,故有必要进行进一步的深入探讨(图1)。
通过室内试验及数值试验研究土工格室加筋体性能是较为常见的方法:周亚梅等[1]通过定速度压缩试验分析了不同格室形状及侧限形式对单个土工格室承载变形特性影响;郑超毅等[2]通过多组模型试验证明了土工格室在提高地基承载力,减少地基沉降方面的作用;高昂等[3]、邓鹏等[4]孙州等[5]分别通过循环加载、大比尺直剪试验及对比实验,研究了不同加筋形式、格室高度、埋深及焊距等参数在其提高地基承载性能方面的影响。侯娟等[6]通过建立单个高强土工格室加筋和未加筋地基的有限元模型对比分析了土工格室对土体有格室侧壁的摩擦力及环箍约束作用;汪海年等[7]利用离散连续耦合算法分析了格室体高度及焊炬对加筋效果的影响。
理论研究方面,弹性地基梁板理论是分析土工格室变形的常用方法,其中传统地基梁理论较为简便,但其忽略格室体水平摩阻效应会夸大竖向变形,因而部分学者在其基础上进行了一定的改进。张福海等[8]、张玲等[9]在分析格室变形时分别利用修正的双参数地基模型与假定的摩阻力分布模式来考虑摩阻力的影响,但由于其只计算摩阻力对剪力的影响而忽略了对弯矩的影响,使得计算结果与传统方法十分接近,陈仁朋等[10]通过进一步研究分析,得出了桩土应力比、沉降受筋材抗拉模量变化的影响不大,这是由于格室体自身具有较大的刚度,在路堤荷载下只发生有限的挠曲变形,其拉应变对竖向附加应力的贡献不大。于是,为弥补上述不足,张玲等[11-13]、赵明华等[14-16]、马缤辉等[17]在地基梁界面设置了水平弹簧,进一步优化了变形计算结果,其中张玲等[13]注意到桩与土在变形刚度方面具有较大差异,采用具有不同刚度的弹簧体系表征桩与土的这种明显区别,为得到格室体变形曲线,假定桩土交界处土工格室变形协调,在二维情况下实现了桩土应力比的解析解答。然而一般情况下,当采用地基梁方法计算此类问题时,由于难以考虑桩土刚度差异,也通常忽略土拱效应影响,会出现计算结果较为保守的情况。
于是,又有部分学者采用薄板理论来计算格室体的变形,从而避免上述地基梁方法存在的不足。饶为国等[18-20]、谭慧明等[21]及张军等[22]、郑俊杰等[23]分别基于矩形薄板理论分析了土工格室的变形情况,其中郑俊杰等提出了薄板复合弹性模量的概念,但鉴于此方法对于布桩方式的适用性存在一定局限,因而不能用来分析梅花形布桩方式时的情况。赵明华等[24]基于对上述学者的研究成果,采用小挠度弹性圆薄板模型模拟土工格室加筋体,本文在此基础上引入土拱效应的影响并构造非线性代数方程组,建立了“路堤–格室垫层–桩土加固区”共同作用模型,通过迭代求解方法得到土工格室变形情况并进一步得出计算桩土应力比、沉降及桩土差异沉降的新方法,通过实例验证和参数分析与前人方法进行了结果对比,证明了本文方法的合理性。
1. 土拱模型建立
1.1 内外土柱界面摩阻力分布
图2为路堤“土柱模型”,参考文献[25],假定其侧摩阻力发挥系数在等沉面与路堤底部之间由0变化到1,因此,土柱界面摩阻力分布为
τe(z)=δΔsτeu(z)。 (1) 式中 τe为z截面处内外土柱交界处的摩阻力;δ为z截面处内、外土柱的相对位移;Δs为路堤底部桩土差异沉降;τeu为z截面处内、外土柱之间的极限摩阻力。
τeu(z)=fKe(z)pes=fKe(z)(γez−σes), (2) 式中,f为内外土柱之间的摩擦系数,f=tanϕe,Ke为z截面处内、外土柱之间土压力系数,γe为填土体重度,pes为外土柱截面总应力,σes为z截面处因荷载转移外土柱所减少的应力,自重应力扣除σes即为外土柱实际应力。
在z=
H−He 处,Ke=K0,而在z=H处,Ke=Kp,将土柱间相对位移δ与桩土差异沉降Δs的关系表示为Ke(z)=(Kp−K0)δ(z)Δs+K0, (3) 由土力学相关知识可知Kp=tan2(45+φe/2),K0=1-sinφe,ϕe为路堤土内摩擦角。
联立上述3式,有
τe(z)=δ(z)Δsf[(Kp−K0)δ(z)Δs+K0](γez−σes(z)), (4) 式中,f为内外土柱之间的摩擦系数,f=tanϕe。
1.2 受力机制分析
如图3所示,分析dz厚度的内土柱在z方向受力,有
σepAp+γez+γedz+τeUpdz=(σep+dσep)Ap+γe(z+dz), (5) 式中 σep为z截面处内土柱附加应力,即因荷载转移内土柱所增加的应力;Ap为桩身(桩帽)横截面面积,Ap=πdp2/4,其中,dp为桩体(桩帽)直径;Up为横截面周长,Up=πdp。
上式进一步化简为
dσepdz=4dpτe。 (6) 将式(4)代入式(6),有
dσepdz=[4f(Kp−K0)dpΔs2δ2+4fK0dpΔsδ](γez−σes)。 (7) 同时根据z截面处总附加应力为0,有
(1−m)σes−mσep=0, (8) 式中,m为置换率,m=Ap/Ae。
联立式(7),(8)得
dσepdz=[4f(Kp−K0)dpΔs2δ2+4fK0dpΔsδ](γez−m1−mσep)。 (9) 截面的差异压缩量δ:
δ=∫z0σepEedz+∫z0σesEe′dz, (10) 式中,Εe和Εe'分别为路堤填土的压缩模量与回弹模量,此处令二者相等来使计算更加简便。式中第一部分为内、外土柱横截面竖向应力增加产生压缩变形,式中第二部分为内、外土柱横截面竖向应力减小而产生的回弹变形。
对式(10)进一步微分,得
dδdz=σepEe+σesEe。 (11) 与式(8)联立得
dzdδ=(1−m)Eeσep 。 (12) 结合式(9)与式(12)并进行整理,而后采用分离变量法可最终得到
−(1−m)2m2γezln(1−mmγez−σep)−1−mmσep=4(1−m)f(Kp−K0)Ee3dpΔs2δ3+2(1−m)fK0EedpΔsδ2+Ce(z) , (13) 式中,Ce(z)是关于z的待定函数。此式表示内土柱附加应力σep与土柱截面差异压缩量δ之间的关系。
1.3 差异沉降与桩土应力比的关系
根据实际情况,当δ=0时
σep=0, σes=0。 (14) 将这一条件代入式(13)中,可得
Ce(z)=−(1−m)2m2γezln(1−mmγez)。 (15) 将式(15)代入式(13),并考虑路堤底面处,即z=H时,差异压缩量δ=Δs,又有
pep=γeH+σep, (16) 式中,pep是桩顶应力,H为路堤高度。
整理可得
Δs=3dp4fKpEe+2fK0Ee⋅[1−mm2γeHln((1−m)γeHγeH−mpep)−1m(pep−γeH)]。 (17) 又因为路堤底面桩土应力比ne与pep的关系为
pep=neγeHnm−m+1。 (18) 将式(18)代入式(17),可得
Δs=3dp4fKpEe+2fK0Ee⋅[1−mm2γeHln(nem−m+1)−γeHm(ne−nem+m−1nem−m+1)], (19) 由此表示出桩土应力比ne与差异沉降Δs的关系。
2. 考虑土拱效应的土工格室加筋体变形分析
参考文献[24]已有研究,未考虑土拱效应时,桩顶及桩间土控制方程分别建立如下所示:
D∇4wp−(kxp,u+kxp,d)h24∇2wp+pep=qp, (20) D∇4ws−(kxs,u+kxs,d)h24∇2ws+pes=qs, (21) 式中,D为薄板的弯曲刚度
D=Eh312(1−ν2), (22) 式中,E为板的弹性模量,
ν 为板的泊松比,∇2 为拉普拉斯算子∇2=d2dρ2+1ρddρ, (23) wp和ws分别表示格室体在桩顶和桩间土部分的挠曲函数,由Winkler假定,pes=ks ws,ks为桩间土基床系数。kxp,u与kxp,d分别为桩顶范围内格室体上、下界面水平摩阻系数,kxs,u与kxs,d分别为桩间土范围内格室体上、下界面水平摩阻系数,h为格室体厚度。qp和qs分别表示桩顶范围及桩间土范围内所受上部荷载。
桩顶范围内格室体挠度求解为
wp(ρ)=C1I0(√λ1ρ)+C2−(qp−pp)ρ2(kxp,u+kxp,d)h2, (24) λ1=(kxp,u+kxp,d)h24D, (25) 式中,IN为第一类N阶虚变量Bessel函数,在此解中N=0;C1,C2为待定系数,ρ表示距离圆板中心的水平距离。
Δ=(kxs,u+kxs,d)2h416D2−4ksD。 (26) 当Δ<0时,桩间土范围内的格室体的挠度求解为
ws(ρ)=C3α0(ρ)+C4β0(ρ)+C5χ0(ρ)+C6κ0(ρ)+qsks, (27) 式中,α0,β0,χ0,κ0为线性独立函数,C3,C4,C5,C6为待定系数。
当Δ>0时,桩间土范围内的格室体的挠度求解为
ws(ρ)=C3I0(√−λ21ρ)+C4K0(√−λ21ρ)+C5I0(√−λ22ρ)+C6K0(√−λ22ρ)+qsks, (28) {λ21λ22=−12[(kxs,u+kxs,d)h24D±√Δ], (29) 式中,KN为第二类N阶虚变量Bessel函数,在此解中N=0。
由上述各式可进一步得出桩顶及桩间土范围内格室体的转角、弯矩及剪力的表达式。
薄板在ρ=dp/2处的连续条件为
{wp|ρ=dp2=ws|ρ=dp2 , θρ,p|ρ=dp2=θρ,s|ρ=dp2 ,Mρ,p|ρ=dp2=Mρ,s|ρ=dp2 , FSρ,p|ρ=dp2−FSf,p|ρ=dp2=FSρ,s|ρ=dp2−FSf,s|ρ=dp2 。 (30) 桩顶范围内,θρ,p,Mρ,p及FSρ,p分别表示土工格室的径向转角、径向弯矩及径向剪力;桩间土范围内则用θρ,s,Mρ,s及FSρ,s分别表示。FSf,s为桩间土范围内界面摩阻引起的格室体径向截面剪力。
在ρ=de/2处有边界条件:
{θρ,s|ρ=de2=0 ,FSρ,s|ρ=de2=0 。 (31) 假设qp已知,还有
wp|ρ=0=pepkp, (32) 式中,kp为桩体变形刚度系数。
联立式(30)~(32),即可求出参数C1~C6及pep。实际上,桩土刚度差异将导致在路堤荷载作用下桩土上部的路堤土发生差异沉降,因而产生土拱效应,土拱效应会进一步改变桩与桩间土上的荷载,桩顶会形成应力集中,即pep>pes,前文所导得的土拱效应公式(17)可表示pep与Δs的关系。
文献[26]指出,格室体界面与填料之间的摩阻与剪切位移会在受到上部力的作用时显示为近似双曲线关系,通常将其简化为理想弹塑性模型,据此文献[27]选用如图3所示进行描述。
{τ=σntanφguuu (u<uu) ,τ=τmax=σntanφg (u≥uu) 。 (33) 式中 τ为摩阻力;
σn 摩擦面正应力;ϕg界面摩擦角;uu为极限相对位移;τmax为界面极限摩阻力。又有摩阻力与位移间的近似线性关系,得到
{kxp,u=tanφguuqp,kxp,d=tanφguupep ,kxs,u=tanφguuqs,kxs,d=tanφguupes 。 (34) 根据上述分析,将式(30)~(33),(35)联立,从而构成非线性代数方程组,用来分析土拱效应影响下,土工格室加筋垫层挠曲变形情况。由于直接求解较为困难,为简化求解过程,本文采用迭代求解方法,步骤如下:
(1)首先初始计算时暂且忽略土拱效应影响,认为qp,1与qs,1相等并均等于q,根据式(34)进行计算,获得kxp,d,kxp,u,kxs,u,kxs,d的具体结果,同时由于pep与pes未知,故也近似为q进行计算并代入式(34)计算出kxp,d与kxs,d的值,联立方程组(30)~(32)得Δs1,pp,1,ps,1等参数。
(2)将步骤(1)中求得的Δs1代入式(17)中进行计算,反算出qp,2和qs,2,再利用步骤(1)中的方式将这两个值代入(34)并联立(30)~(32)求得各个参数。
(3)当到达某次运算如第j次运算时,类似步骤(1)、(2)的方式,qp,j与qs,j利用Δsj-1得到,此时式(34)具体表现为式(35),以此计算界面摩阻系数,然后联立方程组(30)~(32)得到格室体挠度曲线及Δsj等相关参数。
{kxp,u=tanφguuqp,j,kxp,d=tanφguupep,j-1 ,kxs,u=tanφguuqs,j,kxs,d=tanφguupes,j-1 。 (35) (4)按照步骤(1),(2),(3)的方式对每次数据进行反复迭代计算,直到Δsj与Δsj-1差值满足初始设置的误差要求时结束运算,输出所需结果。
3. 算例验证
本文选取京珠高速公路临长段k111+620~750段中k111+720中心格室体进行变形计算,此段公路为填方区,且下卧较深厚软土层。为处理大面积软土区域,使其承载性能达到预期效果,对软土深厚>5 m的部分路段,采用“沉管碎石桩+土工格室”双向增强复合地基进行处治。本算例选取路段采用梅花形布桩方式,碎石采用未风化干净砾石,砾石粒径20~40 mm,含泥量<5%,自然级配。图4为路基典型设计断面,表1为软基主要物理力学指标,表2为其他路段相关数据。
表 1 软土主要物理力学性质指标Table 1. Main physical and mechanical properties of soft soil含水率/% 孔隙比e 液限/% 塑性指数IP 黏聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 压缩系数/MPa-1 密度/(g·cm-3) 33~50 0.8~1.2 40~45 10~25 3~25 10~28 0.3~1.0 1.7~2.0 表 2 路段相关数据Table 2. Relevant statistics of road天然地基承载力/kPa 碎石桩设计直径dp/cm 桩间距sa/m 桩长Lp/m 格栅屈服强度σ/MPa 格栅厚度hg/cm 垫层厚度h/cm 路堤土填土重度γ/(kN·m-3) 内摩擦角/(°) 路堤高度H/m 总沉降S/cm 桩土应力比n 55 38.5 1.5 10 22.5 10 50 20 30 6 32.5 4~6 结合现有研究,桩体变形刚度和基床系数通常由静载荷试验、理论计算或参考规范获取,而界面摩阻系数、格室垫层变形刚度及弹性模量等可参考前人研究[27-28]得出,如表3所示。
表 3 相关计算参数取值Table 3. Values of relevant parameters格室厚度h/m 格室复合弹性模量E/MPa 格室复合泊松比ν 界面摩擦角ϕg 界面屈服位移uu/mm 桩土变形刚度kp/(kN·m-1) 基床系数ks/(kPa·m-1) 0.1 55 0.35 40° 2 200 300 根据上述参数,采用本文方法,计算所选取路段下格室体变形,进一步得到了沉降与桩土应力比,如表4所示。由表可知,格室上下界面摩阻力及土拱效应可明显增大桩土应力比,而采用本文方法所得的沉降计算值与实测值均较为接近,证明本文方法具有合理性。通过对比表中网上、网下桩土应力比的计算结果可知土工格室加筋体可明显起到调节荷载分配的积极作用。
表 4 计算结果与实测结果对比Table 4. Comparison between calculated and measured results方法对比 网上桩土应力比ne 网下桩土应力比n 沉降S/cm 现场实测 — 4~6 32.50 忽略kx与土拱 — 5.00 33.51 本文方法 考虑kx忽略土拱 — 5.49 31.99 考虑kx与土拱 4.71 5.81 31.20 4. 桩土刚度比kp/ks、路堤填土压缩模量Ee及路堤填土内摩擦角ϕe对桩土应力比ne与n的影响
限于文章篇幅,本文将桩体刚度系数Kp取为固定值500 kN/m,通过分析部分重要计算参数对网上网下桩土应力比ne与n和对格室体变形的影响情况进而得出土拱、垫层等对路堤荷载在桩与土部分的分配情况的影响。
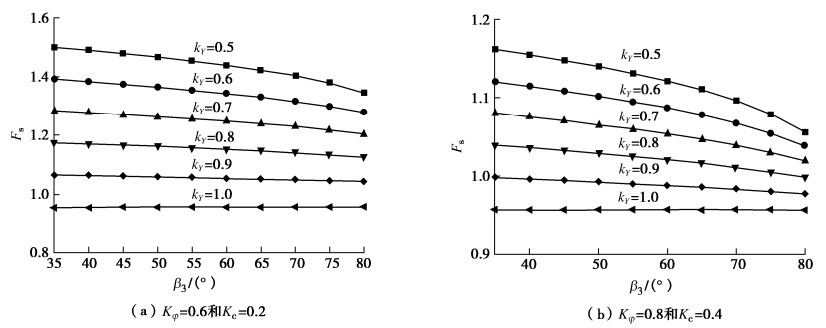
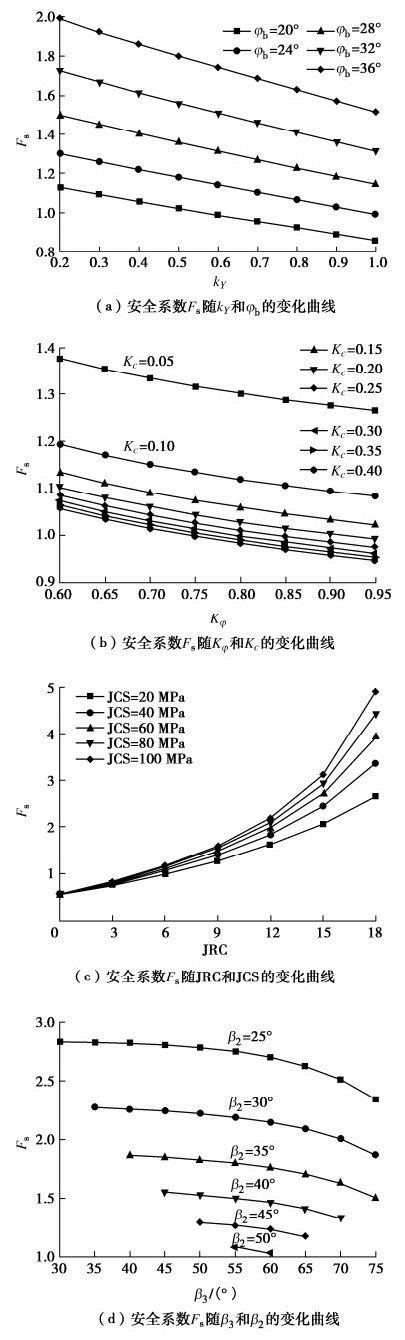
由图5可知,kp/ks的值在很大程度上决定ne与n的计算结果,格室垫层对荷载的调节作用在桩土刚度比较小时不明显,而随着kp/ks的值的增大几乎呈线性增加,且这个作用效果与垫层模量正相关;图6表示Ee影响荷载分配的情况,ne与n随着Ee的增加呈现近似的非线性增加,且速率变缓,此外,格室垫层模量E对n与ne的影响分别在Ee较小与较大时表现明显;图7描述的是ϕe影响ne与n的情况,其中,ne随着ϕe的增大而增长且趋势基本不变,n随着ϕe的增大而增长且趋势渐缓,此外,在ϕe较小时,格室垫层模量对n的影响较大。
将上述分析结果与未考虑土工格室垫层作用时所计算的桩土应力比值(约为12左右)相比较,可以明显看出,土工格室垫层在降低土拱效应及调节荷载向桩顶集中方面有显著效果,且此效果随着填土性质的下降而愈发明显。
5. 结论
(1)本文在假定内、外土柱界面侧土压力系数与摩阻力发挥程度均与界面相对位移相关的基础上,对传统土柱模型进行了改进,得出本文土拱效应分析模型,进而运用数学方法建立路堤底部桩土应力比与桩土差异沉降的函数关系,这一改进土柱模型能够在土柱间摩阻力与差异变形之间建立联系,并能够得出相较其他方法而言更为简单清晰的s–ne关系式。
(2)土工格室垫层在实际工程中为三维立体结构,会受到水平方向的界面摩阻力及竖直方向的路堤荷载与地基反力,本文基于此受力特点视格室垫层为薄板模型并建立挠曲控制方程获得挠曲函数,结合土拱效应的影响,建立了考虑变形协调的路堤–土工格室–桩土加固区共同作用模型,并给出了迭代求解步骤。
(3)由参数分析可知,格室垫层发挥作用会降低路堤土拱效应,并调节荷载向桩顶分配,这一效果随着土性质的变差而愈发显著。格室体上下界面的摩阻效应有利于降低其变形,具体而言,随着摩阻系数增大到一定值后,界面摩阻力会对结构产生附加的弯矩和剪力,这些作用将主导荷载重新分配。
(4)通常格室垫层上下表面与路堤填土的摩阻力存在差异,这将使格室体中面产生位移,为简化分析本文未考虑这一情况,也忽略了其由于挠曲所造成拉伸,这样的简化方法虽然不会明显影响最终桩土应力比及沉降的结果,但在加筋体内力分析,尤其是在求解最大拉应力时,难免产生一定误差,因此尚需深入研究寻求更为合理的方法。
-
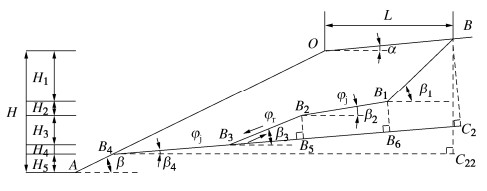
表 1 参数分析图 5参数取值
Table 1 Values of parameters in Fig. 5
参数 kY φb/(°) Kφ Kc JRC JCS
/MPaβ3/(°) β2 /(°) β/(°) L/m β1/(°) 图 5(a) 0.2~1.0(0.1) 20~36(4) 0.8 0.4 6 50 50 40 60 16 60 图 5(b) 0.8 28 0.650.6~0.95
(0.05)0.05~0.40
(0.05)6 30 60 45 60 15 60 图 5(c) 0.65 20 0.6 0.3 0~18(3) 20~100(20) 50 40 60 22 60 图 5(d) 0.6 20 0.8 0.4 10 40 30~75(5) 25~50(5) 58 10 60 -
[1] EBERHARDT E, STEAD D, COGGAN J S. Numerical analysis of initiation and progressive failure in natural rock slopes—the 1991 Randa rockslide[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(1): 69–87. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00076-5
[2] DA HUANG, CEN D F, MA G W, et al. Step-path failure of rock slopes with intermittent joints[J]. Landslides, 2015, 12(5): 911–926. doi: 10.1007/s10346-014-0517-6
[3] 朱雷, 黄润秋, 严明, 等. 基于裂纹扩展模式的岩质斜坡阶梯状滑移破裂机制研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(7): 1216–1224. http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract16953.shtml ZHU Lei, HUANG Run-qiu, YAN Ming, et al. Step-path failure mechanism of rock slopes based on crack coalescence modes in rock mass[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(7): 1216–1224. (in Chinese) http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract16953.shtml
[4] 郭牡丹. 基于岩体结构面特征的三维网络模拟研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2014. GUO Mu-dan. Study on 3-Dimensional Network Simulation Based on the Character of Structural Planes in Rock Mass[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[5] 黄润秋, 许强. 中国典型灾难性滑坡[M]. 北京: . 科学出版社, 2008. HUANG Run-qiu, XU Qiang. Catastrophic landslides in China[M]. Beijing: . China Science Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[6] GARCÍA M, PASTÉN C, SEPÚLVEDA S A, et al. Dynamic numerical investigation of a stepped-planar rockslide in the Central Andes, Chile[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 237: 64–75. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.02.001
[7] TANNANT D D, GIORDAN D, MORGENROTH J. Characterization and analysis of a translational rockslide on a stepped-planar slip surface[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 220: 144–151. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.004
[8] ZHAO L H, LI D J, TAN H H, et al. Characteristics of failure area and failure mechanism of a bedding rockslide in Libo County, Guizhou, China[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(7): 1367–1374. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01188-6
[9] 杨绪波. 大型岩质边坡开挖的岩体结构效应研究-以云南澜沧江小湾水电站#4山梁边坡为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学,, 2005. YANG Xu-bo. Study on the rock mass structure effect of large rock slope during excavation-taking slope NO. 4 in Xiaowan hydropower project on Lancang river of Yunnan as an example[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2005. (in Chinese)
[10] BRIDEAU M A, YAN M, STEAD D. The role of tectonic damage and brittle rock fracture in the development of large rock slope failures[J]. Geomorphology, 2009, 103(1): 30–49. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.04.010
[11] 黄润秋, 陈国庆, 唐鹏. 基于动态演化特征的锁固段型岩质滑坡前兆信息研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(3): 521–533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201703001.htm HUANG Run-qiu, CHEN Guo-qing, TANG Peng. Precursor information of locking segment landslides based on transient characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(3): 521–533. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201703001.htm
[12] JENNINGS J E. A mathematical theory for the calculation of the stability of slopes in open cast mine[C]// Proceeding of the Symposium on the Planning Open Pit Mines. Johannesburg, 1970.
[13] 邹宗兴. 顺层岩质滑坡演化动力学研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2014. ZOU Zong-xing. Research on the Evolution Dynamics of the Consequent Bedding Rockslides[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2014. (in Chinese)
[14] 重庆市设计院. 工程地质勘察规范DBJ50—043—2005[S]. 2005. Chongqing Design Institute. Code for Engineering Geological Investigation DBJ50—043—2005[S]. 2005. (in Chinese)
[15] 陈祖煜, 汪小刚, 杨健, 等. 岩质边坡稳定分析—原理、方法、程序[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2005. CHEN Zu-yu, WANG Xiao-gang, YANG Jian, et al. Rock Slope Stability Analysis-Theory Methods and Programs[M]. Beijing: China WaterPower Press, 2005. (in Chinese)
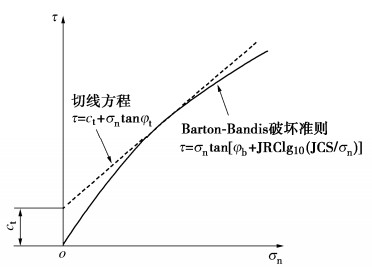
[16] BARTON N. Review of a new shear-strength criterion for rock joints[J]. Engineering Geology, 1973, 7(4): 287–332. doi: 10.1016/0013-7952(73)90013-6
[17] BARTON N. The shear strength of rock and rock joints[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1976, 13(9): 255–279. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0148906276900036
[18] BANDIS S, LUMSDEN A C, BARTON N R. Experimental studies of scale effects on the shear behaviour of rock joints[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1981, 18(1): 1–21. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/014890628190262X
[19] HOEK E. Rock Engineering[M]. Netherlands: A A Balkema, 1995: 70–72.
[20] PRASSETYO S H, GUTIERREZ M, BARTON N. Nonlinear shear behavior of rock joints using a linearized implementation of the Barton-Bandis model[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 9(4): 671–682. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2017.01.006
[21] 唐志成, 夏才初, 刘远明. 岩桥渐进弱化的Jennings抗剪强度准则[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(11): 2093–2099. http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract14891.shtml TANG Zhi-cheng, XIA Cai-chu, LIU Yuan-ming. Modified Jennings shear strength criterion based on mechanical weakening model of rock bridges[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(11): 2093–2099. (in Chinese) http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract14891.shtml
[22] 邓华锋, 齐豫, 李建林, 等. 水–岩作用下断续节理砂岩力学特性劣化机理[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(4): 634–643. http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract18591.shtml DENG Hua-feng, QI Yu, LI Jian-lin, et al. Degradation mechanism of intermittent jointed sandstone under water-rock interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(4): 634–643. (in Chinese) http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract18591.shtml
[23] ZHANG X P, WONG L N Y. Crack initiation, propagation and coalescence in rock-like material containing two flaws: a numerical study based on bonded-particle model approach[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2013, 46(5): 1001–1021.
[24] 王根龙, 伍法权, 张茂省. 平面滑动型岩质边坡稳定性极限分析上限法[J]. 工程地质学报, 2011, 19(2): 176–180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201102005.htm WANG Gen-long, WU Fa-quan, ZHANG Mao-sheng. Method of upper bound limit analysis for plane sliding of rock slopes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(2): 176–180. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201102005.htm
[25] 梁文辉. 锦屏一级水电站引渠边坡稳定性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2009. LIANG Wen-hui. Study on Stability of Approach Channel Slope for Jinping 1 Hydropower Station[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2009. (in Chinese)
[26] 舒继森, 王兴中, 周毅勇. 岩石边坡中滑动面水压分布假设的改进[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2004, 33(5): 509–512. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD200405003.htm SHU Ji-sen, WANG Xing-zhong, ZHOU Yi-yong. Improving on assumption for water pressure distributing on failure surface in rock slope[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2004, 33(5): 509–512. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD200405003.htm
[27] ZHAO L H, ZUO S, LI L, et al. System reliability analysis of plane slide rock slope using Barton-Bandis failure criterion[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2016, 88: 1–11.




 下载:
下载: