Permeability mechanism of PVC-P geomembrane at peripheral joints of high membrane-faced rockfill dams
-
摘要: 高面膜堆石坝坝面PVC-P土工膜防渗结构表现优越,差异位移致使周边缝处防渗结构中PVC-P土工膜处于大延伸率状态,是防渗体系的薄弱环节。针对变形态PVC-P土工膜防渗性能是否满足运行期工程技术要求,选用自主研制的变形态土工膜渗透试验仪展开了多组延伸率试样渗透性能试验研究,利用低场核磁共振技术探究了变形态PVC-P土工膜微观渗透演变机理。结果表明:变形态PVC-P土工膜防渗性能衰减,渗透系数随延伸率的增加而增大;延伸率的增长使得膜内孔喉发育、含量增加及孔喉连通性增强,这是防渗性能衰减的本质原因。尽管研究成果表明变形态PVC-P土工膜仍具有较低的渗透系数,但高面膜堆石坝周边缝处PVC-P土工膜拉伸变形复杂,可能存在局部损伤或破损情况,建议采取工程技术措施降低其延伸率,以延长服役周期。Abstract: The PVC-P geomembrane in the impervious structure of high-membrane faced rockfill dams has excellent impermeability. However, it has large elongation at the peripheral joints due to differential displacement, which is the weak section of the impervious system. To identify whether the permeability of the PVC-P geomembrane in tensile deformation meets the engineering requirements during the operation, a series of permeability tests at several elongations are carried out by a self-developed permeability tester for geomembrane in tensile deformation, and the microscopic permeability of the PVC-P geomembrane in tensile deformation microscopically is explored by the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology. The results show that the impermeability of the PVC-P geomembrane decreases, and the permeability coefficient increases with the increase of elongation. It further causes the development of pore throats, the increase of content and the enhancement of pore-throat connectivity within the geomembrane, which is the essential reason for the decrease of the impermeability. The PVC-P geomembrane in tensile deformation still has a low permeability coefficient, however, it has complicated tensile deformation at the peripheral joints of the high-membrane faced rockfill dams, which may cause local damages or breakage of the geomembrane. Consequently, it is recommended to take engineering measures to reduce the elongation to prolong the service life.
-
0. 引言
具有防渗性能优、适应变形能力强、低碳环保、施工便捷、易修复和造价低等优点的PVC-P土工膜广泛应用于水利、市政、隧道、矿山和交通运输等工程领域[1-4]。据国际大坝委员会135公告统计,263座以土工膜为主体防渗材料的大坝中59.0%使用了PVC-P土工膜[5-6],虽然工程实践已证明PVC-P土工膜的适用性,但施工时风荷载引起鼓胀变形、温度作用造成局部褶皱、地下水位上升致使水库库盘防渗膜气胀和周边缝处差异位移沉降引起的大拉伸变形等仍是亟待解决的关键技术问题[7-9]。水荷载作用下高堆石坝周边缝处差异位移引起的拉应变达46%~312%[10],膜防渗结构呈现运行初期剧烈变形最终趋于稳定的趋势[11],长期处于变形态PVC-P土工膜能否满足防渗要求关系整个工程安全运行[12]。
传统上采用土工膜垂直渗透试验仪和柔性壁渗透仪测定恒定渗透压力及一定时间内的渗透量表征土工膜的防渗性能,运用达西定律或菲克方程得到渗透系数或水力传导率,但其渗透机理仍存在争议[13-14],目前尚未见适用于大拉伸变形态土工膜渗透特性评价体系的文献或报道。低场核磁共振技术是一种具有快速、无损、准确等优点的信息测定技术[15],利用天然具有独特多尺度特性的自旋探针,从原子尺寸至100 nm空间尺度、10-9~102 s时间尺度上原位检测试样微观结构特征和动力信息[16],被广泛应用于农业食品、能源勘探、高分子材料和生命科学等领域研究。目前已有研究学者利用低场核磁共振技术量测并分析冻土样品中氢质子弛豫时间得到水份分布信息[17],并且该技术已成功应用到多种材料的微观结构分析,为PVC-P土工膜渗透机理和周边缝处膜防渗结构渗透特性研究奠定了基础。
为探究变形态PVC-P土工膜渗透性能,本文自主研发了一种变形态土工膜渗透量测定试验仪,展开了多组渗透压力及初始延伸率水力特性试验,研究了变形态PVC-P土工膜的渗透性能变化规律,利用低场核磁共振技术得到了膜渗透机理与渗透量、孔隙之间的关系。研究成果可供高面膜堆石坝周边缝处PVC-P土工膜渗透性能评价参考。
1. 试验及方法
1.1 试验材料
试验材料选用国内某知名土工合成材料生产厂家,选用压延工艺生产的PVC-P土工膜,其主要成分组成及含量为:质量占比57.4%PVC树脂,20.0%增塑剂,0.5%抗氧化剂,2.1%稳定剂和20.0%无机物填充剂。单幅卷材长45.0 m,宽2.0 m,物理力学特性指标详见表 1。
表 1 PVC-P土工膜主要物理力学特性表Table 1. Main physical and mechanical properties of PVC-P geomembrane技术指标 横向 纵向 厚度/mm 2.0±0.2 2.0±0.2 单位面积质量/(g·cm-2) 1.77 1.77 断裂强度/MPa 9.65 10.10 断裂延伸率/% 310.04 289.99 注:执行技术标准为《SL235—2012土工合成材料测试规程》[18](以下简称《规程》)。 1.2 定伸渗透试验仪
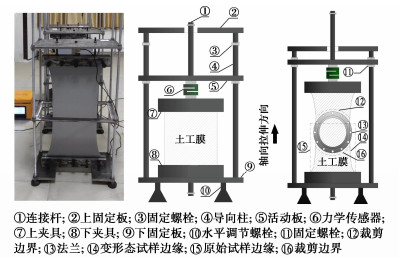
定伸渗透试验仪主要由延伸率保持器和土工膜垂直渗透试验装置组成。延伸率保持器实现定量拉伸变形控制,保持膜处于恒定变形状态;土工膜垂直渗透试验装置符合规程要求,可完成恒定变形态土工膜渗透性能测试。
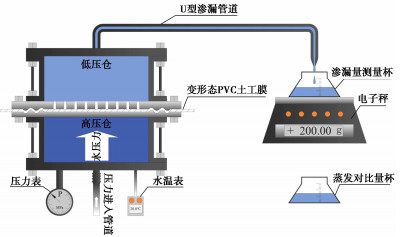
延伸率保持器主要由上固定板、下固定板、导柱、上夹具、下夹具、滑动板、连接杆、调平螺栓和固定螺栓等组成(图 1)。土工膜垂直渗透试验装置最大试验压力2.5 MPa,主要由上法兰盘、下法兰盘、低压仓、高压仓和量测设备等组成(图 2),上法兰盘中部设排水孔(孔径0.5 mm,间距10 mm),排水孔内嵌透水石以防止水压力致使土工膜产生额外变形;内边缘处设有圆形密封槽,槽内放置硅胶密封圈与高压仓相连;高压仓内径16 cm,高10 cm,底部设有压力传感器控制试验压力;低压仓与高压仓尺寸相同,顶部设置U型溢流管,试验时低压舱和溢流管内部充满水;量测设备主要包括量瓶和高精度电子秤,量瓶用于收集通过变形态土工膜的水量,高精度电子秤30 min/次记录量瓶收集到水的质量。
1.3 试样和试验方法
(1)试样
试样剪取位置距卷材边缘不小于100 mm,采用梯形取样法避免不同试样位于同一纵向和横向位置,土工膜垂直渗透试验试样为圆形,面积为200 cm2。为满足土工膜垂直渗透试验装置试样尺寸要求,并考虑轴向拉伸一定变形量产生的侧向收缩,定伸试样设计尺寸为40 cm×50 cm。
(2)定伸试样垂直渗透试验
为保证试验成果的准确性,具体试验操作步骤如下:
a)将试样装配至延伸率保持器上、下夹具中,令试样中心线与上、下夹具中心点处于同一铅垂线上,调节夹具将试样紧实固定。
b)将延伸率保持器装配至万能试验机,设定位移加载速率为5 mm/min,保持试验环境温度为20±2℃,待拉伸变形量满足设定条件后停止拉伸,利用滑动板上下紧固螺栓保持试样处于恒定延伸率,将延伸率保持器置于20±2℃恒定温度的储存间。
c)待应力松弛稳定后将法兰盘置于试样厚度均匀的中间部位,对齐法兰螺孔后使用螺栓与螺帽紧密固定上、下法兰盘,使其紧密夹持变形试样保证不回缩;然后将其平放在低压仓上,开展垂直渗透试验,并记录渗透水质量直至该试验结束。
d)按以上步骤完成其余渗透压力及所有延伸率试样的试验。
(3)低场核磁试验
为保证低场核磁共振试验测量数据的准确性,具体操作步骤如下:
a)待垂直渗漏试验结束后,从装置上取下试样,擦干表面,选用65 mm环刀在有效渗流区域裁取3个核磁试样并称重,运用不含H元素的聚四氟乙烯夹具夹紧试样,放入低场核磁共振仪[19]。
b)设置低场核磁共振仪参数。磁场主频12 MHz,探头线圈直径为150 mm;相邻回波时间间隔为0.3 ms,重复采样时间间隔为2000 ms,累加采样次数为32次,回波个数为2000,波谱仪接收参数增益100%。
c)运行试验仪器获得试验数据,并依据测得CPMG信号反演T2图谱。
d)重复上述步骤完成所有试样的低场核磁共振试验。
(4)试验方案
试验模拟工程中上游坝坡坡脚和趾板部位周边缝结构工作状态,设定渗透压力为1.0~1.5 MPa,升压梯度为0.1 MPa;试验主要研究较大拉伸变形仍未失效的延伸率,设计延伸率分别为50%,80%,125%,相应变形态试样应力松弛180 d后处于相对平衡的应力分别为2.50,3.28,3.82 MPa。为比对分析防渗性能的衰减程度,设PVC-P土工膜母材对照组。
1.4 试验成果分析方法
(1)渗透系数
PVC-P土工膜的厚度一般为1.0~2.5 mm,渗漏主要为扩散形式,依据Pand等[20]的研究成果渗透系数可采用达西定律表征土工膜的渗透系数:
k=vδAΔht。 (1) 式中:k为渗透系数(cm/s);v为渗透水量(cm3);δ为试样厚度(cm);A为试样过水面积(cm2);Δh为上下面水位差(cm);t为通过水量v的历时(s)。
拉伸后试样厚度减少[21],试验结束时测量膜的厚度;试验历时长,水温变化会产生一定的误差,按《规程》[18]修正水密度、黏滞系数,因试验量测的是渗透水质量,式(1)改写为
ks=mδtρsAΔhtηs。 (2) 式中:ks为标准化渗透系数(cm/s);m为渗透水重量(g);ρs为20℃水的密度(g/cm3);δt为变形态试样厚度(cm);ηs为20℃水的黏滞系数(kPa·s)。
(2)低场核磁共振试验
低场核磁共振是以1H等原子核为探针,被均匀磁场射频磁化后对射频的响应,质子释放能量的过程被特定线圈检测得到核磁共振信号,核磁信号随时间的变化曲线被称为FID曲线。FID曲线包含了膜内1H原子核含量与分布信息[22-24],经傅里叶转换,可得膜内1H原子核横向弛豫时间(T2)随时间分布的曲线:
1T2=1T2B+1T2S+1T2D=1T2B+ρSV+1T2D。 (3) 式中:T2B为在足够大的容器中测得的孔隙流体的弛豫时间(ms);T2S为固体和液体接触面的弛豫时间(ms);T2D为梯度磁场下扩散引起的弛豫时间(ms);ρ为横向弛豫率(μm/ms),与固体材料颗粒的物理和化学性质有关;S为水分所处孔隙的表面积(m2);V为水分所处孔隙的体积(m3)。
对于PVC-P膜中的孔隙量纲是微米级,式(3)中的T2S弛豫和T2D弛豫可以忽略,且假设材料满足快速扩散的条件,即膜的分布曲线为
1T2≈ρSV。 (4) 式中:S/V与孔隙的形状和孔隙半径相关。
SV=FSr。 (5) 式中:FS为孔隙的形状系数(球形、圆柱形以及裂缝的形状系数分别为3.0,2.0,1.0),本文假设土工膜中的水存在于微小裂缝中,取FS;r为孔隙半径(μm)。
联合式(4),(5)可得
1T2≈ρFSr。 (6) 由式(6)可得孔隙半径与成正比,即波峰的峰面积可表征PVC-P膜中孔隙总量,波峰结束时间反映了最大孔隙半径。
利用孔隙度为1%,5%,10%,20%,30%的标样得到单位体积核磁信号与孔隙度的分布关系并进行线性拟合曲线作为标线。依据低场核磁共振获得PVC-P土工膜的第i个核磁信号强度及标线,依据下式计算对应孔隙度:
φi=Mrinrσr⋅nωσωMω⋅VωVr×100%。 (7) 式中:Mri指PVC-P试样第i个T2信号强度(无量纲);Mω为标准样品的信号强度(无量纲);σω为标准样品的波谱仪接受增益(无量纲);σr代表测试样品的接受增益(无量纲);nω为标准样品的累加次数(无量纲);nr代表测试样品的累加次数(无量纲);Vω为标准样品的体积(mL);Vr为测试样品的体积(mL)。
则PVC-P土工膜试样的总孔隙度表达式为
ϕ=l∑i=1ϕ i 。 (8) 式中:l为质子开始释放吸收的脉冲能量至释放结束接收线圈获得的所有信号强度对应的孔隙度数量;ϕ为孔隙度(%)。
2. 试验成果及初步分析
2.1 垂直渗透试验成果及初步分析
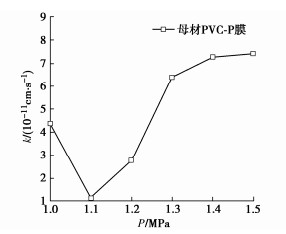
按照式(2)整理试验数据可得所有试验PVC-P土工膜的渗透系数。图 3展示了母材渗透系数与渗透压力分布曲线,曲线整体上呈现随渗透压力增大先减小后增大,最终趋于平缓的趋势。渗透系数在渗透压力1.0~1.1 MPa呈减小趋势,1.1 MPa达到最小值;1.1~1.3 MPa内随渗透压力增加呈快速增长趋势;1.3~1.5 MPa内随渗透压力增加缓慢增长,并趋于稳定。表明PVC-P土工膜的渗透系数非恒定值,与渗透压力大小有关。
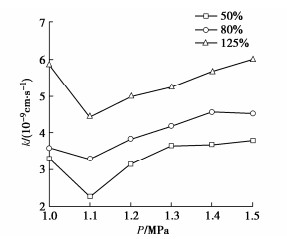
图 4展示了3组变形态PVC-P土工膜渗透系数与渗透压力分布曲线,均呈现先降低后升高的趋势,1.1 MPa达到最小值,与母材分布曲线基本相似。由图 4可知变形态试样渗透系数量级均为10-9 cm/s,所有渗透压力试验下,渗透系数随延伸率的增长而增大,均大于母材渗透系数10-11 cm/s量级。虽然50%,80%和125%延伸率试样的渗透系数在不同试验压力下存在差异,但差值较小,表明渗透压力对变形态PVC-P土工膜渗透系数的确定影响不明显。变形态PVC-P土工膜与传统黏性土防渗材料相比仍具有较好的防渗性能。
2.2 低场核磁共振试验成果分析
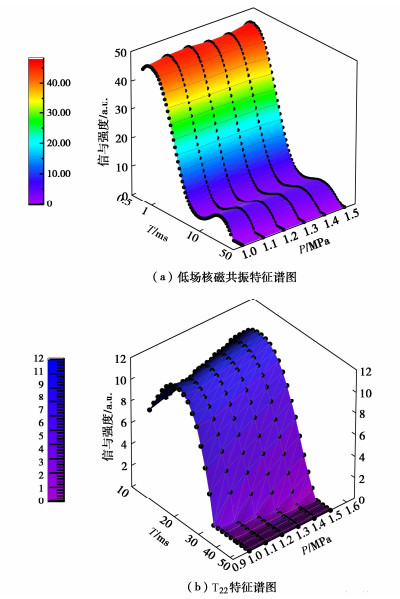
图 5(a)展示PVC-P土工膜母材(初始延伸率为0)不同渗透压力下低场核磁共振测试CPMG信号反演T2特征谱图。由图 5(a)可知,试验用PVC-P土工膜T2特征谱存在两个峰面,左侧峰(以下简称T21峰)代表了膜内高分子链中共价H原子信号,信号强度在49.15~50.08 a.u.,反映了膜内相互紧密缠结的高分子链交联牢固,其峰面积越大,表明H原子数量越多。所有试验压力下T2特征谱右侧峰(以下简称T22峰)的峰值信号强度在10.26~11.89 a.u.(图 5(b)),远低于T21峰值信号强度,表明T22峰面积代表了膜内孔隙中自由水H原子总量,峰面积越大,自由水越多,相应孔隙越多,波峰结束时间代表了膜内孔隙的最大值。
图 6展示了所有试验压力下PVC-P土工膜母材T22峰特征谱分布,1.0 MPa峰顶点信号强度值大于1.1 MPa信号强度,之后随渗透压力增加而增大,当渗透压力为1.5 MPa时信号强度为最大值,1.1 MPa下信号强度达到最小值,这与垂直渗透试验分析成果一致。T22峰面积反映了孔隙总量,1.0~1.5 MPa峰面积分别为206.86,202.89,227.51,244.37,261.56,281.69 a.u.s,1.0 MPa峰面积大于1.1 MPa峰面积,之后随渗透压力增加而增大;1.5 MPa渗透压力下峰面积达到最大值,表明孔隙总量最大,1.1 MPa渗透压力下峰面积为最小值,孔隙总量最小,峰面积的变化趋势与垂直渗透试验分析成果一致。
T22峰波峰结束时间反映了孔径最大值,由图 6可知,波峰结束时间随渗透压力增加呈增大趋势,其中1.0,1.1 MPa及1.3,1.4 MPa最大孔径值差值较大,表明大孔径发育程度高;1.1,1.2 MPa及1.4,1.5 MPa最大孔径值差值较小,表明大孔径发育程度低。波峰结束时间与峰值强度、峰面积以及垂直渗透试验分析成果变化趋势存在差异,渗透系数的变化并非完全取决于峰值强度和峰面积,需进一步量化分析膜内孔径演变规律,揭示PVC-P土工膜渗透机理。
3. 分析与讨论
3.1 土工膜渗透机理分析
高分子PVC-P土工膜属于致密性材料,孔隙具有开孔、闭孔、连通孔和封闭孔特征,抗渗性主要取决于开孔和连通孔的大小和数量。开孔和连通孔一般选用孔隙狭窄处即孔喉表征,孔喉半径的大小影响了孔隙间的连通性。孔隙流体流动一定程度受到细小喉道阻力和孔隙表面黏滞力的限制,是导致PVC-P土工膜渗透性和流体渗流能力低的主要原因。
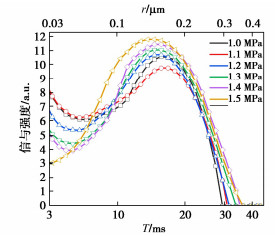
由图 6可知,所有试验压力下T22峰反演分析最小孔喉半径0.05 μm,最大孔喉半径0.35 μm,由式(8)可得1.0~1.5 MPa渗透压力下试样的孔隙度分别为0.4789%,0.4643%,0.4833%,0.4889%,0.5134%,0.6013%,孔隙度分布趋势与垂直渗透试验成果一致。表 2展示了所有试验渗透压力T22特征谱反演PVC-P土工膜孔隙分布,为厘清孔喉尺寸对渗透性能的作用,按照孔喉半径大小分为3个区间,并给出了各区间内孔喉数量占比。由表 2可知孔喉半径0.05~0.15 μm范围内占比最高,除1.5 MPa渗透压力下稍有增高外,其他渗透压力下变化微小,表明受渗透压力变化影响较小;孔喉半径0.15~0.25 μm围内,随渗透压力的增加呈现的趋势与孔隙度分布趋势相同,峰值强度和孔隙分布占比均高于孔喉半径0.25~0.35 μm,表明该范围内孔喉半径影响渗透性能显著;孔喉半径0.25~0.35 μm内,虽然孔喉分布占比最小,但随渗透压力的增加呈现增大的趋势,表明该范围内孔喉半径对渗透性能具有一定的影响。
表 2 PVC-P土工膜母材孔喉分布表Table 2. Distribution of pore throat of PVC-P geomembrane base metal孔喉半径/μm 孔喉分布/% 1.0 MPa 1.1 MPa 1.2 MPa 1.3 MPa 1.4 MPa 1.5 MPa 0.05~0.15 0.2970 0.2890 0.2969 0.2818 0.2829 0.3506 0.15~0.25 0.1634 0.1487 0.1602 0.1697 0.1807 0.2003 0.25~0.35 0.0194 0.0267 0.0262 0.0374 0.0498 0.0504 综上分析,除1.5 MPa渗透压力的孔隙度偏高外(最大差值为0.137%),其它试验压力的孔隙度差值不大于0.049%,表明1.0~1.4 MPa试验压力范围内渗透性能受渗透压力变化的影响较小,主要表现为在0.15~0.35 μm内孔喉的发育或萎缩。
3.2 变形态PVC-P渗透机理分析
本文研究的高面膜堆石坝是指坝高不大于150 m的高坝,因此周边缝处承受的水压力最大值按1.4 MPa考虑。依据3.1节分析成果可知,PVC-P土工膜在1.0~1.4 MPa内渗透性能受压力变化影响不大,为探究变形态PVC-P土工膜渗透机理,以1.0 MPa压力为例分析初始延伸率变化条件下孔隙的演变机制。
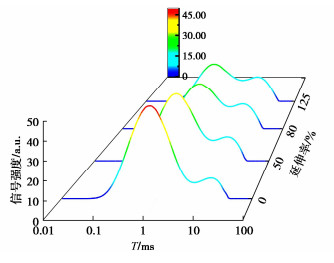
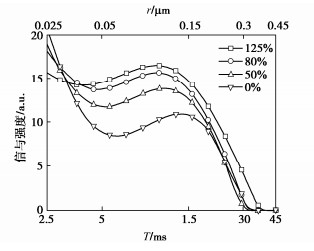
图 7展示了1.0 MPa渗透压力下0%,50%,80%,125%延伸率的T2特征谱。由图 7可知,T21峰信号强度随延伸率的增大而减小,延伸率的增加使得试样厚度减小,相应核磁试样的体积变小,其共价H原子含量减少,这是信号强度随延伸率增大而减小的原因。图 8展示了所有延伸率PVC-P土工膜T22峰特征谱分布,由图 8可知T22峰值信号强度随延伸率的增大整体增强,表明相同的半径的孔喉含量增加;延伸率增大波峰弛豫时间起点左移,波峰终点弛豫时间右移,表明孔喉呈发育趋势;峰面积随延伸率增加而增大,说明孔隙度呈增大趋势。延伸率为0%,50%,80%,125%的T22峰面积分别为206.86,278.9,332.46,414.88a.u.s,孔隙度分别为0.48%,1.88%,3.06%,4.36%,均呈增长趋势且相邻增幅逐渐增加,表明延伸率越大孔隙越发育;孔喉分布的区间分别为0.073~0.27,0.052~0.29,0.048~0.314,0.039~0.361 μm,区间范围呈扩增趋势,表明孔隙的发育存在闭孔发育为开孔及连通孔的发育。
表 3展示了所有试验延伸率T22特征谱反演变形态PVC-P土工膜孔隙分布,为厘清延伸率对孔喉尺寸的作用,根据T22特征谱弛豫时间对应的孔喉半径范围将其分为5个区间,并给出了各区间范围内孔喉数量占比;由表 3可知同一范围孔喉半径分布均随延伸率增加而增大,增幅由大到小分别为0.05~0.15 μm > 0.15~0.25 μm > 0.25~0.35 μm > 0.03~0.05 μm > 0.35~0.40 μm,整体上孔喉呈发育趋势,表明存在开孔孔径和数量增长以及孔喉连通性增强现象。孔喉半径在0.03~0.05 μm内,延伸率大于50%试样孔喉分布占比不为0,表明延伸率增大会致使部分闭孔发育为开孔;0.05~0.15 μm内延伸率不大于50%试样孔喉分布占比增加是由孔喉半径增大引起的,而延伸率大于50%试样,增加的孔喉分布占比是由小于0.05 μm的孔喉发育和该范围内半径增大的孔喉组成;0.15~0.25 μm内孔喉数量的增长源于部分半径小于0.15 μm的孔喉发育;0.25~0.35 μm内孔喉分布占比呈增长趋势,总体占比较小,而在0.35~0.40 μm内延伸率小于125%试样的孔喉分布为0,表明此范围内孔喉新增数量主要来源于部分半径小于0.25 μm的孔喉发育;发育为0.35~0.40 μm内的孔喉仅出现在125%延伸率,表明延伸率越大孔喉发育越显著。
表 3 所有试验延伸率试样孔喉分布表Table 3. Distribution of pore throat of specimen at all elongations孔喉半径/μm 孔喉分布 0% 50% 80% 125% 0.03~0.05 0 0 0.1266 0.6039 0.05~0.15 0.2970 1.3989 2.1896 2.6535 0.15~0.25 0.1634 0.4370 0.6491 0.8537 0.25~0.35 0.0194 0.0435 0.0951 0.2187 0.35~0.40 0 0 0 0.0254 综上分析,变形态PVC-P土工膜孔隙整体上呈发育趋势,具体表现为闭孔发育为开孔、孔喉半径增大和孔喉分布占比的增长,延伸率越大孔隙发育越显著,相应孔隙度越大,这是抗渗性能随延伸率增大而衰减的主要原因。
4. 结论
针对面膜堆石坝周边缝处膜防渗结构中变形态PVC-P土工膜的渗透性能,本文采用自主研发的定伸渗透试验仪展开了变形态PVC-P土工膜渗透试验,获得了渗透系数衰变趋势;基于低场核磁共振技术从微观角度探究了渗透性能演变机理,主要得到3点结论。
(1)变形态PVC-P土工膜抗渗性能随延伸率增大呈衰减趋势,相较于母材渗透系数由10-11 cm/s量级增大至10-9 cm/s,无损伤及局部拉伸破坏条件下,其防渗性能优于传统黏性土防渗材料。
(2)延伸率的增大导致孔隙发育显著、孔隙度增大,归因于闭孔发育为开孔、孔喉半径增大和孔喉分布占比增长,这是抗渗性能随延伸率增大而衰减的主要原因。
(3)尽管变形态PCV-P土工膜仍具有较低的渗透系数,但工程实际中拉伸变形是复杂多样的,可能存在局部损伤或破损状况,建议采取工程技术措施降低出现大延伸率或损伤破坏的可能性,以延长服役周期。
-
表 1 PVC-P土工膜主要物理力学特性表
Table 1 Main physical and mechanical properties of PVC-P geomembrane
技术指标 横向 纵向 厚度/mm 2.0±0.2 2.0±0.2 单位面积质量/(g·cm-2) 1.77 1.77 断裂强度/MPa 9.65 10.10 断裂延伸率/% 310.04 289.99 注:执行技术标准为《SL235—2012土工合成材料测试规程》[18](以下简称《规程》)。 表 2 PVC-P土工膜母材孔喉分布表
Table 2 Distribution of pore throat of PVC-P geomembrane base metal
孔喉半径/μm 孔喉分布/% 1.0 MPa 1.1 MPa 1.2 MPa 1.3 MPa 1.4 MPa 1.5 MPa 0.05~0.15 0.2970 0.2890 0.2969 0.2818 0.2829 0.3506 0.15~0.25 0.1634 0.1487 0.1602 0.1697 0.1807 0.2003 0.25~0.35 0.0194 0.0267 0.0262 0.0374 0.0498 0.0504 表 3 所有试验延伸率试样孔喉分布表
Table 3 Distribution of pore throat of specimen at all elongations
孔喉半径/μm 孔喉分布 0% 50% 80% 125% 0.03~0.05 0 0 0.1266 0.6039 0.05~0.15 0.2970 1.3989 2.1896 2.6535 0.15~0.25 0.1634 0.4370 0.6491 0.8537 0.25~0.35 0.0194 0.0435 0.0951 0.2187 0.35~0.40 0 0 0 0.0254 -
[1] 束一鸣, 吴海民, 姜晓桢. 中国水库大坝土工膜防渗技术进展[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(增刊1): 1-9. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2016S1001 SHU Yiming, WU Haimin, JIANG Xiaozhen. Progress of geomembrane seepage control technology for China Reservoir dam[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(S1): 1-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2016S1001
[2] KERMANI B, STOFFELS S M, XIAO M. Evaluation of effectiveness of geotextile in reducing subgrade migration in rigid pavement[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2019, 27(1): 1-43.
[3] HUANG Y Y, XIE T, FEI D W, et al. Working behavior feedback of composite geomembranes based on seepage monitoring data[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2021(6): 28.
[4] LIU S, WANG Y, FENG D. Compatibility of tailings-nonwoven geotextile under stress and the effect of sand filter[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2020, 28(2): 1-26.
[5] KOERNER R M, WILKES J A. 2010 ICOLD Bulletin on geomembrane sealing systems for dams[J]. Geosynthetics, 2012, 30(2): 34-36, 38, 40, 42-43.
[6] SCUERO A, VASCHETTI G. Geomembrane sealing systems for dams: ICOLD Bulletin 135[J]. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions, 2017, 2(1): 29.
[7] 张宪雷, 刘云锋, 顾克, 等. 高面膜土石坝防渗结构中土工膜弯折(褶皱)试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(8): 1555-1561. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201908021 ZHANG Xianlei, LIU Yunfeng, GU Ke, et al. Experimental study on geomembrane bending (folding) in anti-seepage structure of membrane-faced rockfill dam[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(8): 1555-1561. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201908021
[8] 王柳江, 刘斯宏, 孙来, 等. 平原水库运行条件下的土工膜气胀试验研究[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(6): 522-527. WANG Liujiang, LIU Sihong, SUN Lai, et al. Experimental study on the air expansion of geomembrane under operation condition of plain reservoir[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 45(6): 522-527. (in Chinese)
[9] ROWE R, ABDELATTY K M. Leakage and contaminant transport through a single hole in the geomembrane component of a composite liner[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139: 357-366.
[10] 郦能惠. 高混凝土面板堆石坝新技术[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2007. LI Nenghui. Recent Technology for High Concrete Face Rockfill Dams[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2007. (in Chinese)
[11] AMJAD R M N, KUMAR S S. Predicting the settlement of geosynthetic-reinforced soil foundations using evolutionary artificial intelligence technique[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2021, 49(5): 1280-1293.
[12] OMIDI O, LOTFI V. Seismic plastic-damage analysis of mass concrete blocks in arch dams including contraction and peripheral joints[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2017, 95: 118-137.
[13] OZSU E, ACAR Y. Liquid conduction tests for geomembranes[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 1992, 11: 291-318.
[14] AMINABHAVI T M, NAIK H G. Chemical compatibility testing of geomembranes-sorption/desorption, diffusion, permeation and swelling phenomena[J]. Geotextiles & Geomembranes, 1998, 16(6): 333-354.
[15] XIAO Q. Drying process of sodium alginate edible films forming solutions studied by LF NMR[J]. Food Chemistry, 2018, 250: 83-88.
[16] 徐国雷, 张宪雷, 马仲阳. 基于低场核磁共振技术面膜堆石坝中PVC膜渗透机理[J]. 水电能源科学, 2022, 40(12): 138-142. XU Guolei, ZHANG Xianlei, MA Zhongyang. Mechanism of PVC membrane permeation in face rock fill dam based on low-field NMR technology[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2022, 40(12): 138-142. (in Chinese)
[17] WEI L, CHAI S, XUE M L, et al. Structural damage and shear performance degradation of fiber–lime–soil under freeze–thaw cycling[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2022, 50(5): 845-57.
[18] 土工合成材料测试规程: SL 235—2012[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2012. Specification for Test and Measurement of Geosynthetics: SL 235—2012[S]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[19] 张宪雷, 尹春杰, 马仲阳, 等. 基于低场核磁共振技术PVC-P土工膜细观渗透机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2024, 46(4): 880-889. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20221546 ZHANG Xianlei, YIN Chunjie, MA Zhongyang, et al. Micropermeation mechanism of PVC-P geomembrane by low field NMR technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 46(4): 880-889. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20221546
[20] PAN D Z, WANG L Z, PAN C H. State-space solution of seabed-geotextile systems subjected to cyclic wave loadings[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2007, 25(4/5): 242-250.
[21] ZHANG X L, WU Y Y, MA Z Y, et al. Mechanical properties of PVC geomembrane under uniaxial tension based on non-contact measurement[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2023, 30(3): 259-273.
[22] ALHAJJI E, MRAD O. A low field NMR study of water adsorbed on silica and alumina surfaces[J]. Composite Interfaces, 2012, 19(5): 313-320.
[23] BLACK P B, TICE A R. Comparison of soil freezing curve and soil water curve data for Windsor sandy loam[J]. Water Resources Research, 1989, 25(10): 2205-2210.
[24] WEBBER J B W, CORBETT P, SEMPLE K T, et al. An NMR study of porous rock and biochar containing organic material[J]. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 178(18): 94-98.
-
其他相关附件



 下载:
下载: