Characterization of pressure arching effect of arch shell surrounding rock considering deviation of principal stress axis
-
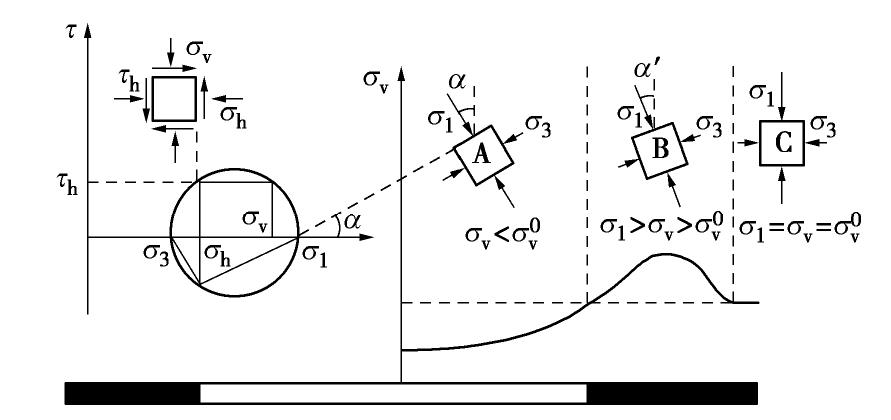
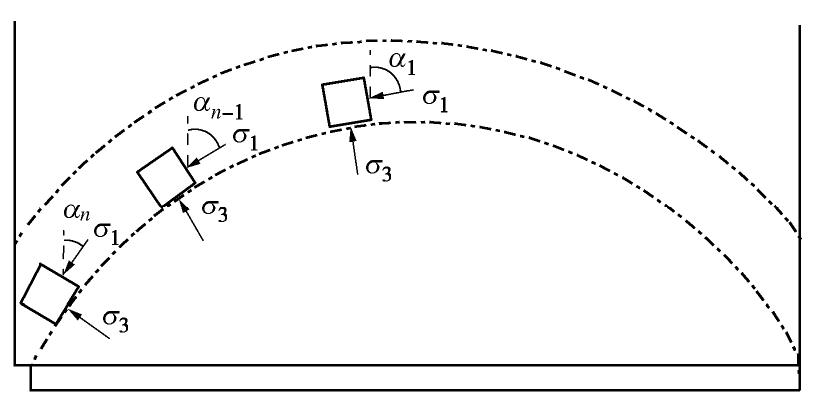
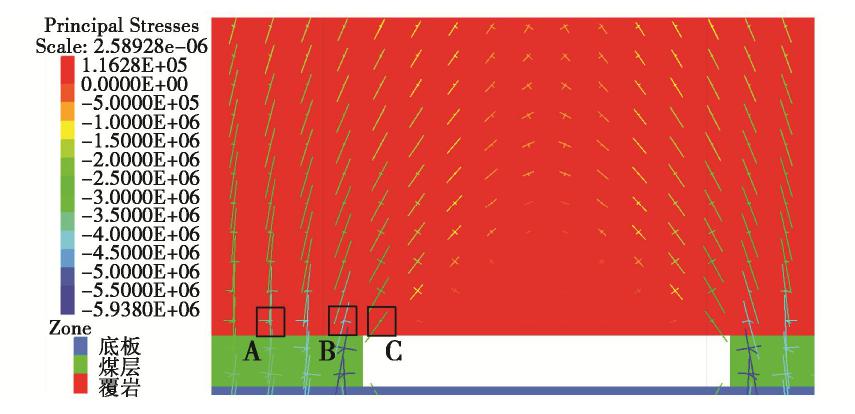
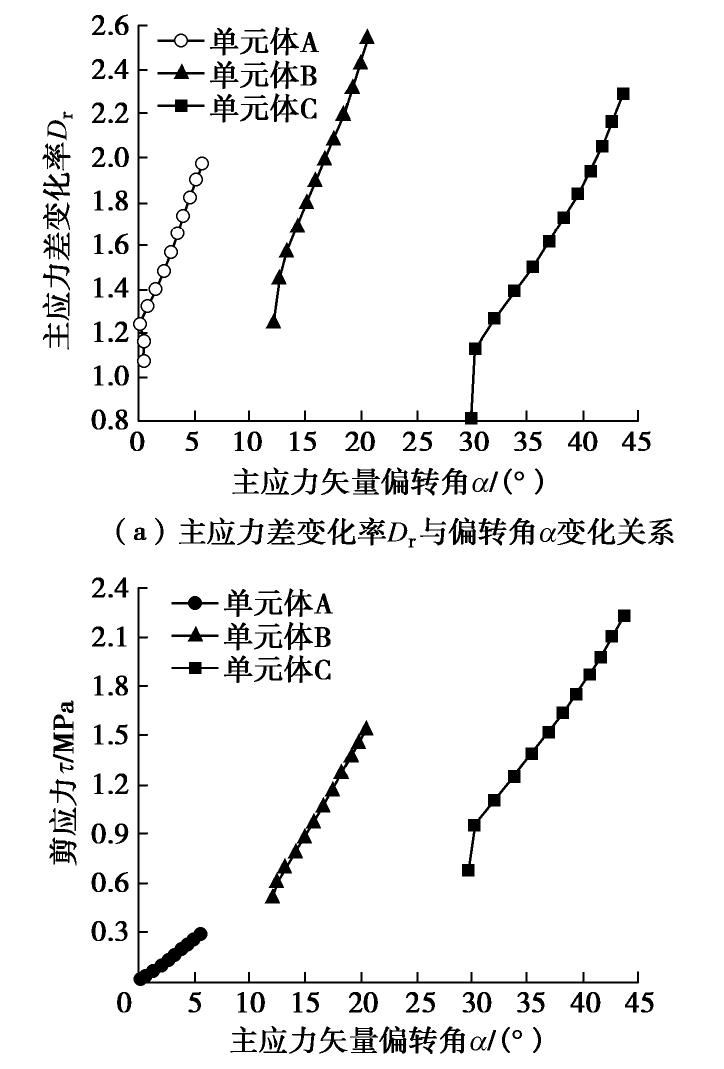
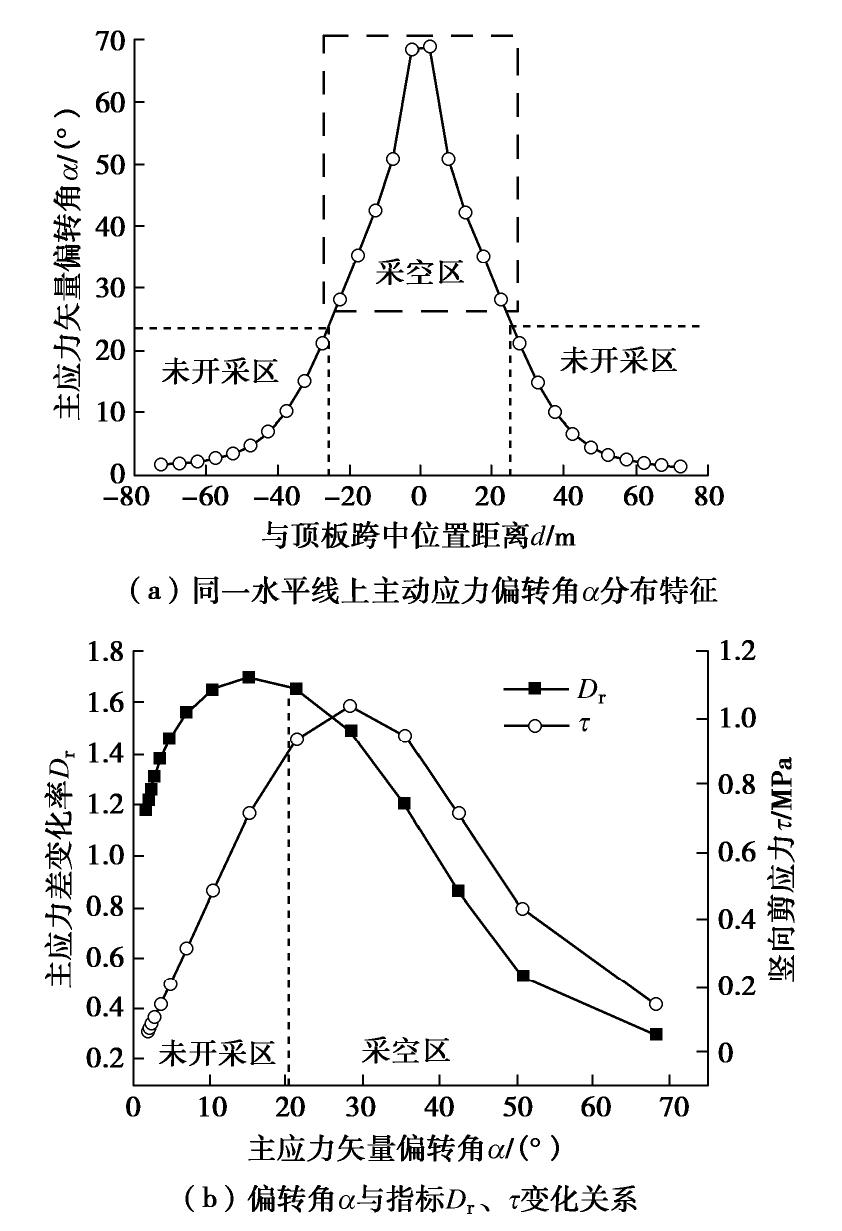
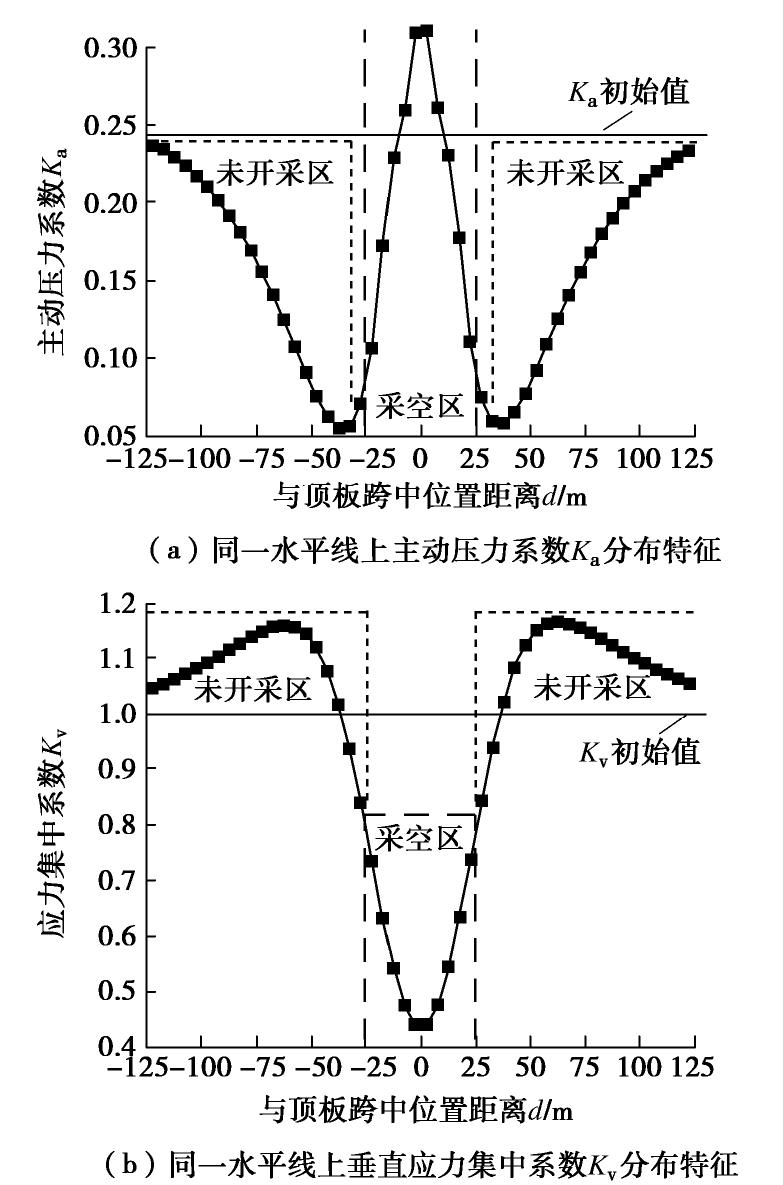
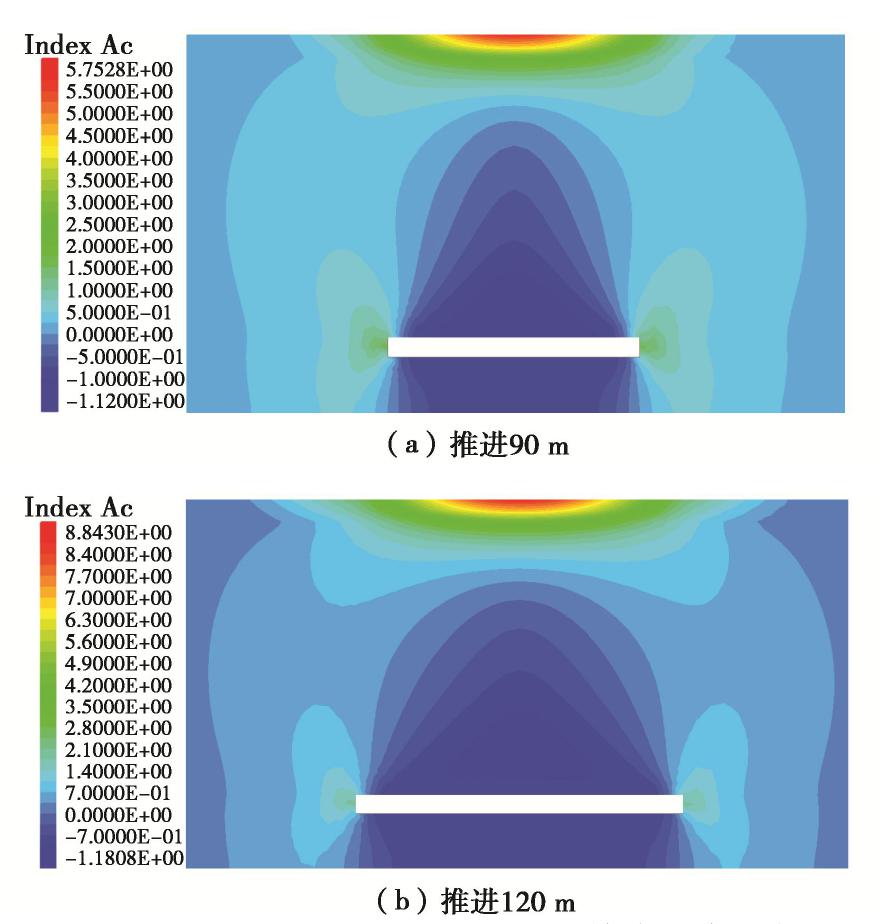
摘要: 拱效应是开挖区周围岩土体压力迁移及重分布的综合表现,广泛存在于矿山地下工程自承载区围岩。针对采场覆岩断裂拱外部存在远场拱壳结构的实际特点,基于Terzaghi土拱效应原理解析开采卸荷作用下岩层主应力矢量偏转响应特征,通过讨论主应力轴偏转影响下采场覆岩竖向压力主动释放状态及垂直应力分布特征,分析远场围岩压力拱关键部位压应力成拱指标。利用FLAC3D数值软件对采场覆岩主应力矢量偏转成拱规律进行模拟计算,结果表明:远场围岩主应力偏转角由初始最大主应力、侧压系数和采动后剪应力增量及主应力差变化率控制,同一层位覆岩主应力偏转角沿采空区跨中向边界呈递减分布,悬露岩层垂直应力随主应力偏转角增大而降低,压力拱拱顶主应力偏转角、主动压力系数及成拱指标峰值大于拱脚区域,拱脚及拱腰部位升高的垂直应力表现为支承压力。根据解析得出的岩层竖向压力释放力学判据和压应力成拱指标,表征了主应力轴偏转影响下远场围岩加卸载状态和拱效应演化特征。Abstract: The arching effect is the comprehensive performance of pressure transferr and redistribution of rock and soil mass around the excavated area, which widely exists in the self-bearing surrounding rock of underground mining projects. Aiming at the actual characteristics of the far-field arch shell structure outside the fractured arch of overlying strata in the mining area, the deviation response characteristics of the principal stress vector of the rock strata under the action of mining unloading are analyzed based on the principle of Terzaghi's soil arching effect, and by discussing the active released state of vertical pressure and the vertical stress distribution characteristics of overlying strata under the influence of deviation of the principal stress axis, the arching index of compressive stress of key part of the pressure arch in far-field surrounding rock is proposed. The numerical software FLAC3D is used to simulate and calculate the arching law of deviated principle stress of overlying strata in the mining area, and the results show that the deviation angle of the principal stress in the far-field surrounding rock is controlled by the initial major principal stress, lateral pressure coefficient, shear stress increment and changing rate of principal stress difference after mining; the deviation angle of the principal stress of rock strata decreases from the midspan to both sides of the goaf boundary at the same horizontal position; the vertical stress of the exposed rock strata decreases with the increasing deviation angle of the principal stress; the deviation angle of the principal stress, active pressure coefficient and peak value of arching index at the arch top are greater than those in the arch foot region; and the rising vertical stress in the arch foot and arch waist behaves as the bearing pressure. According to the derived mechanical criterion for releasing state of the vertical pressure in rock strata and the arching index of compressive stress, the loading and unloading states of the far-field surrounding rock and the evolution characteristics of pressure arching effect under the influence of deviation of the principal stress axis are characterized.
-
0. 引言
振杆密实法是一种新兴的可液化地基与黄土地基处理方法,该法通过振动杆在沉杆过程中与土体发生共振,土体吸收振动能量并进一步密实[1-2]。Chow[3]、程远等[4]分别介绍了振杆密实法在美国、中国等地可液化地基中的应用,该方法无需填料,施工简便,取得了显著效果。已有研究表明,振杆密实法的处理效果与施工参数密切相关。Massarsch等[5]应用谱分析原理求得振杆-土的共振频率以低频为主(≤20 Hz),不同土性之间略有差异;程远等[6]研究发现粉土地基的最佳振动频率为17 Hz。Brown等[7]、Wallays等[8]基于静力触探、地表沉降测量等原位测试方法对不同振杆形状的处理效果进行了对比,发现十字杆的处理效果最好,Y字杆次之,Terra杆最差。Janes[9]建议采用振杆密实法进行地基处理时需要进行不同振点间距现场试验以确定合适间距。Massarsch等[10]研究表明大间距长留振的处理效果不如小间距短留振。
上述研究成果主要应用于可液化地基,振杆密实法在湿陷性黄土地基中采用上述施工参数是否适用仍不明确。本文利用自主研发的振杆密实施工设备在湿陷性黄土地基的应用开展现场试验研究,探究了振动频率、喷气压力、钻头形式、振点间距对施工效率和处理效果的影响。研究成果可为振杆密实法在湿陷性黄土地基中的进一步应用提供技术参考。
1. 试验方案与场地工程概况
1.1 试验设备
采用自主研发的适用于黄土地基的智能化振杆密实施工设备进行现场试验,该设备主要包括①振动系统;②喷气系统;③智能化控制系统;④附属机构系统4部分组成[2]。施工设备详细参数见表1。
表 1 施工设备主要参数Table 1. Main parameters of construction equipments电机功率/kW 激振力/kN 喷气压力/MPa 可调频率/Hz 深度/m 振杆直径/m 90 530 0.5~1.2 0~30 ≤15 0.7 1.2 试验方案
振杆密实法的处理效果受施工设备、土层参数和施工工艺共同影响,其施工参数主要有:振动频率、钻头形式、喷气压力、振点间距。基于此,在试验场地内开展振杆密实单点试验和群点试验:
(1)单点试验:通过试振不同的振动频率和组合钻头形式对湿陷性黄土地基进行处理,对比施工效率和振孔尺寸,寻找最优施工参数,为群点试验提供参考。
(2)群点试验:在单点试验的基础上,选取一定的振动参数对区域进行集中处理,群点试验由27个单点组成,呈正三角形布置。通过改变不同的喷气压力与振点间距,探究其对加固效果的影响,群点试验处理7 d后进行静力触探试验,测试地基承载力变化,静力触探试验每个振区测3个点,分别为振点中心,两点之间,三点形心。
1.3 场地工程概况
本次试验场地位于中兰客专靖远县高铁站场坪区附近,场地内地层岩性主要为第四系全新统冲洪积层(Q4al+pl)砂质黄土,含水率为7.2%~11.5%,孔隙比0.975~1.121,干密度为1.27~1.36 g/cm3,具自重湿陷性,湿陷系数δs=0.010~0.087,自重湿陷系数δzs=0.005~0.024,湿陷性土层厚21~37.3 m,需对其进行地基处理,设计处理深度为8 m。
2. 振杆密实法施工参数分析
2.1 振动频率的影响
参考土体的共振频率,设计了不同振动频率下(14,15,16,17 Hz)下的单点振动试验。图1(a)为不同振动频率下施工速率或振孔参数柱状图。由图1(a)可以看出,随着振动频率的增大,沉杆速率、提升速率先增大后减小,在16 Hz处有最大值。
此外,振孔深度随振动频率的变化趋势与施工速率相似,在16 Hz处有最大值,振孔深度为2.5 m。而不同振动频率下的振孔直径基本相同,为0.7 m,14 Hz下略低,为0.65 m。如果把振杆-地基土看成一个共振体,当振动沉杆的振动频率接近于处理土体的固有频率时,振杆与土体产生强迫振动,此时共振体的振幅达到最大,沉杆过程功率消耗最低,施工速率最快,密实效率达到最佳。因此判断该场地的湿陷性黄土地基,振杆-土的共振频率为16 Hz。
2.2 组合钻头形式的影响
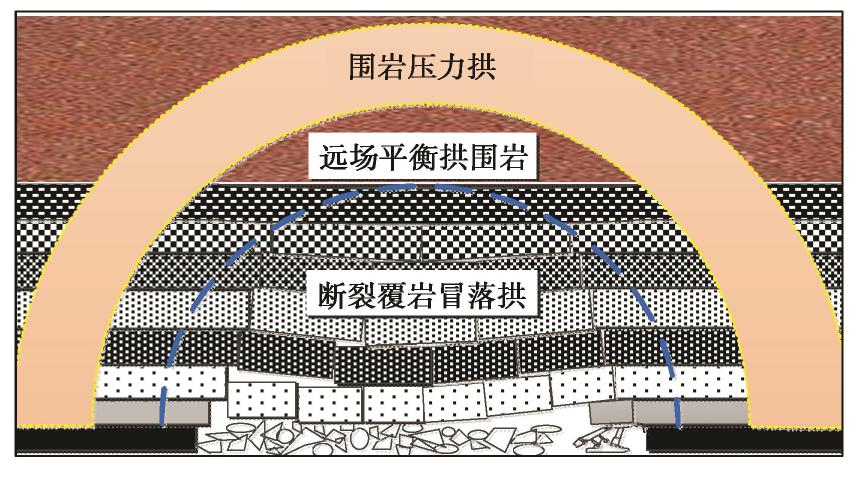
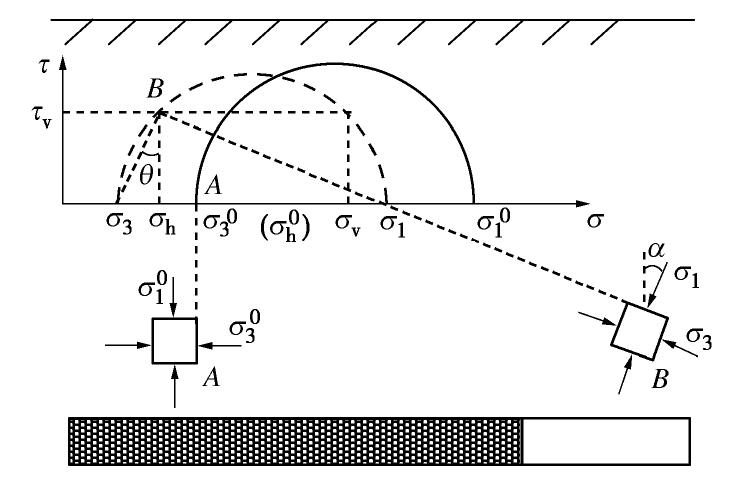
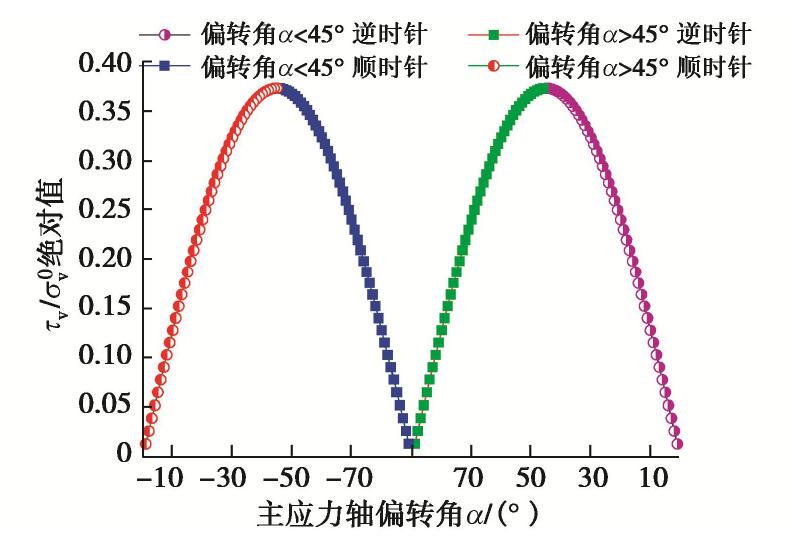
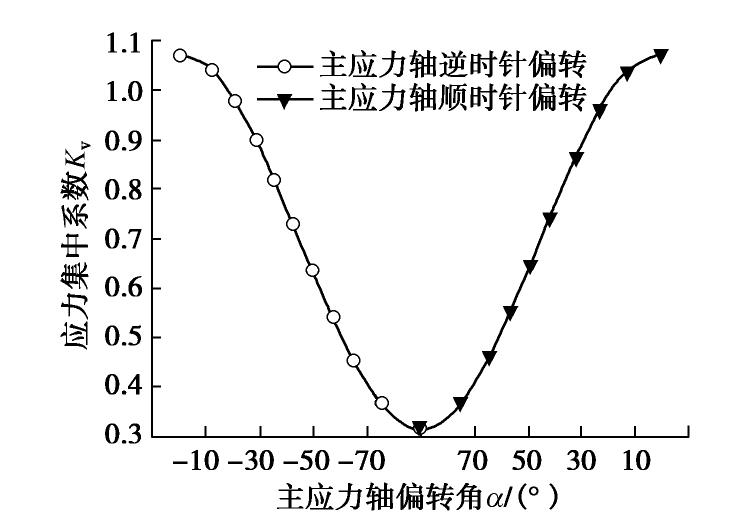
在可液化地基处理中,振杆形状对处理效果的影响显著。然而通过现场试振发现,黄土的强结构性使得钻头形式比振杆形式对其影响更大。因此设计了3种组合形式的钻头(图2)进行单点试振试验,得到不同组合钻头形式的施工速率与振孔参数柱状图如图1(b)所示。
由图1(b)可以看出,相对于普通钻头,3种组合钻头的施工速率和振孔深度均有明显提升,施工速率提高约100%~200%,振孔深度增大约50%,这主要是因为普通钻头在沉杆过程中翼片间会发生黏结堵塞现象,使得钻头阻力增大,沉杆困难,甚至无法打至设计深度。而组合钻头的翼片间相互错开,在刺入土体过程中可以将黏结在翼片之间的土体破坏,减少黏结现象,从而有效提高沉杆速率。此外,对比不同形式的组合钻头可以看出,A型钻头的沉杆速率、提升速率、振孔深度均最大,因此判断在该场地条件下,这种形式的组合钻头最适宜。不同钻头的振孔直径均为0.7 m,表明振孔直径与振杆直径有关,与钻头形式无关。
2.3 喷气压力的影响
为了探究喷气压力对加固效果的影响,分别设置不同的喷气压力(0.6,0.8,1.0 MPa),基于单点试验结果,控制振动频率为16 Hz,钻头形式为A型,振点间距为1.2 m,进行了群点试验。
不同测点处锥尖阻力与侧壁阻力随深度变化的关系曲线如图3所示。可以看出,不论气压大小,两点之间、三点形心处的锥尖阻力和侧壁阻力较处理前提升约150%~250%,表明振杆密实法有效提高了孔间土的强度及密实度。在两点之间,0.6 MPa处理区的锥尖阻力和侧壁阻力均为最大,1.0 MPa处理区最小,表明小气压对两点之间强度增长有益。在三点之间,1.0 MPa处理区的锥尖阻力和侧壁阻力最大,0.6 MPa与0.8 MPa的试验数值相对较小,原因在于1.0 MPa的气压加上留振作用破坏了0.4 m厚的两点间的土层,且未经有效压实。综合对比3个不同气压处理区的静力触探试验结果发现,喷气压力为0.8 MPa时两点之间、三点形心处较未加固区都有较大提高,且分布较均匀,可推荐作为施工参数使用。
2.4 振点间距的影响
分别设置不同振点间距(1.1,1.2,1.4 m),控制振动频率为16 Hz,钻头形式为A型,喷气压力为0.8 MPa进行现场群点试验。试验发现,当振点间距为1.1 m时,由于间距过小,振点间易发生串孔现象,导致振杆倾斜,无法形成振坑。
不同间距下锥尖阻力及侧壁阻力随深度变化曲线如图4所示。可以看出,相对于处理前,处理后的振区的锥尖阻力明显提升约200%~300%。对比不同振点间距的锥尖阻力可以发现,在振点中心处,1.2 m处理区与1.4 m处理区的锥尖阻力比较接近,表明振点间距对振孔中心处的强度影响不大。在两点中之间、三点形心处,1.2 m处理区的锥尖阻力和侧壁阻力明显比1.4 m处理区的大约50%,表明振点间距越小,加固效果越显著。振杆密实法对地基土的加固是依靠振动能量,而振动能量是以振动波的形式传递,波的传播随距离增大逐渐衰减,振点间距越小,振动波的叠加效应也越明显。此外,由于是群点试验,振点间距越小,挤密效果亦更好,但振点间距过小容易造成串孔现象。在该场地条件下,参照《铁路工程地质原位测试规程》(TB 10018—2018)中天然地基基本承载力经验公式,计算得到该场地设计承载力(180 kPa)对应的锥尖阻力约为3.2 MPa。1.2 m和1.4 m振点间距处理后的地基土,除表层土体外,均达到设计指标。
3. 结论
本文对振杆密实法处理湿陷性黄土地基的施工参数开展了现场试验研究,主要结论如下:
(1)在本文的场地条件下,振杆密实法处理湿陷性黄土的最优振动频率为16 Hz,该频率下施工速率和密实效果最佳。
(2)黄土的强结构性使得钻头形式比振杆形式对其施工影响更为显著。设计了几种不同的组合钻头,其中A型钻头能防止钻头处的土体黏结,进而提高施工效率。
(3)提出了气动辅助振杆密实的施工方式,基于静力触探试验对不同喷气压力下的处理效果进行了评价。分析结果表明0.8 MPa气压下土体强度提升明显,且静力触探曲线较为均匀,可参考作为施工参数。
(4)不同振点间距的群点试验结果表明,振杆密实法处理后的湿陷性黄土地基锥尖阻力和侧壁阻力提升约200%~300%。振点间距越小,加固效果越显著,但振点间距过小容易造成串孔现象,以1.2~1.4 m为宜。
-
表 1 煤岩层材料力学参数
Table 1 Material and mechanical parameters of coal and rock strata
岩性 重度/(kN·m-3) 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 黏聚力/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 砂岩 25.00 36.50 0.22 2.60 1.50 30 煤 13.10 12.70 0.29 1.20 0.60 27 粉砂岩 24.60 37.90 0.20 4.50 3 40 -
[1] 宋振骐, 郝建, 石永奎, 等. "实用矿山压力控制理论"的内涵及发展综述[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 38(1): 5-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201901001.htm SONG Zhen-qi, HAO Jian, SHI Yong-kui, et al. Summary of connotation and development of “practical mine pressure control theory”[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 38(1): 5-19. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201901001.htm
[2] 文志杰, 景所林, 宋振骐, 等. 采场空间结构模型及相关动力灾害控制研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(1): 57-66. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2019.01.007 WEN Zhi-jie, JING Suo-lin, SONG Zhen-qi, et al. Research on stope spatial structure model and related dynamic disaster control[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(1): 57-66. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2019.01.007
[3] 钱鸣高, 石平五, 许家林. 矿山压力与岩层控制[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 2010. QIAN Ming-gao, SHI Ping-wu, XU Jia-lin. Mine Pressure and Rock Formation Control[M]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 2010. (in Chinese)
[4] 杜晓丽, 宋宏伟, 陈杰. 煤矿采矿围岩压力拱的演化特征数值模拟研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2011, 46(6): 863-867. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201106005.htm DU Xiao-li, SONG Hong-wei, CHEN Jie. Numerical simulation study on evolution characteristics of pressure arch of surrounding rock in coal mining[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2011, 46(6): 863-867. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201106005.htm
[5] 宋宏伟, 杜晓丽. 岩土空洞周围的压力拱及其特性[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2012. SONG Hong-wei, DU Xiao-li. Pressure Arch Around Rock and Soil Cavity and Its Characteristics[M]. Beijing: Coal Industry Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[6] 谢广祥. 综放工作面及其围岩宏观应力壳力学特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2005, 30(3): 309-313. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2005.03.009 XIE Guang-xiang. Mechanical characteristics of the macroscopic stress shell of fully mechanized caving face and its surrounding rock[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2005, 30(3): 309-313. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2005.03.009
[7] 史红, 姜福兴. 充分采动阶段覆岩多层空间结构支承压力研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2009, 34(5): 605-609. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.05.006 SHI Hong, JIANG Fu-xing. Research on supporting pressure of overlying strata multilayer spatial structure in full mining stage[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(5): 605-609. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.05.006
[8] 杨振国, 李铁. 高位关键层对压力拱演化规律影响的研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2015, 46(4): 40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2015.04.011 YANG Zhen-guo, LI Tie. Research on the influence of high key layer on the evolution law of pressure arch[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2015, 46(4): 40-43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4495.2015.04.011
[9] HUANG Z P, BROCH E, LU M. Cavern roof stability mechanism of arching and stabilization by rockbolting[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2002, 17(3): 249-261. doi: 10.1016/S0886-7798(02)00010-X
[10] 梁晓丹, 刘刚, 赵坚. 地下工程压力拱拱体的确定与成拱分析[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 33(3): 314-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX200503018.htm LIANG Xiao-dan, LIU Gang, ZHAO Jian. Determination of pressure arch in underground engineering and analysis of arch formation[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 33(3): 314-317. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX200503018.htm
[11] WANG Y C, JING H W, ZHANG Q, LUO N, YIN X. Prediction of collapse scope of deep-buried tunnels using pressure arch theory[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2016(4): 1-10.
[12] 陈若曦, 朱斌, 陈云敏, 等. 基于主应力轴旋转理论的修正Terzaghi松动土压力[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(5): 1402-1406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.05.009 CHEN Ruo-xi, ZHU Bin, CHEN Yun-min, et al. Modified Terzaghi loosening earth pressure based on principal stress axis rotation theory[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(5): 1402-1406. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.05.009
[13] 黎春林. 盾构隧道施工松动土压力计算方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(9): 1714-1720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201409024.htm LI Chun-lin. Method for calculating loosening earth pressure during construction of shield tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(9): 1714-1720. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201409024.htm
[14] 汪丁建, 唐辉明, 李长冬, 等. 考虑主应力偏转的土体浅埋隧道支护压力研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(5): 804-810. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201605005.htm WANG Ding-jian, TANG Hui-ming, LI Chang-dong, et al. Research on support pressure of shallow tunnel in soil considering deflection of principal stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(5): 804-810. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201605005.htm
[15] 赖丰文, 陈福全, 万梁龙. 考虑不完全土拱效应的浅层地基竖向应力计算[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(7): 2546-2554. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201807027.htm LAI Feng-wen, CHEN Fu-quan, WAN Liang-long. Calculation of vertical stress of shallow foundation considering incomplete soil arching effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(7): 2546-2554. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201807027.htm
[16] ZHAO Y H, WANG S R, ZOU Y F, et al. Pressure-arching characteristics of fractured strata structure during shallow horizontal coal mining[J]. Tehnicki Vjesnik, 2018, 25(5): 1457-1466.
[17] REZAEI M, HASSANI M F, MAIDI A. Determination of longwall mining-induced stress using the strain energy method[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2015, 48(6): 2421-2433.
[18] BASARIR H, OGE I F, AYDIN O. Prediction of the stresses around main and tail gates during top coal caving by 3D numerical analysis[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2015, 76: 88-97.
[19] XUE D J, WANG J Q, ZHAO Y W, et al. Quantitative determination of mining-induced discontinuous stress drop in coal[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 111: 1-11.
[20] 任艳芳, 齐庆新. 浅埋煤层长壁开采围岩应力场特征研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(10): 1612-1618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201110002.htm REN Yan-fang, QI Qing-xin. Research on stress field characteristics of surrounding rock in shallow coal seam longwall mining[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(10): 1612-1618. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201110002.htm
[21] 霍丙杰, 于斌, 张宏伟, 等. 多层坚硬顶板采场覆岩"拱壳"大结构形成机理研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(11): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201611004.htm HUO Bin-jie, YU Bin, ZHANG Hong-wei, et al. Study on the formation mechanism of the "arch shell" large structure of the overlying strata in the stope with multi-layer hard roof[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2016, 44(11): 18-23. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201611004.htm
[22] XIA B W, FU Y H, ZHANG X, et al. Impact analysis of hard roof on the morphological evolution of stress arch[J]. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 2019, 12(1): 153-162.
[23] 徐祝贺, 李全生, 李晓斌, 等. 浅埋高强度开采覆岩结构演化及地表损伤研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(8): 2728-2739. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202008004.htm XU Zhu-he, LI Quan-sheng, LI Xiao-bin, et al. Structural evolution of overburden and surface damage caused by high-intensity mining with shallow depth[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(8): 2728-2739. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202008004.htm
[24] 王家臣, 王兆会, 杨杰, 等. 千米深井超长工作面采动应力旋转特征及应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(3): 876-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202003003.htm WANG Jia-chen, WANG Zhao-hui, YANG Jie, et al. Mining-induced stress rotation and its application in longwall facewith large length in kilometer deep coal mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(3): 876-888. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202003003.htm
[25] 谢和平, 周宏伟, 刘建锋, 等. 不同开采条件下采动力学行为研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(7): 1067-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201107002.htm XIE He-ping, ZHOU Hong-wei, LIU Jian-feng, et al. Research on mining dynamics behavior under different mining conditions[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(7): 1067-1074. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201107002.htm
[26] 宋振骐, 刘义学, 陈孟伯, 等. 岩梁裂断前后的支承压力显现及其应用的探讨[J]. 山东矿业学院学报, 1984(1): 29-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY198401002.htm SONG Zhen-qi, LIU Yi-xue, CHEN Meng-bo, et al. Discussion on the appearance and application of supporting pressure before and after rock beam fracture[J]. Journal of Shandong Institute of Mining and Technology, 1984(1): 29-41. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY198401002.htm
[27] 陈国舟, 周国庆. 考虑土拱效应的滑移面间竖向应力研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(3): 374-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201403002.htm CHEN Guo-zhou, ZHOU Guo-qing. Study on vertical stress between sliding surfaces considering soil arching effect[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2014, 43(3): 374-379. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201403002.htm
[28] 李建贺, 盛谦, 朱泽奇, 等. Mine-by试验洞开挖过程中围岩应力路径与破坏模式分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(4): 821-830. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201704006.htm LI Jian-he, SHENG Qian, ZHU Ze-qi, et al. Analysis of stress path and failure mode of surrounding rock during mine-by test tunnel excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(4): 821-830. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201704006.htm
[29] 庞义辉, 王国法, 李冰冰. 深部采场覆岩应力路径效应与失稳过程分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(4): 682-694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202004003.htm PANG Yi-hui, WANG Guo-fa, LI Bing-bing. Stress path effect and instability process analysis of overlying strata in deep stopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(4): 682-694. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202004003.htm
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 褚洪涛. 低能强夯联合水泥土搅拌桩在路基工程中的应用. 广东建材. 2025(03): 122-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘齐建,苏耀辉,黄奕彬,邓涛. 地面超载下摩擦单桩负摩阻力的连续介质力学解. 建筑科学与工程学报. 2024(02): 173-180 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李子林. 大跨度排架结构储豆堆场地基处理方案研究. 福建建材. 2024(04): 69-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘余杰. 水泥土搅拌桩在农村公路桥梁基础施工中的应用研究. 交通世界. 2024(13): 40-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张浩,赵宇,王中,刘维正. 芯桩承载扩体预制桩的荷载传递计算分析. 岩土工程学报. 2024(12): 2503-2512 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 周节定,胡磊,王乾浩. 同步同心式斜撑桩侧摩阻力现场试验研究. 建筑施工. 2023(04): 770-772+785 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 郑贺,鲍宇,刘汉臣. MC劲性复合桩在硬土层中应用的试验研究. 地基处理. 2023(03): 262-268 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 朱田. 分布式光纤测试技术在水泥土复合管桩检测中的应用. 水利与建筑工程学报. 2023(05): 63-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: