Experimental study on characteristics of pore water pressure and dissipated energy of saturated calcareous sand under complex loading conditions
-
摘要: 钙质砂是一种由海洋生物残骸沉积而成的特殊岩土体,为我国南海岛礁主要的吹填材料,研究其动力特性意义重大。通过一系列不排水循环剪切三轴试验,分析饱和钙质砂孔压特性发展规律;引入能量法,建立钙质砂孔压和损耗能的内在联系。结果表明,饱和钙质砂的极限残余孔压比随固结应力比呈先增大后减小的变化趋势,循环加载过程所累积的损耗能与试样初始静剪应力比及相对密实度有关,受循环应力比影响极小,可通过构建的能量模型较好地预测不同试验条件下饱和钙质砂的损耗能。研究成果能为钙质砂地基的稳定性分析提供理论依据和技术支撑。Abstract: Calcareous sand, the special soil, is the main material for the filling of islands and reefs in the South China Sea, which is biogenic sediments and skeletal remains of marine organisms. It is of great importance to study its dynamic characteristics. By a series of undrained cyclic triaxial tests on the calcareous sand, the characteristics of pore water pressure are investigated. Besides, the energy method is used to establish the relation between the pore water pressure and the dissipated energy. The results show that the ultimate residual pore pressure ratio of the saturated calcareous sand increases first and then decreases with the change of consolidation stress ratio. The accumulated dissipated energy during cyclic loading is related to the initial static shear stress ratio and relative density of the sample, and has few influences on the cyclic stress ratio. The dissipated energy of the saturated calcareous sand under different test conditions can be predicted by the energy model. The research provides theoretical basis and technical support for the stability analysis of calcareous sand foundations.
-
0. 引言
钙质砂是由珊瑚骨骼、贝类、虫黄藻类等海洋生物残骸沉积而成,其主要组成成分是碳酸钙[1-3],是我国南海岛礁吹填的主要材料。因其生成环境、成因以及物质组成等因素影响,钙质砂具有颗粒易破碎、形状极不规则、内孔隙发育、微观结构复杂等显著区别于陆源石英砂的特点[4-6]。随着“一带一路”国家战略和建设“海洋强国”政策方针的推进,研究钙质砂工程力学特性具有重要意义[7-9]。
钙质砂作为填方工程的天然材料,其应力状态复杂多变,土体受到各向异性应力状态影响而产生初始静剪应力,在建(构)筑物的自重和动荷载(波浪、地震和交通荷载等)作用下,易引起地基强度降低、变形过大以及液化失稳等灾害。实际上,动荷载作用下剪切应力做功将导致材料损伤效应的累积,不排水条件下表现为孔压增长。因此,可以将孔压的升高与土体颗粒在运动或重排过程中所耗损的能量建立关联。损耗能作为标量,相较于应力、应变等矢量,可直接数学叠加,大幅度降低分析难度。Nemat-Nasser等[10]首先提出了耗散能量的概念,建立其与残余孔压的关系,来有效地评估孔隙水压力的产生和发展过程。Kokusho[11]和Pan等[12]提出了土骨架破坏产生的单位体积耗散能与应变和残余孔压累积直接相关,为评价砂土在不规则循环应力条件下的抗液化能力提供了有效方法。总体而言,上述研究主要针对石英砂,能否适用于钙质砂仍需进一步探究。
本文以饱和钙质砂为研究对象,开展不排水条件下循环剪切三轴试验,探究相对密实度、初始静剪应力以及循环应力对其孔压发展的影响;同时,引入能量法,建立钙质砂孔压与损耗能之间联系,提出基于能量损耗的液化评价方法,为钙质砂地基稳定性分析提供理论依据和技术支撑。
1. 试验材料与方案
1.1 试验材料
本文试验材料为中国南海某岛礁的天然钙质砂,颗粒多呈灰白色,形状有片状、块状、棒状等,颗粒内孔隙多、微观结构复杂,如图 1所示。
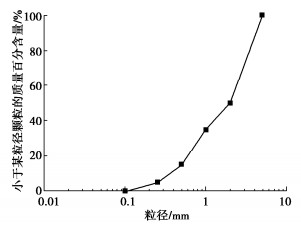
经过现场取材、清水冲洗、烘干等过程后,对粒径大于5 mm的颗粒进行剔除,处理后颗粒分布级配曲线如图 2所示,主要基本物理性质参数见表 1。不难发现,试样基本不含0.1 mm以下的细颗粒,不均匀系数和曲率系数分别为6.84和0.78,属于不良级配砂土。
表 1 钙质砂物理性质指标Table 1. Physical properties of calcareous sand相对质量密度 d50/
mm不均匀系数 曲率系数 最大孔隙比 最小孔隙比 2.79 2.0 6.84 0.78 1.15 0.87 1.2 试验方案
结合实际工况,采用CKC三轴试验系统模拟复杂应力条件下饱和钙质砂循环剪切试验,先进行有效围压为100 kPa的等向固结后再根据试验设计的初始静偏应力状态进行非等向固结,具体方案如表 2所示。初始静剪应力比SSR和循环应力比CSR可通过式(1)和(2)计算。
表 2 不排水循环剪切试验方案Table 2. Summary of undrained cyclic triaxial tests试验系列 相对密实度
Drqs/
kPaqcyc/
kPaSSR CSR Nf Ⅰ 70%
(密砂)0 20 0 0.1 232 0 25 0 0.125 74 0 30 0 0.15 17 0 40 0 0.2 6 20 30 0.1 0.15 168 20 45 0.1 0.225 19 20 50 0.1 0.25 3 50 50 0.25 0.25 53 50 60 0.25 0.3 11 50 70 0.25 0.35 6 80 70 0.4 0.35 14 80 80 0.4 0.4 7 -10 25 -0.05 0.125 78 -10 30 -0.05 0.15 39 -10 35 -0.05 0.175 8 -20 20 -0.1 0.1 210 -20 25 -0.1 0.125 11 -20 30 -0.1 0.15 8 -40 20 -0.2 0.1 57 -40 25 -0.2 0.125 16 -40 30 -0.2 0.15 8 Ⅱ 30%
(松砂)0 15 0 0.075 943 0 20 0 0.1 120 0 25 0 0.125 37 0 30 0 0.15 18 24 30 0.12 0.15 61 24 35 0.12 0.175 16 24 40 0.12 0.2 5 40 15 0.2 0.075 175 40 20 0.2 0.1 9 50 12.5 0.25 0.0625 17 50 15 0.25 0.075 2 -10 12.5 -0.05 0.0625 382 -10 15 -0.05 0.075 180 -10 20 -0.05 0.1 11 -20 10 -0.1 0.05 246 -20 12.5 -0.1 0.0625 202 -20 15 -0.1 0.075 12 -40 5 -0.2 0.025 104 -40 7.5 -0.2 0.0375 13 -40 10 -0.2 0.05 2 SSR=qs2p′0, (1) CSR=qcyc2p′0。 (2) 式中:qs为初始静剪偏应力;qcyc为循环偏应力;p′0为平均有效正应力。
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 孔压特性发展规律
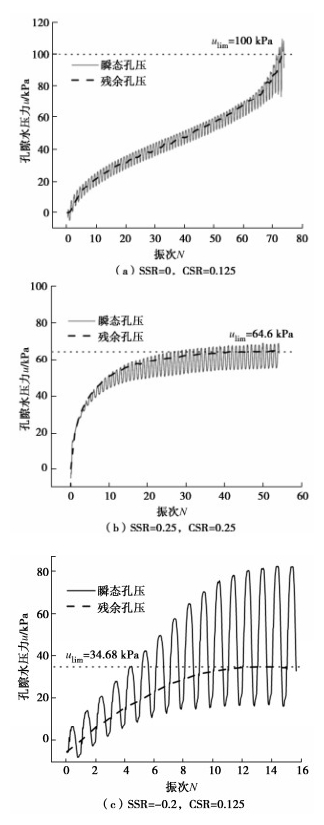
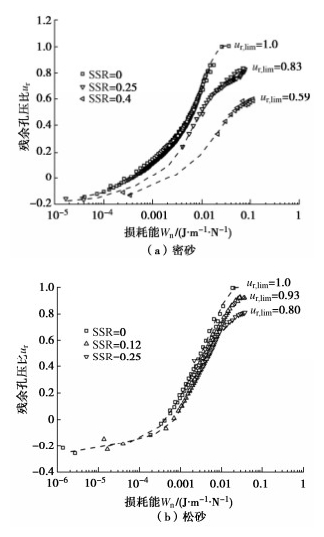
图 3给出不同初始偏应力作用下饱和密砂的孔压发展规律曲线。孔隙水压力可分为两类:①随着循环荷载作用实时变化的孔压,即实线所示的瞬态孔压,这种孔压会随着循环荷载的卸载而快速消散;②每个循环加载结束,试样未及时恢复的孔压,即虚线所示的残余孔压。从图 3(a)中可以看出,对于等向固结的试样,残余孔压在前期随着荷载的施加而逐渐累积,而在后期快速增长,直至达到荷载施加前的有效围压,ulim=100 kPa。如图 3(b)所示,在压缩静偏应力作用下,孔压在加载初期迅速累积,随着循环荷载持续进行,残余孔压逐渐趋于稳定,ulim=64.6 kPa。在拉伸静偏应力作用下,孔压发展与压缩静偏应力时有类似的变化趋势,孔压在加载初期累积较快而后基本保持不变,ulim=34.68 kPa。
同时,通过式(3)和(4)定义固结应力比Kc和残余孔压比ur。
Kc=σv0σh0, (3) ur=uσh0。 (4) 式中:σv0和σh0分别为初始有效竖向应力和水平应力,u为残余孔压。
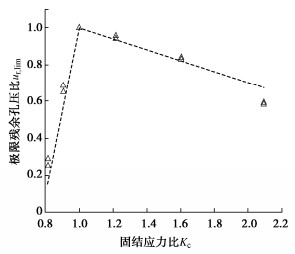
图 4给出了饱和密砂的极限残余孔压比和固结应力比的关系曲线。从图中可以看出,饱和密砂的极限残余孔压比随着固结应力比的增大呈先增大后减小的趋势,在Kc=1(等向固结)时,极限残余孔压比达到最大值ur, lim=1,且大致上呈线性分布,与循环应力幅值大小无明显关系。
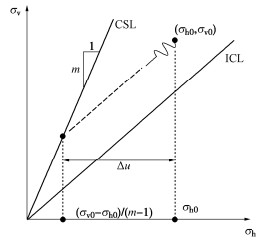
对于同一材料的砂土,其在循环荷载作用下有效应力路径将沿着平行于等向固结线(ICL)的方向逐渐靠近临界状态线(CSL),而与循环应力幅值无关,如图 5所示。因此,对于给定的初始应力状态(σh0,σv0),会与临界状态线相交于一点,且理论上初始应力点与最终应力点之间的水平距离Δu为试验中的极限残余孔压,如式(5)所示。根据ur和Kc定义,可得到两者关系如式(6),符合图 4所示的线性关系。
ulim=Δu=σh0−σv0−σh0m−1, (5) ur, lim=ulimσh0=1−Kc−1m−1。 (6) 2.2 损耗能演化规律
动荷载作用下饱和砂土损耗的能量主要用于颗粒的相对运动和重新排列。因此,引入能量法,提出基于损耗能的砂土液化评价方法。循环加载过程中一个振次的损耗能W可用应力-应变滞回圈的面积表示,即:
W=n−1∑i=112(qi+1+qi)(εa, i+1−εa, i)。 (7) 式中:n为计算增量的总个数,qi和εa, i分别为第i个增量的偏应力和轴向应变。
图 6分别给出饱和钙质砂在不同初始静偏应力作用下残余孔压比与正交化损耗能的内在关系,正交化损耗能Wn为损耗能W与初始有效水平正应力σh0的比值。结果显示:饱和密砂的残余孔压初期增长缓慢,随着Wn的增大而较快增长,最后趋于稳定;在饱和松砂中也观察到类似的变化趋势。这说明残余孔压与损耗能的关系主要取决于初始应力条件。
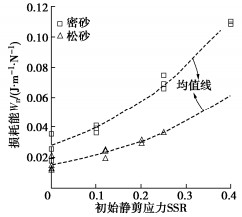
从图 7可以看出,饱和钙质砂在失稳破坏时所积累的损耗能随着初始静剪应力的增加而增加;对于同一初始应力状态,密砂所需能量始终大于松砂。研究表明[13-14],饱和砂土在循环荷载作用下损耗能主要与初始应力和相对密实度有关,受循环荷载幅值影响极小,具体可用式(8)表示:
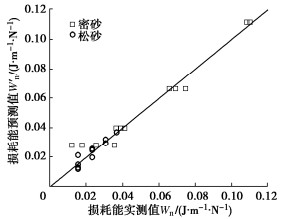
W′n=10a(Dr−0.78)10b(SSR−1.0)。 (8) 式中:a和b为经验参数,根据本次试验数据可分别取0.65,1.5。图 8对损耗能的试验实测值与通过式(8)所得的预测值进行对比,发现两者基本落在斜率为1的对角线两侧,表明能量模型可较好地预测不同试验条件下饱和钙质砂的损耗能。
3. 结论
(1)饱和钙质砂的极限残余孔压比随固结应力比呈先增大后减小的趋势,在Kc=1时存在最大值,临界状态理论可以解释此现象。
(2)不排水循环加载条件下饱和钙质砂的损耗能与试样的初始静剪应力比和相对密实度有关,受循环应力比影响极小,可通过构建的能量模型较好地预测不同试验条件下饱和钙质砂所累积的损耗能。
-
表 1 钙质砂物理性质指标
Table 1 Physical properties of calcareous sand
相对质量密度 d50/
mm不均匀系数 曲率系数 最大孔隙比 最小孔隙比 2.79 2.0 6.84 0.78 1.15 0.87 表 2 不排水循环剪切试验方案
Table 2 Summary of undrained cyclic triaxial tests
试验系列 相对密实度
Dr/
kPa/
kPaSSR CSR Nf Ⅰ 70%
(密砂)0 20 0 0.1 232 0 25 0 0.125 74 0 30 0 0.15 17 0 40 0 0.2 6 20 30 0.1 0.15 168 20 45 0.1 0.225 19 20 50 0.1 0.25 3 50 50 0.25 0.25 53 50 60 0.25 0.3 11 50 70 0.25 0.35 6 80 70 0.4 0.35 14 80 80 0.4 0.4 7 -10 25 -0.05 0.125 78 -10 30 -0.05 0.15 39 -10 35 -0.05 0.175 8 -20 20 -0.1 0.1 210 -20 25 -0.1 0.125 11 -20 30 -0.1 0.15 8 -40 20 -0.2 0.1 57 -40 25 -0.2 0.125 16 -40 30 -0.2 0.15 8 Ⅱ 30%
(松砂)0 15 0 0.075 943 0 20 0 0.1 120 0 25 0 0.125 37 0 30 0 0.15 18 24 30 0.12 0.15 61 24 35 0.12 0.175 16 24 40 0.12 0.2 5 40 15 0.2 0.075 175 40 20 0.2 0.1 9 50 12.5 0.25 0.0625 17 50 15 0.25 0.075 2 -10 12.5 -0.05 0.0625 382 -10 15 -0.05 0.075 180 -10 20 -0.05 0.1 11 -20 10 -0.1 0.05 246 -20 12.5 -0.1 0.0625 202 -20 15 -0.1 0.075 12 -40 5 -0.2 0.025 104 -40 7.5 -0.2 0.0375 13 -40 10 -0.2 0.05 2 -
[1] 蔡正银, 陈元义, 朱洵, 等. 级配对珊瑚砂颗粒破碎与变形特性的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(4): 661-670. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220884 CAI Zhengyin, CHEN Yuanyi, ZHU Xun, et al. Influences of gradation on particle breakage and deformation characteristics of coral sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(4): 661-670. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220884
[2] 汪稔, 吴文娟. 珊瑚礁岩土工程地质的探索与研究: 从事珊瑚礁研究30年[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 27(1): 202-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201901022.htm WANG Ren, WU Wenjuan. Exploration and research on engineering geological properties of coral reefs: engaged in coral reef research for 30 years[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 202-207. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201901022.htm
[3] LI B J, LEI G, GUO P P, et al. Experimental investigation into limit void ratio characteristics of calcareous sands considering various factors[J]. Geofluids, 2021: 3686852.
[4] 王伟光, 姚志华, 李婉, 等. 侧限高压下珊瑚砂-石英砂混合料的压缩特性及颗粒破碎行为[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(增刊1): 6-11. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2022S1002 WANG Weiguang, YAO Zhihua, LI Wan, et al. Compression characteristics and particle crushing behavior of coral sand-quartz sand mixture under confined high pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(S1): 6-11. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2022S1002
[5] 汪成贵, 束善治, 肖杨, 等. 考虑钙质砂颗粒破碎的分数阶边界面本构模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(6): 1162-1170. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220229 WANG Chenggui, SHU Shanzhi, XIAO Yang, et al. Fractional-order bounding surface model considering breakage of calcareous sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(6): 1162-1170. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20220229
[6] COOP M R. The mechanics of uncemented carbonate sands[J]. Géotechnique, 1994, 44(3): 607-6264.
[7] COOP M R, SORENSEN K K, BODAS FREITAS T, et al. Particle breakage during shearing of a carbonate sand[J]. Géotechnique, 2004, 54(3): 157-163. doi: 10.1680/geot.2004.54.3.157
[8] 刘崇权, 汪稔. 钙质砂物理力学性质初探[J]. 岩土力学, 1998, 19(1): 32-37, 44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX199801005.htm LIU Chongquan, WANG Ren. Preliminary study on physical and mechanical properties of calcareous sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 1998, 19(1): 32-37, 44. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX199801005.htm
[9] 蔡正银, 侯贺营, 张晋勋. 考虑颗粒破碎影响的珊瑚砂临界状态与本构模型研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(6): 989-995. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201906001 CAI Zhengyin, HOU Heying, ZHANG Jinxun, et al. Critical state and constitutive model for coral sand considering particle breakage[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(6): 989-995. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201906001
[10] NEMAT-NASSER S, SHOKOOH A. A unified approach to densification and liquefaction of cohesionless sand in cyclic shearing[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1979, 16(4): 659-678. doi: 10.1139/t79-076
[11] KOKUSHO T. Liquefaction potential evaluations: energy-based method versus stress-based method[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2013, 50(10): 1088-1099. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2012-0456
[12] PAN K, YANG Z X. Evaluation of the liquefaction potential of sand under random loading conditions: equivalent approach versus energy-based method[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 2020, 24(1): 59-83. doi: 10.1080/13632469.2017.1398693
[13] LIANG L Q, FIGUEROA J L, SAADA A S. Liquefaction under random loading: unit energy approach[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1995, 121(11): 776-781. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1995)121:11(776)
[14] JAFARIAN Y, TOWHATA I, BAZIAR M H, et al. Strain energy based evaluation of liquefaction and residual pore water pressure in sands using cyclic torsional shear experiments[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2012, 35(2): 13-28.




 下载:
下载: