Coupling model for consolidation and contaminant transport in compactedclay liners under non-isothermal condition
-
摘要: 考虑到污染场地内部产热会使得压实黏土衬垫处于非等温分布状态,建立了非等温分布条件下压实黏土衬垫中固结与污染物运移的耦合模型,并采用有限差分法对该耦合模型进行了求解。将所建耦合模型的计算结果分别与热扩散试验结果和已有理论模型的计算结果展开对比分析,对耦合模型的正确性进行了验证。基于所建耦合模型,通过某一算例分析了温度梯度M、加荷速率Q和Freundlich吸附系数Kf对污染物运移过程的影响。结果表明:污染物浓度和底部通量会随M绝对值的增大而增大,且一定温度梯度下的底部通量可达不考虑温度梯度时底部通量的2倍以上;Q的增大一方面会减慢污染物运移速率,另一方面会使得运移过程达到稳态时的污染物浓度增大;Kf的增大会减慢污染物运移过程,与不考虑吸附作用相比,考虑吸附作用可使得运移过程达到稳态时所需时间延长3倍及以上。Abstract: Considering that the heat production inside the contaminated site will make the compacted clay liner (CCL) be in a non-isothermal distribution state, a consolidation-contaminant transport coupling model for the CCL subjected to non-isothermal condition is established, and the finite difference method is used to solve the coupling model. The correctness of the established coupling model is verified by comparing the calculated results of the coupling model with the results of the thermal diffusion tests and those of the existing theoretical models, respectively. Based on the established coupling model, the effects of temperature gradient, loading rate and Freundlich adsorption coefficient on the transport process of contaminant are analyzed through an example. The results show that the concentration and bottom flux of contaminants increase with the increase of the absolute value of temperature gradient. Under a certain temperature gradient, the bottom flux of contaminant can be more than twice the bottom flux without considering the temperature gradient. On the one hand, the increase of loading rate will slow down the transport rate of contaminant. On the other hand, it will increase the concentration of contaminant when the transport process reaches a steady state. The increase of Freundlich adsorption coefficient will slow down the transport process of contaminant. The time required for the transport process to reach the steady state can be prolonged by three times or more when the adsorption effect is considered.
-
0. 引言
对于垃圾填埋场、危险废物处置场等污染场地的防渗阻隔问题,底部衬垫系统是污染场地防渗系统的重要组成部分,主要用于阻止和延缓渗滤液中污染物的向下扩散与迁移[1-4]。压实黏土是底部衬垫系统的重要组成材料,由于其具有较低的渗透性和较好的化学相容性,因而被广泛用于污染场地的防渗系统中。尽管如此,危害性较大的污染物仍可通过对流、扩散等方式击穿压实黏土衬垫,从而对周围土体及地下水造成污染[1-9]。为此,许多学者对污染物在压实黏土衬垫中的运移问题展开了研究[5-9]。
在污染物一维运移的解析理论方面,一些学者探究了压实黏土衬垫中污染物的运移问题[6-7]。如陈云敏等[6]求解得到了污染物在成层黏土衬垫中一维扩散运移的解析解;张文杰等[7]建立了污染物在压实黏土衬垫中的一维对流–扩散–吸附解析模型。与此同时,针对不同情况,一些学者提出了污染物在包含压实黏土衬垫的复合衬垫系统中一维运移的解析解[5, 8-9]。如Foose[5]在考虑扩散–吸附情况下,获得了有机污染物在土工膜与黏土层组成的复合衬垫中一维瞬态运移的解析解;Pu等[9]针对底部衬垫系统为复合衬垫系统的情况,采用解析方法研究了有机污染物在压实黏土衬垫中的运移问题。然而,上述研究均忽略了温度对污染物运移过程的影响。
现场测定数据显示,污染场地(如垃圾填埋场)内污染土体中发生的化学反应会使得场地内部的温度高达90℃,而场地外部土体和地下水的温度一般较低,因此压实黏土衬垫中存在温度梯度[10-12]。温度梯度的存在不仅会使得污染物在压实黏土衬垫中发生热扩散,还会影响土体的物理力学性质以及与污染物运移过程相关的参数,进而影响污染物运移过程[12-18]。对于非等温分布条件下压实黏土衬垫中污染物的运移问题,目前相关的理论和试验研究较少[15-17]。
在非等温分布条件下污染物运移问题的试验研究中,Rosanne等[19-20]通过开展试验研究指出,压实黏土中存在因温度梯度引起的污染物热扩散现象。在理论方面,已有学者开展了考虑不同情况的相关解析理论研究[12-17]。如吴珣等[12]通过某些简化假定推导得到了非等温分布条件下有机污染物一维运移的解析解;张春华[14]通过假定污染物的扩散系数等参数不随温度发生变化,发展了考虑热扩散、降解等作用下有机污染物在压实黏土衬垫中一维运移的解析解;Yan等[15]建立了考虑分子扩散–吸附–热扩散情况下污染物在多孔介质中一维运移的解析模型;Peng等[16-17]研究了考虑热扩散情况下复合衬垫系统中污染物的运移问题,并提出了双层复合衬垫和三层复合衬垫中污染物一维运移的解析模型。但上述研究均未考虑土体固结对污染物运移过程的影响。
在底部衬垫系统服役过程中,由于其上部通常会堆填大量的固废垃圾体,这使得压实黏土衬垫会受到较大竖向应力,从而使得压实黏土衬垫发生固结变形[21-23],进而影响污染物运移过程。因此,需考虑土体固结对污染物运移过程的影响。目前,有关压实黏土衬垫中固结与污染物运移的耦合问题已有较多的研究[24-26]。然而,这些研究大多忽略了温度的影响。田改垒等[27]基于小变形固结理论建立了可考虑热效应的渗透–扩散–固结耦合模型,但该模型忽略了温度变化对污染物运移过程中相关参数的影响,且所对应的工况与污染场地中的工况不一致。此外,为获得污染物在压实黏土衬垫中一维运移时的解析解,上述研究中多采用线性等温吸附方程来描述土颗粒的吸附特征,这与黏土颗粒实际的非线性特性存在区别[28-30]。
针对以上研究情况,本文在已有研究的基础上,建立了非等温分布条件下压实黏土衬垫中固结与污染物运移的耦合模型,并采用有限差分法对该耦合模型进行了求解。通过将耦合模型的计算结果分别与Rosanne等[19]所开展的热扩散试验结果、张文杰等[7]所求解析解的计算结果、Alshawabkeh等[31]所提数值模型的计算结果进行对比分析,验证了所建耦合模型的正确性。基于所建耦合模型,分析了相关参数变化对污染物运移过程的影响。
1. 压实黏土衬垫中的耦合模型
1.1 计算简图
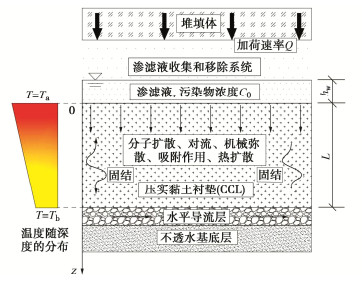
如图 1为非等温分布条件下压实黏土衬垫(CCL)中固结与污染物运移耦合模型的计算简图。图 1中,从上至下依次为堆填体、渗滤液收集和移除系统、渗滤液、CCL、水平导流层及不透水基底层。这里假定CCL始终处于饱和状态,其厚度为L,坐标系z由CCL上边界垂直向下,hw为CCL上部的渗滤液水头;C0为污染物浓度,这里假定污染物浓度保持恒定[16-17, 30]。为研究非等温分布条件对固结及污染物运移过程的影响,同时考虑到温度的传导速度较快,这里假定CCL中的温度T随深度呈线性分布,Ta和Tb分别为上部和底部的温度[12-18]。此外,考虑到污染场地在运行过程会不断堆填固废垃圾体,从而使得CCL受到的竖向应力不断增大,这里设定堆填体产生的加荷速率为Q,并记堆填总时间(即加荷时间)为tc。
1.2 基本假定
由于底部衬垫系统的水平面积较大,CCL的固结问题可近似为一维问题。已有试验研究表明,CCL的渗透系数会随温度的升高而增大[32-33],但温度变化对土体压缩曲线和压缩模量的影响较小[34-35]。基于试验研究结果,作如下基本假定:①CCL是均质、各向同性的,且处于饱和状态;②CCL中固相(土颗粒)和液相(孔隙水)均不可压缩,土体变形固结是由于液相的排出所引起;③液相的排出会导致土体的孔隙率减小,但土体的变形量远小于土体的厚度,即小变形假定成立;④液相中污染物的浓度很低,忽略污染物浓度变化对土体物理力学性质的影响;⑤土中液相的渗流符合Darcy定律;⑥温度变化不会导致CCL的压缩性改变,仅影响CCL的渗透系数。
为研究污染物在CCL中的一维运移问题,在上述基本假定的基础上,还需补充以下3点假定:①污染物在CCL中的扩散遵循Fick第二定律,土颗粒对污染物的吸附状态已达到平衡吸附状态;②污染物为单一离子或有机物;③污染物的运移方式考虑分子扩散、对流、机械弥散、吸附和热扩散。
1.3 CCL的一维固结控制方程
在CCL一维固结过程中,液相和固相的质量守恒方程有[36]:
−∂(nvtcρf)∂z=∂(nρf)∂t, (1a) −∂[(1−n)vsρs]∂z=∂[(1−n)ρs]∂t, (1b) 式中,n为CCL的孔隙率,vtc为液相中因土体固结产生的流动速度,ρf为液相的密度,vs,ρs分别为固相的移动速度和密度,t为时间。
由于固相和液相的密度保持不变,根据式(1a),(1b)有:
−∂(nvtc)∂z=∂n∂t, (2a) −∂[(1−n)vs]∂z=∂(1−n)∂t。 (2b) 根据式(2)可得
∂vs∂z+∂vdc∂z=0, (3) 式中,vdc为由于土体中因固结引起的达西流速,vdc=n(vtc−vs)。
根据达西定律,土体中液相的流动速度为
vd=vdc+vdh, (4a) vdc=−kvγw∂uex∂z, (4b) vdh=−kvγw∂uh∂z, (4c) 式中,kv为液相的渗透系数,γw为液相的重度,uex为因外荷载作用产生的超孔隙水压力,其会导致土体发生固结作用,uh为渗滤液水头产生的超孔隙水压力,其会导致液相发生流动,但不会使得土体发生固结变形[36],vdh为因渗滤液水头产生的达西流速。
根据CCL中所作的非等温分布假定可得
T(z)=Ta+Mz, (5) 式中,M为CCL中的温度梯度(℃/m),M= (Tb−Ta)/(Tb−Ta)LL。
对于液相的渗透系数kv,参考文献[37],渗透系数kv与温度T的关系可近似表达为
kv=(0.029T+0.420)⋅kv(T0=20∘C), (6) 式中,kv(T0)为温度为T0时的渗透系数。
结合式(5),(6),渗透系数kv与深度z关系为
kv(z)=kv(T0)⋅(Nz+Qa), (7) 式中,N=0.029M,N为渗透系数梯度(1/m),Qa=0.029Ta+0.420,kv(0)=kv(T0)Qa,kv(0)为CCL上部的渗透系数。
对于因渗滤液水头产生的达西流速vdh,其不产生固结效应,这里假定渗滤液水头hw保持不变,并在该水头下达到了稳定渗流状态,则有
vdh=−kv(z)γwduhdz。 (8) 对式(8)进行一定的变换,并利用式(7)的表达式进行积分可得
vdh=Nkv(T0)hwln[(N/Qa)L+1]。 (9) 在CCL中,根据液相中的渗流连续性条件可得
∂vdc∂z=mv∂σ′∂t, (10) 式中,mv为体积压缩系数,σ′为有效应力。
根据式(4b),(10)可进一步写为
∂∂z(kv(z)γw∂uex∂z)=−mv∂σ′∂t。 (11) 根据土体的有效原理可知:
σ′=σ−uex−uh−us, (12) 式中,σ为总应力,us为静水压力。
由于渗滤液水头下的渗流已达稳定渗流状态,且静水压力不随时间变化,则根据式(12)和上部荷载的加荷条件,式(11)可进一步改写为
∂∂z(kv(z)γw∂uex∂z)={mv∂uex∂t−mvQ(t<tc)mv∂uex∂t(t⩾tc) 。 (13) 式(13)即为非等温分布条件下CCL的一维固结控制方程。
1.4 CCL中污染物的一维运移方程
当CCL发生固结变形时,液相会发生流动,固相(土颗粒)也会发生相对移动。根据质量守恒定律,考虑分子扩散、对流、机械弥散、吸附和热扩散时污染物的一维运移方程可写为[12-17, 36]
∂(nC)∂t+∂[(1−n)ρsS]∂t=∂∂z(nD∂C∂z)−∂(nvtC)∂z−∂[1−n)vsρsS]∂z+∂∂z(nDT∂T∂z), (14) 式中,C(z,t)为液相中污染物的浓度,S为单位质量土颗粒所吸附的污染物质量,D为水动力弥散系数,D=De+Dmd,De为有效扩散系数,Dmd=αLvt,Dmd为机械弥散系数,αL为纵向弥散度,vt=vtc+vth,vt为液相的流动速度,vth为液相中因渗滤液水头产生的流动速度,vth=vdh/vdhnn,DT为污染物的热扩散系数。
根据污染物的一维运移机理,以垂直向下方向为正方向的污染物通量J(z,t)的表达式可写为
J=−nD∂C∂z+[nvtC+(1−n)vsρsS]−nDT∂T∂z。 (15) 对于S和C的关系,参考已有研究结果,这里采用Freundlich非线性平衡吸附模型来描述固相对污染物的非线性吸附特性[28-30],即
S=KfCF, (16) 式中,Kf为与吸附能力相关的Freundlich吸附系数,F为拟合常数。
当拟合常数F=1时,则式(16)可退化为经典的线性等温吸附模型,即
S=KfC=KdC, (17) 式中,Kd为线性吸附系数。
对于有效扩散系数De。一方面,有研究指出有效扩散系数De会随孔隙率n的减小而减小[28, 30];另一方面,有效扩散系数De会随温度T的增大而增大[15, 38-39]。综合考虑两者的影响,De可表示为
De=D0(T0)nβTT0μT0μT, (18) 式中,D0(T0)为温度为T0时的自由扩散系数,β为经验指数,μT0,μT分别为温度T0和T时污染物的动力黏度。
De=D0(T0)nβ[1+A(T−T0)], (19) 式中,A为与有效扩散系数相关的温度系数。
将式(5)代入式(19)可得
De=D0(T0)nβ(Gz+H), (20) 式中,G=AM,H=1+A(Ta−T0)。
对于污染物的热扩散系数DT,参考文献[13~17]和式(20),其表达式为
DT=CSTDe=CSTD0(T0)nβ(Gz+H), (21) 式中,ST为索雷特系数。
根据上述关系式,式(14)可进一步改写为
∂[nC+(1−n)ρsKfCF]∂t=[D0(T0)nβ+1(Gz+H)+nαLvt].∂2C∂z2+{∂[D0(T0)nβ+1(Gz+H)+nαLvt]∂z−[nvt+(1−n)vsρsKfCF−1]+MSTD0(T0)nβ+1(Gz+H)}∂C∂z−C∂{[nvt+(1−n)vsρsKfCF−1]−MSTD0(T0)nβ+1(Gz+H)}∂z。 (22) 同理,根据关系式,污染物通量J(z,t)的表达式可进一步改写为
J=−[D0(T0)nβ+1(Gz+H)+nαLvt]∂C∂z+[nvtC+(1−n)vsρsKfCF−CMSTD0(T0)nβ+1(Gz+H)]。 (23) 1.5 初始条件和边界条件
为便于分析,这里以渗滤液水头下的渗流达到稳定时刻为初始时刻,并假定在该时刻开始堆填固废垃圾体。因此,CCL一维固结的初始条件可写为
uex(z,0)=0。 (24) 对于CCL一维固结的边界条件,这里可将上下边界条件均视为完全排水边界情况,则有:
uex(0,t)=0, (25) uex(L,t)=0。 (26) 对于污染物在CCL中的一维运移问题,CCL在初始时刻未受到污染,因而可假定其初始条件为
C(z,0)=0。 (27) 由于CCL的上边界直接与渗滤液接触,而下边界为水平导流层,因而上下边界条件可写为[6, 16-17]
C(0,t)=C0, (28) C(L,t)=0。 (29) 上述即为非等温分布条件下压实黏土衬垫(CCL)中考虑固结与污染物运移的耦合模型,该耦合模型包括CCL的一维固结控制方程式(13)和CCL中污染物的一维运移方程式(22),以及相应的初始条件和边界条件式(24)~(29)。
2. 耦合模型的有限差分解
对于非等温分布条件下CCL中固结和污染物运移的耦合模型,由于耦合模型中控制方程的系数均是变化的,属于变系数偏微分方程,因而以下将采用有限差分法对耦合模型进行求解。
2.1 一维固结控制方程的有限差分解
根据式(7),对控制方程式(13)进行整理可得
Cv0(Nz+Qa)∂2uex∂z2+Cv0N∂uex∂z={∂uex∂t−Q(t<tc)∂uex∂t(t⩾tc), (30) 式中,Cv0=kv(T0)mvγw,Cv0为温度为T0时CCL的固结系数。
设Δz,Δt分别为计算空间步长和时间步长,并将空间坐标和时间坐标分别进行I等分和J2等分,则有zi=iΔz,Δz=L/I,ti=iΔt,j=0,1,2,⋯,J1,⋯ J2,Δt=tc/J1=t0/J2,t0为给定时间。因此,控制方程式(30)的Crank- Nicholson型隐式差分格式可写为
Cv0(NΔzi+Qa)(ujexi+1−2ujexi+ujexi−12Δz2+uj+1exi+1−2uj+1exi+uj+1exi−12Δz2)+Cv0Nujexi+1−ujexi−12Δz={uj+1exi−ujexiΔt−Q(j⩽J1)uj+1exi−ujexiΔt(j>J1)。 (31) 相应的初始条件和边界条件可写为
u0exi=0, (32) ujex0=0, (33) ujexI=0。 (34) 利用式(29)中的隐式差分格式以及相应的求解条件式(32)~(34),即可对非等温分布条件下CCL中的一维固结过程进行求解。
对于CCL中固相的移动速度vs,对式(3)进行整理,两边积分可得
vs(L,t)−vs(z,t)=vdc(z,t)−vdc(L,t)。 (35) 由于CCL底部固相不发生移动(即vs(L,t)=0),因此任意位置固相的移动速度vs可表达为
vs(z,t)=vdc(L,t)−vdc(z,t)。 (36) 基于有限差分解的计算结果和上述关系式,即可确定达西速度vdc、移动速度vs和孔隙率n等参数。与此同时,利用达西速度vdc,vdh可以分别确定对应液相的流动速度vtc,vth。
2.2 一维运移方程的有限差分解
参考式(13)中的有限差分方法,对式(22)展开有限差分,其Crank-Nicholson型隐式差分格式可写为
TjiCj+1i−CjiΔt=Xji(Cj+1i+1−2Cj+1i+Cj+1i−12Δz2)+Xji(Cji+1−2Cji+Cji−12Δz2)+YjiCji+1−Cji−12Δz−ZjiCji, (37) 其中,
Tji=nji+(1−nji)ρsKfCjF−1i, (38) Xji=D0(T0)njβ+1i(GΔzi+H)+njiαLvjti, (39) Yji=MSTD0(T0)njβ+1i(GΔzi+H)−[njivjti+(1−nji)vjsiρsKfCjF−1i]+12Δz{D0(T0)nji+1β+1[GΔz(i+1)+H]+nji+1αLvjti+1−D0(T0)nji−1β+1[GΔz(i−1)+H]−nji−1αLvjti−1}, (40) Zji=12Δz{[nji+1vjti+1+(1−nji+1)vjsi+1ρsKfCjF−1i+1]−MSTD0(T0)nji+1β+1[GΔz(i+1)+H]−[nji−1vjti−1+(1−nji−1)vjsi−1ρsKfCji−1F−1]+MSTD0(T0)njβ+1i−1.[GΔz(i−1)+H]} 。 (41) 相应的初始条件和边界条件可写为
C0i=0, (42) Cj0=C0, (43) CjI=0 。 (44) 对于非等温分布条件下CCL中污染物的一维运移问题,利用差分方程式(37)及相应的求解条件式(42)~(44)即可进行求解。
对于污染物通量J,其差分格式可写为
Jji=−XjiCji+1−Cji−12Δz+ΔjiCji, (45) 式中,
Δji=[njivjti+(1−nji)vjsiρsKfCjF−1i−MSTD0(T0)njβ+1i(GΔzi+H)]。 (46) 需要说明的是,对于边界处的差分格式,可利用相邻节点展开有限差分。
基于差分方程式(31),(37),可利用Matlab软件编制相应的程序,从而对CCL中考虑固结与污染物运移的耦合问题展开运算。
3. 耦合模型的验证
为验证CCL中固结与污染物运移耦合模型的正确性,以下将耦合模型的有限差分解分别与Rosanne等[19]热扩散试验结果、张文杰等[7]所求解析解、Alshawabkeh等[31]所提数值模型进行对比分析。
3.1 与热扩散试验结果的对比
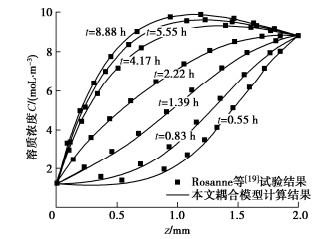
Rosanne等[19]对非等温分布条件下压实黏土中溶质的一维运移问题开展了室内试验研究。在该试验中,压实黏土厚度为2 mm,孔隙率为0.6,溶质为NaCl溶液,其初始浓度为1 moL/m3。压实黏土上下边界的温度分别为12,38℃,且上下边界的浓度分别为1.21,8.83 moL/m3。参考其他文献的模拟方法[20],这里采用在24.9℃时测定得到的有效扩散系数De=6.0×10−11 m2/s及A=0.025/∘C来近似描述溶质的扩散特性。在该试验中,测定得到的索雷特系数ST=0.13/∘C。需说明的是,对于该热扩散试验,尽管所建耦合模型的初始条件和边界条件等与该试验的相关条件存在一些不同之处,但这些不同之处均可通过调整相关参数以实现对热扩散试验过程的模拟。
图 2所示为所建耦合模型有限差分解的计算结果和Rosanne等[19]热扩散试验结果的对比情况。从图 2可以看出,不同时间下所建耦合模型计算所得的溶质浓度分布情况与Rosanne等[19]的试验结果基本吻合,这一定程度说明了所建耦合模型的正确性。同时,对比结果也表明本文所建耦合模型可较为准确预测溶质在压实黏土中的热扩散过程。
![]() 图 2 耦合模型计算结果和Rosanne等[19]热扩散试验结果对比Figure 2. Comparison between calculated results by proposed coupling model and test results by Rosanne et al.
图 2 耦合模型计算结果和Rosanne等[19]热扩散试验结果对比Figure 2. Comparison between calculated results by proposed coupling model and test results by Rosanne et al.3.2 与解析解的对比
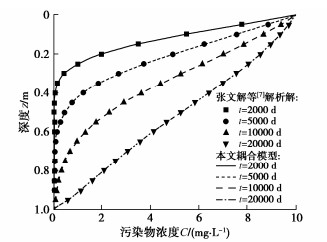
张文杰等[7]研究了污染物在CCL中的一维运移问题,并通过假定土颗粒的吸附模型为线性吸附模型推导得到了相应的解析解,但该解答中未考虑土体固结和温度的影响,因而相关系数均假定为常数。为进一步验证所建耦合模型的正确性,将所建耦合模型的有限差分解与张文杰等[7]所求的解析解进行对比。除指定参数外,取如下基本物理力学参数:厚度L=1.0 m,体积压缩系数mv=0.05 1/MPa,固相密度ρs=2.76 kg/m3,液相密度ρf=1.0 kg/m3,初始孔隙率n0=0.42,加荷速率Q=0.3125 kPa/d,加荷时间tc=3200 d,参考温度T0= 20℃,渗透系数kv(T0)= 2.96×10-10 m/s,渗滤液水头hw=1.0 m,底部温度Tb=20℃,温度梯度M=-30℃/m,自由扩散系数D0(T0)= 8.60×10-10 m2/s,经验指数β=1.82,Freundlich吸附系数Kf=0.63 cm3/g,拟合常数F=0.8,索雷特系数ST=0.05/℃,温度系数A=0.025/℃,污染物浓度C0=10 mg/L,纵向弥散度αL= 0.02 m。需说明的是,计算参数的选定参考了相关文献中所采用的数据及相关试验的测定结果[7, 13-17, 28, 30]。污染物在CCL中运移时的初始条件和边界条件取本文所建耦合模型中采用的相应条件,这里不再赘述。
图 3所示为本文所建耦合模型有限差分解的计算结果和张文杰等[7]所求解析解的计算结果的对比情况。从图 3可以看出,所建耦合模型计算所得的浓度分布情况与张文杰等[7]所求解析解的计算结果十分一致,这说明所建耦合模型可用于预测考虑对流–扩散–吸附时CCL中污染物的一维运移过程。
![]() 图 3 本文耦合模型与张文杰等[7]解析解计算结果的对比Figure 3. Comparison between proposed coupling model and analytical solution proposed by Zhang et al.
图 3 本文耦合模型与张文杰等[7]解析解计算结果的对比Figure 3. Comparison between proposed coupling model and analytical solution proposed by Zhang et al.3.3 与已有耦合模型的对比
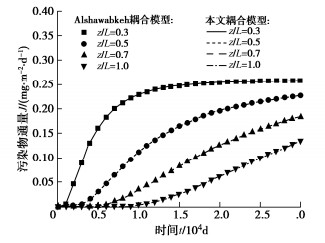
Alshawabkeh等[31]建立了考虑小变形固结与污染物运移的耦合模型(简称Alshawabkeh耦合模型)。相比于本文所建耦合模型,Alshawabkeh耦合模型忽略了固结变形引起的相关参数变化以及机械弥散等因素的影响,且该研究并未考虑温度引起的热扩散对污染物运移过程的影响。为验证本文所提方法用于求解耦合问题的正确性,可将本文所建耦合模型的计算结果与Alshawabkeh耦合模型的计算结果进行对比。除指定参数外,这里设定相关计算参数同3.2节中的参数。需说明的是,由于Alshawabkeh耦合模型中所考虑的吸附模型为等温线性吸附模型[31],因而这里取Kd=Kf和F=1,其他条件同本文所建耦合模型时所采用的相应条件,这里不再赘述。
图 4所示为本文所建耦合模型的计算结果和Alshawabkeh耦合模型的计算结果的对比情况。从图 4可以看出,所建耦合模型计算所得污染物通量随时间的变化情况与Alshawabkeh耦合模型的计算结果十分一致,这说明所建耦合模型可用于计算土体固结与污染物运移的耦合问题。
4. 算例分析
为认识非等温分布条件下CCL中考虑固结时污染物的运移特性,除指定参数外,这里以3.2节中的参数为例,探究温度梯度、加荷速率及Freundlich吸附系数等因素对污染物在CCL中运移规律的影响。
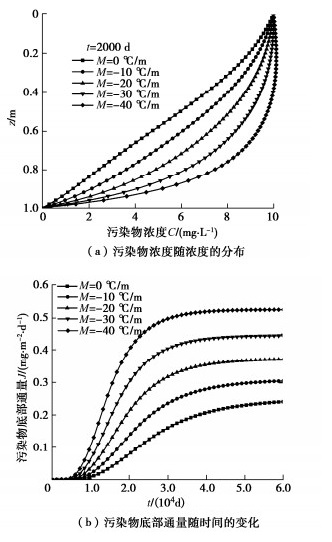
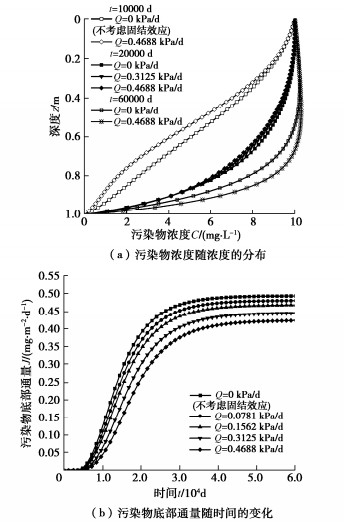
4.1 温度梯度的影响
图 5描述了不同温度梯度M下污染物浓度随深度的分布规律和污染物底部通量随时间的变化规律。从图 5(a)可知,M的绝对值越大,相同时间内同一深度处污染物的浓度越高,这说明CCL中的温度梯度会加快运移速率。从图 5(b)可以看出,污染物底部通量随M绝对值的增大出现明显增大,如t=60000 d时,相比于M=0 ℃/m时,M为–10,–20,–30,–40 ℃/m时的底部通量分别增大了26.3%,54.2%,84.3%和117%。此外,底部通量变化规律表明,M绝对值的增大会使得污染物运移过程更早趋于稳定。
出现上述规律的原因在于:温度梯度M绝对值的增大不仅会加快热扩散过程,还会增大污染物在CCL中运移时的有效扩散系数,进而加快了污染物的运移速率,并增大底部通量。分析表明,温度梯度M会加快污染物在CCL中的运移速率,且在一定温度梯度下,污染物的底部通量可达不考虑温度梯度时底部通量的2倍以上。因此,实际工程中应考虑CCL中的温度梯度对污染物运移过程的影响[12-17]。
4.2 加荷速率的影响
图 6给出了不同加荷速率Q下污染物浓度随深度的分布规律和污染物底部通量随时间的变化规律。从图 6(a)可看出,在运移初期(如t≤2.0×104 d),相同时间内同一深度处污染物浓度会随Q的增大而减小,这反映了CCL的固结效应一定程度会减慢运移速率;但运移过程达到稳态时(如t=6.0×104 d时),加荷速率Q的增大反而使得污染物的浓度增大。从图 6(b)可知,加荷速率Q越大,相同时间内污染物底部通量越小,如t=6.0×104 d时,相比于不考虑固结效应(Q=0.0 kPa/d)时的情况,Q=0.3125 kPa/d时(对应最终荷载为1 MPa)染物的底部通量减小了约10.0%。与此同时,从图 6(b)中可以看出,不考虑固结效应会低估污染物的运移过程达到稳态的时间。
上述规律表明,CCL的固结效应会减慢污染物的运移速率,并减小运移时的底部通量,这与Pu等分析得到的规律一致[30],但同时,固结效应也会使得运移过程达到稳态时的浓度增大。对于运移速率减慢和底部通量减小的原因,这主要是由于固结效应会使得土体孔隙率减小,进而使得与污染物运移相关的系数减小,如有效扩散系数和热扩散系数减小。对于运移过程达到稳态时浓度增大的原因,这主要是由于当考虑固结效应时,相关参数的比值会发生变化,如对流速度与水动力弥散系数的比值会增大,因而改变了运移过程达到稳态时污染物浓度的分布规律[7, 14]。
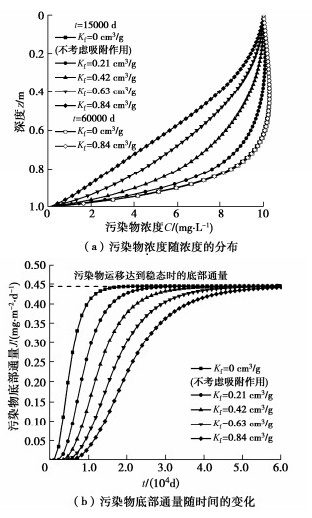
4.3 Freundlich吸附系数的影响
图 7给出了不同Freundlich吸附系数Kf下污染物浓度随深度的分布规律和污染物底部通量随时间的变化规律。从图 7中可知,Freundlich吸附系数Kf对污染物运移过程有着显著影响,在运移初期(如t=1.5×104 d),Kf的增大使得相同时间内同一深度处污染物的浓度显著降低,同时也使得相同时间内污染物的底部通量减小。但随着运移过程的进行,当运移过程达到稳态时(如t=6.0×104 d),不同Kf下污染物的浓度分布曲线几乎完全重合,且不同Kf下底部通量趋于同一稳定值。若定义污染物底部通量达0.445 mg/m2/d时所需的时间为运移稳态时间(图 7(b)),则相比不考虑吸附作用时,Freundlich吸附系数Kf=0.63 cm3/g时的运移稳态时间增大了约200%。
出现上述运移规律的主要原因:CCL的吸附作用主要对污染物运移过程起着阻滞作用,因而主要影响运移速率快慢[28-30]。当运移过程达到稳态时,吸附作用对浓度分布规律和底部通量的影响可忽略。研究表明,CCL对污染物的吸附作用有利于延缓运移过程,且与不考虑吸附作用时相比,考虑吸附作用可使得运移过程达到稳态时所需的时间延长3倍及以上。因此,在选择CCL时,应考虑其吸附特性[28, 30]。
5. 结论
(1)CCL中的温度梯度会加快污染物运移速率,相同时间内污染物的浓度和底部通量会随温度梯度M绝对值的增大而增大,且在一定温度梯度下,底部通量可达不考虑温度梯度时底部通量的2倍以上。因此,实际工程中应考虑温度梯度对运移过程的影响。
(2)加荷速率Q(CL的固结效应)对污染物运移过程的影响是多方面的。一方面,Q的增大会使得土体的孔隙率减小,从而减慢了运移速率,也减小了底部通量;另一方面,Q的增大也会使得污染物运移过程达到稳态时的浓度增大。因此,实际工程中应综合考虑固结效应对运移过程的影响。
(3)Freundlich吸附系数Kf的增大会减慢污染物在CCL中的运移过程,且与不考虑吸附作用时相比,考虑吸附作用可使得污染物运移过程达到稳态时所需的时间延长3倍及以上。当污染物的运移过程达到稳态时,土颗粒对污染物的吸附作用可忽略。在选择CCL时,应考虑土体的吸附特性。
-
图 2 耦合模型计算结果和Rosanne等[19]热扩散试验结果对比
Figure 2. Comparison between calculated results by proposed coupling model and test results by Rosanne et al.
图 3 本文耦合模型与张文杰等[7]解析解计算结果的对比
Figure 3. Comparison between proposed coupling model and analytical solution proposed by Zhang et al.
-
[1] 陈云敏. 环境土工基本理论及工程应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(1): 1–46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201401003.htm CHEN Yun-min. A fundamental theory of environmental geotechnics and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(1): 1–46. (inChinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201401003.htm
[2] SHACKELFORD C D. The ISSMGE Kerry Rowe Lecture: The role of diffusion in environmental geotechnics 1[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2014, 51(11): 1219–1242. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2013-0277
[3] 张春华, 吴家葳, 陈赟, 等. 基于污染物击穿时间的填埋场复合衬垫厚度简化设计方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(10): 1841 –1848. ZHANG Chun-hua, WU Jia-wei, CHEN Yun, et al. Simplified method for determination of thickness of composite liners based on contaminant breakthrough time[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(10): 1841–1848. (in Chinese)
[4] TOUZE-FOLTZ N, XIE H J, STOLTZ G. Performance issues of barrier systems for landfills: a review[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2021, 49(2): 475-488. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2020.10.016
[5] FOOSE G J. Transit-time design for diffusion through composite liners[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(1): 590–601.
[6] 陈云敏, 谢海建, 柯瀚, 等. 层状土中污染物的一维扩散解析解[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2006, 28(4): 521–524. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.04.018 CHEN Yun-min, XIE Hai-jian, KE Han, et al. Analytical solution of contaminant diffusion through multi-layered soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 28(4): 521–524. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.04.018
[7] 张文杰, 黄依艺, 张改革. 填埋场污染物在有限厚度土层中一维对流–扩散–吸附解析解[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(7): 1197–1201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201307004.htm ZHANG Wen-jie, HUANG Yi-yi, ZHANG Gai-ge. Analytical solution for 1D advection-diffusion-adsorption transport of landfill contaminants through a soil layer with finite thickness[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(7): 1197–1201. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201307004.htm
[8] FENG S J, PENG M Q, CHEN Z L, et al. Transient analytical solution for one-dimensional transport of organic contaminants through GM/GCL/SL composite liner[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 479–492. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.413
[9] PU H F, QIU J W, ZHANG R J, et al. Analytical solutions for organic contaminant diffusion in triple-layer composite liner system considering the effect of degradation[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2020, 15(4): 907–921. doi: 10.1007/s11440-019-00783-0
[10] CALDER G V, STARK T D. Aluminum reactions and problems in municipal solid waste landfills[J]. Practice Periodical of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste Management, 2010, 14(4): 258–265. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.1944-8376.0000045
[11] JAFARI N H, STARK T D, THALHAMER T. Spatial and temporal characteristics of elevated temperatures in municipal solid waste landfills[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 59: 286–301. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2016.10.052
[12] 吴珣, 施建勇, 何俊. 非等温条件下有机污染物在黏土衬垫中的扩散分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(3): 120–124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201403024.htm WU Xun, SHI Jian-yong, HE Jun. An analysis of organic contaminant diffusion through clay liner under the condition of transient temperature[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(3): 120–124. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201403024.htm
[13] XIE H J, ZHANG C H, SEDIGHI M, et al. An analytical model for diffusion of chemicals under thermal effects in semi-infinite porous media[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2015, 69: 329–337. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.06.012
[14] 张春华. 填埋场复合衬垫污染物热扩散运移规律及其优化设计方法[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. ZHANG Chun-hua. Mechanisms for Contaminant Transport in Landfill Composite Liners under Thermal Effect and Its Optimization Design Method[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[15] YAN H X, SEDIGHI M, XIE H J. Thermally induced diffusion of chemicals under steady-state heat transfer in saturated porous media[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 153: 119664. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119664
[16] PENG M Q, FENG S J, CHEN H X, et al. Analytical model for organic contaminant transport through GMB/CCL composite liner with finite thickness considering adsorption, diffusion and thermodiffusion[J]. Waste Management, 2021, 120(9): 448–458.
[17] PENG M Q, FENG S J, CHEN H X, et al. An analytical solution for organic pollutant diffusion in a triple-layer composite liner considering the coupling influence of thermal diffusion[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2021, 137: 104283. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104283
[18] MON E E, HAMAMOTO S, KAWAMOTO K, et al. Temperature effects on solute diffusion and adsorption in differently compacted Kaolin clay[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(7): 1–9.
[19] ROSANNE R, PASZKUTA M, TEVISSEN E, et al. Thermodiffusion in compact clays[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2003, 267(1): 194–203. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00670-2
[20] ROSANNE M, PASZKUTA M, ADLER P M. Thermodiffusional transport of electrolytes in compact clays[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 299(2): 797–805. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.03.002
[21] YU Y, ROWE R K. Modelling deformation and strains induced by waste settlement in a centrifuge test[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2018, 55(8): 1116–1129. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2017-0558
[22] CHEN Y M, ZHAN T L T, WEI H Y, et al. Aging and compressibility of municipal solid wastes[J]. Waste Management, 2009, 29(1): 86–95. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2008.02.024
[23] LIU J Y, XU D M, ZHAO Y C, et al. Long-term monitoring and prediction for settlement and composition of refuse in Shanghai Laogang Municipal Landfill[J]. Environmental Management, 2004, 34(3): 441–448. doi: 10.1007/s00267-004-2762-2
[24] PU H F, FOX P J. Model for coupled large strain consolidation and solute transport in layered soils[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 16(2): 04015064. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000539
[25] YAN H X, WU J W, THOMAS H R, et al. Analytical model for coupled consolidation and diffusion of organic contaminant transport in triple landfill liners[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2021, 49(2): 489–499. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2020.10.019
[26] XIE H, YAN H, FENG S, et al. An analytical model for contaminant transport in landfill composite liners considering coupled effect of consolidation, diffusion, and degradation[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2016, 23(19): 1–14.
[27] 田改垒, 张志红. 考虑热效应的污染物在土中扩散、渗透和固结耦合模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(2): 278–287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202202009.htm TIAN Gai-lei, ZHANG Zhi-hong. Coupled model for contaminant diffusion, osmosis and consolidation in soil considering thermal effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(2): 278–287. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202202009.htm
[28] LEE J, FOX P J, LENHART J J. Investigation of consolidation-induced solute transport. I: Effect of consolidation on transport parameters[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(9): 1228–1238. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000047
[29] 张志红, 许照刚, 杜修力. 吸附模式及固结变形对溶质运移规律的影响研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2013, 46(1): 104– 111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201301012.htm ZHANG Zhi-hong, XU Zhao-gang, DU Xiu-li. Study on the effects of adsorption modes and consolidation deformation on solute transport[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2013, 46(1): 104–111. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201301012.htm
[30] PU H, FOX, P J, SHACKELFORD C D, et al. Assessment of consolidation-induced contaminant transport for compacted clay liner systems[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2016, 142(3): 04015091.
[31] ALSHAWABKEH A N, RAHBAR N. Parametric study of one-dimensional solute transport in deformable porous media[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2006, 132(8): 1001–1010.
[32] CHO W J, LEE J O, CHUN K S. The temperature effects on hydraulic conductivity of compacted bentonite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 1999, 14(1/2/3): 47-58.
[33] 何俊, 胡晓瑾, 颜兴, 等. 黏土渗透性温度效应试验[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2017, 37(3): 55–60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLSD201703009.htm HE Jun, HU Xiao-jin, YAN Xing, et al. Experiments on temperature effect of hydraulic conductivity of compacted clay[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2017, 37(3): 55–60. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLSD201703009.htm
[34] 张宇宁, 陈宇龙, 李博. 饱和黏土的一维热固结特性试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(12): 1794–1799. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX201612026.htm ZHANG Yu-ning, CHEN Yu-long, LI Bo. Experimental study of one-dimensional thermal consolidation of saturated clays[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2016, 37(12): 1794–1799. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX201612026.htm
[35] 费康, 戴迪, 付长郓. 热–力耦合作用下黏性土体积变形特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(9): 1752–1758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201909023.htm FEI Kang, DAI Di, FU Chang-yun. Experimental study on volume change behavior of clay subjected to thermo-mechanical loads[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(9): 1752–1758. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201909023.htm
[36] SMITH D W. One-dimensional contaminant transport through a deforming porous medium: theory and a solution for a quasi-steady-state problem[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2000, 24(8): 693–722.
[37] 尹铁锋, 刘干斌, 郭桢, 等. 竖井地基热排水固结理论初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(3): 41–46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201403010.htm YIN Tie-feng, LIU Gan-bin, GUO Zhen, et al. A preliminary study of the theory of consolidation by vertical thermal drain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(3): 41–46. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201403010.htm
[38] HARRIS K R, WOOLF L A. Pressure and temperature dependence of the self-diffusion coefficient of water and oxygen-18 water[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1980, 76: 377–385.
[39] ROWE R K. Short- and long-term leakage through composite liners. The 7th Arthur casagrande lecture[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2012, 49(2): 141–169.
-
期刊类型引用(22)
1. 曹虎,张广清,李世远,汪文瑞,谢彭旭,孙伟,李帅. 基于断裂过程区的压裂驱油水力裂缝扩展模型及应用. 岩土力学. 2025(03): 798-810 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 何昭宇,王冬明,张太国,范世英. 济南地区土岩二元结构边坡加固设计及稳定性研究. 建筑结构. 2024(04): 73-79+66 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 施静怡,吴能森,刘强. 静压桩在成层地基中挤土效应的可视化研究. 河南城建学院学报. 2024(02): 20-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘江涛,李存军,于江华,张彦红,张春彬,孔纲强. 施工顺序对微型钢管桩加固既有基础变形的影响试验研究. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文). 2024(04): 100-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高玉峰,王玉杰,张飞,姬建,陈亮,倪钧钧,张卫杰,宋健,杨尚川. 边坡工程与堤坝工程研究进展. 土木工程学报. 2024(08): 97-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 胡焕校,谢中良,甘本清,卢雨帆,邓超. 透明砂土基本特性及其在注浆模型试验中的应用. 水资源与水工程学报. 2024(04): 179-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李梦晨,赵之仲,薛军,姜益顺. 土质边坡滑坡灾害的分级预警判据. 山东交通学院学报. 2024(03): 46-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 何建新,董旭光,马渊博. 坡顶荷载作用下多级边坡失稳演化机制的透明土试验研究. 西北工程技术学报. 2024(04): 347-355 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘强,吴能森,黄志波,许旭堂,徐祥. 抗滑桩加固二元结构边坡可视化模型试验. 林业工程学报. 2023(02): 172-179 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 赖成联. 基于沉井基础的重力坝坝肩滑坡处理技术. 红水河. 2023(02): 11-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 周昌,马文超,胡元骏,史光明. 基于透明土的库水位骤降下消落带滑坡-伞型锚体系变形破坏机理. 工程地质学报. 2023(04): 1407-1417 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张立乾,田义斌,闫晶,李兵,孟良. 某场地高边坡和洪水综合治理工程研究. 岩土工程技术. 2023(05): 545-552 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 周鹏,柯文斌. 可视化透明土技术在岩土变形测量实验教学中的应用. 教育教学论坛. 2023(50): 9-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 梁越,代磊,魏琦. 基于透明土和粒子示踪技术的渗流侵蚀试验研究. 岩土工程学报. 2022(06): 1133-1140 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 徐志军,王云泰,杜建平,王政权,周洋,王爽. 缩径基桩竖向承载性能的透明土试验研究. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(07): 214-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 卢谅,何兵,肖亮,王宗建,马书文,林浩鑫. 基于透明土的成层土中CPT贯入试验研究. 岩土工程学报. 2022(12): 2215-2224 .  本站查看
本站查看
17. 胡仕明,杨伟红,李涛,李昕堃. 公路隧道洞口顺层边坡变形规律分析. 岩土工程技术. 2022(06): 477-482 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 刘强,吴能森,许旭堂. 基于透明土的黏土边坡土体变形特征试验. 福建工程学院学报. 2022(06): 532-536 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 李元松,王玉,朱冬林,闫海涛,戴哲. 边坡稳定性评价方法研究现状与发展趋势. 武汉工程大学学报. 2021(04): 428-435 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 周义. 尼日利亚某铁路项目挖方边坡溜坍防护方案研究. 住宅与房地产. 2020(06): 226-227 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 翟淑花,孙小华,冒建,程素珍,刘欢欢. 北京山区岩土混合质边坡变形破坏机理分析. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版). 2020(04): 24-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 徐建强,阎宗岭,李海平,马小斐. 黔西岩溶区公路土岩混合边坡致灾模式及调控技术. 公路交通技术. 2019(06): 25-30+42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(18)



 下载:
下载: