Horizontal deformation of piles controlled by capsule expansion technique
-
摘要: 囊体扩张是一种新型地下结构变形主动控制技术,然而其在桩基变形控制机理方面尚未深入研究。采用有限元软件探究了囊体扩张控制桩基水平变形机理,分析了囊体扩张引起桩基和土体变形特性以及囊体-土体-桩体之间相互作用。结果表明:扩张直径0.5 m的囊体对直径为1.2 m的桩可产生最大5.5 mm水平变形,控制效率为60%,囊体扩张对桩基水平变形控制效果良好。囊体扩张会引起邻近土体产生较大的超孔隙水压力,而孔压消散会导致土体压缩而降低桩基控制效率。当扩张距离较小时,桩径对囊体扩张控制效果影响显著。囊体扩张对桩径为0.4~1.6 m的桩均有一定的变形控制效果,尤其适用于小直径桩基的变形控制。随扩张直径的增大,桩基最大水平位移近乎呈线性增大。此外,桩基水平变形随扩张距离增大而减小,但由于扩张对周围孔隙水压力影响范围有限,导致控制效率呈增大趋势。双排囊体扩张控制变形中“遮拦效应”和“反力效应”明显,控制桩基变形应遵循“先远后近,逐排扩张”的原则,以提高控制效果。Abstract: The capsule expansion technique (CET) is a new active deformation control technology, but its mechanism of deformation control of pile foundation has not been thoroughly studied. Numerical analysis is performed to explore the control effects of capsule expansion on horizontal deformation of piles. The deformation characteristics of piles and soils and the interaction among the capsules, soils and piles are further analyzed. The results show that the maximum horizontal deformation of 5.5 mm, is induced by the CET with expansion diameter of 0.5 m, and the control efficiency is 60%. The CET leads to a large excess pore water pressure of the adjacent soils. The dissipation of the excess pore water pressure causes the soils to be compressed under the additional stress. When the expansion distance is small, the pile diameter presents a significant impact on the capsule expansion. The expansion has certain deformation control on the piles with a diameter of 0.4~1.6 m, especially suitable for deformation control of small-diameter pile foundations. As the expansion diameter increases, the maximum horizontal displacement of the pile foundation increases almost linearly. In addition, the horizontal displacement of the pile decreases as the expansion distance increases. However, due to the limited influences of expansion on the surrounding pore water pressure, the control efficiency shows an increasing trend. The "blocking effect" and "reaction effect" are obvious in the deformation control of the double-row capsule expansion. The principle of "far first and then near, row by row expansion" should be followed to improve the control effects in controlling deformation of pile foundations.
-
Keywords:
- capsule expansion technique /
- pile /
- deformation control /
- mechanism analysis
-
0. 引言
随着城市化建设迅速发展,城市地下空间的开发与利用日趋迫切,大量的地下工程建设势必对邻近建筑物产生诸多不利影响[1]。地下工程施工(基坑开挖、盾构隧道等)会对周围地层产生不利扰动,以地层中土体变形和应力扰动的形式传递至邻近桩基础,使其产生不可逆沉降和变形,降低桩基承载力,甚至危害上部结构安全[2-5]。因此,桩基础在附加扰动下的变形控制与治理对上部结构的安全与正常服役非常必要。
目前,针对桩基础变形控制与治理的主要方法包括:①控制扰动来源,即从基坑开挖、盾构隧道等源头上降低其对周围环境的影响[6-7];②切断扰动传递媒介,即通过加固土体、设置隔离桩等方法控制和减小扰动传递媒介-土体的变形[8-9];③保护扰动对象,即直接对桩基础开展有效保护措施[10-12]。刘喆等[13]研究了不同盾构参数下隧道侧穿对既有高架桥桩的受力和变形,结果表明优化盾构参数可有效减小邻近桥桩的水平位移、竖向沉降、弯矩和轴力。此外,隔离桩控制变形效果优于优化盾构参数。郑刚等[14]发现软土中隔离桩对侧方地下结构物竖向位移无显著控制效果,并提出采用埋入式隔离桩来控制隔离桩在位移影响区范围内的桩长,以最大限度发挥隔离桩的阻隔土体变形传递作用,从而有效控制邻近被保护对象。寇晓强等[15]探究了在桩基关键部位采用旋喷加固对桩基变形的控制效果,旋喷加固可有效减小盾构穿越过程中桩基的侧向变形,最大减小变形达42%。但是,现有桩基变形控制措施主要是减小扰动源对邻近桩基的影响,而无法逆转桩基不利影响。
囊体扩张是一种地下工程新型主动控制技术,将浆液注入预先植入土体预定深度范围内的可膨胀囊体,使囊体产生预定深度、预定体积、预定形状的膨胀,实现对目标区域土体的应力和变形的靶向、精细控制,从而实现对目标保护对象的变形精准控制,具有“控得住、控得准、可逆转、高效率”的特点[16]。郑刚等[17]通过现场试验对比分析了囊体扩张技术和袖阀管注浆技术对淤泥质土的变形控制效果,验证了囊体扩张对变形控制的靶向性和高效性。此外,还研究了囊体扩张在不同土层中对土体水平变形影响,结果表明囊体扩张对不同性质土层均有靶向高效的控制效果,但是在不同土质中的控制效果存在一定差异。目前,囊体扩张技术已成功应用于隧道变形控制,该技术不仅能在基坑施工全过程中有效主动地控制隧道变形,而且可以优化施工方案,节约建设成本。而采用被动控制措施不仅会增大施工难度、延长工期、提高成本,而且可能无法高效地控制邻近隧道变形[18]。此外,郑刚[16]、Huang等[19]通过现场试验成功验证了囊体扩张技术在桩基变形控制中的可行性,并且研发了一种适用于囊体扩张的缓凝型注浆材料,以满足多次扩张控制的要求,实现精细化控制[20]。目前,囊体扩张技术在桩基变形控制方面尚未深入探索,控制机理与影响因素值得研究。
本文结合囊体扩张控制桩基水平变形现场试验,采用有限元数值分析方法探究了囊体扩张控制桩基水平变形机理,分析了囊体扩张引起周围土体位移、应力和孔隙水压力的变化趋势,并研究了桩基直径、扩张直径、扩张距离和土体性质对桩基水平变形控制效果的影响规律,进一步揭示了囊体扩张控制桩基变形机理。
1. 现场试验概况
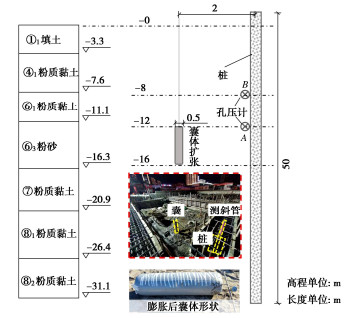
在天津某地铁基坑开展现场试验,场地地质分布以粉质黏土为主,间隔分布有粉砂层,土层详细参数如表 1所示。采用钻孔灌注桩作为试验桩,桩径为1.2 m,桩长为50 m,桩身中预置测斜管,以监测桩基水平位移。在距桩2 m处打孔安装埋设试验扩张囊袋,囊体长度为4 m,未膨胀囊体为直径12 cm的圆柱体,完全膨胀后为直径50 cm的圆柱体(如图 1所示),可注入浆液体积为0.78 m3。囊体扩张深度为-12~-16 m,处于粉质粘土层。此外,在桩侧-8 m和-12 m处布置孔压计以监测囊体扩张引起土体孔隙水压力变化。现场试验布置如图 1所示。
表 1 土层物理和力学参数Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of soils土层r 层厚/m γ/(kN·m-3) E/MPa μ e0 $ \varphi ' $/(°) $ c' $/kPa k/(m·d-1) ①1填土 3.3 19.4 4.0 0.40 0.93 16.1 12.4 5.0×10-1 ④1粉质黏土 4.3 19.4 5.5 0.37 0.79 19.7 14.0 1.0×10-1 ⑥1粉质黏土 3.5 19.9 5.6 0.36 0.74 18.9 13.4 2.0×10-1 ⑥3粉砂 5.2 19.8 12.5 0.28 0.70 27.6 6.5 8.0×10-1 ⑦粉质黏土 4.6 20.8 5.9 0.35 0.59 17.5 13.0 5.0×10-3 ⑧1粉质黏土 5.5 20.2 6.4 0.34 0.53 19.3 12.0 2.0×10-3 ⑧2粉质黏土 4.7 19.8 12.7 0.28 0.70 27.7 11.0 5.0×10-3 ⑨1粉质黏土 5.5 20.6 7.7 0.34 0.60 18.4 12.5 3.0×10-3 ⑩1粉质黏土 3.6 20.4 4.6 0.37 0.66 16.5 15.0 5.0×10-4 ⑩2粉砂 6.5 21.1 11.9 0.30 0.55 32.1 6.0 1.3 ⑪1粉质黏土 4.3 19.6 5.9 0.35 0.66 24.2 15.0 5.0×10-4 ⑪2粉砂 5.0 20.3 16.5 0.26 0.62 32.6 5.0 1.2 ⑪4粉砂 4.7 20.0 12.9 0.27 0.59 32.8 6.5 1.3 ⑫1粉质黏土 4.2 19.9 7.3 0.34 0.70 22.3 20.5 4.0×10-4 ⑬1粉质黏土 12.1 19.6 6.6 0.35 0.75 22.0 26.0 3.0×10-4 通过往囊体中注入水泥基浆液的方式使其膨胀扩张,囊袋完全封闭浆液。浆液配比为水∶水泥∶膨润土∶粉煤灰=1∶1∶0.2∶0.3,该浆液具有流动性好、泌水率低、初凝时间长等特点,可适用于囊体扩张技术应用。此外,所采用的水泥基注浆材料的收缩性较低,14 d后收缩率仅为1.2%,随后收缩率几乎无变化。在囊体扩张过程中,注浆速度为30 L/min,注浆压力为0.6~0.8 MPa。达到预定注浆量后,测量桩身水平变形,并在注浆结束2 d后再次测量超孔压消散稳定后桩身水平位移。囊体扩张对桩基水平变形控制效率($ \eta $)定义为孔压消散固结后最大水平位移(dc)与囊体扩张后瞬时最大水平位移(de)之比:
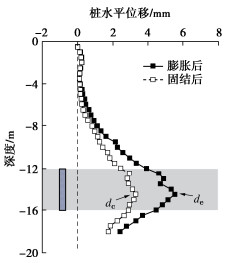
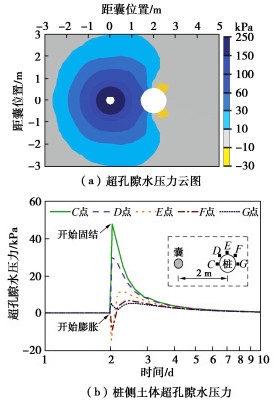
$$ \eta = \frac{{{d_{\text{c}}}}}{{{d_{\text{e}}}}} \times 100\% 。 $$ (1) 试验结果表明,囊体扩张导致距离2 m处A点(-12 m,粉砂层)孔隙水压力增大了40.5 kPa,B点(-8 m,粉质黏土层)孔隙水压力增大了21.3 kPa。A点和B点超孔隙水压力在囊体扩张8 h后基本消散完毕。囊体扩张引起桩基变形如图 2所示。扩张后桩基瞬时最大水平位移为5.5 mm,固结稳定后最大水平位移为3.3 mm,故囊体扩张对桩基水平变形控制效率为60%。桩基变形与囊体扩张深度对应,这证实囊体扩张对桩基变形控制具有良好的靶向性。
2. 数值模型建立与验证
2.1 数值模型建立
(1)模型网格及边界
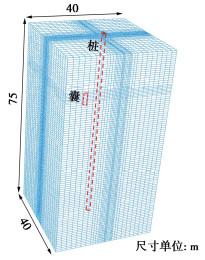
基于现场试验情况和工程地质条件,采用ABAQUS软件进行水土耦合有限元分析计算。数值模型尺寸为长、宽、高分别为40,40,75 m,以消除边界效应影响。模型侧边界约束法向自由度,模型底面边界采用固定边界约束。囊体中心位于模型中心线,囊体与桩的中心距离为2m。数值模型网格划分如图 3所示,囊体与桩体之间网格加密处理。模型包括136576个8节点六面体流体渗流单元(C3D8P)用于模拟土体和2064个8节点六面体实体单元(C3D8)用于模拟囊体和桩体。
(2)土体和结构参数
模型中土体按现场试验土层分布设置,土体本构采用莫尔-库仑本构模型,详细参数如表 1所示。试验桩采用线弹性模型模拟,弹性模量为30 GPa,泊松比为0.2。囊体采用线弹性模型模拟,弹性模量为1 GPa,泊松比为0.2。囊体扩张的膨胀模拟需满足:①按设计囊体形状膨胀,本文中为圆柱形;②囊体膨胀过程中无位移约束,即囊体在膨胀过程中允许在土层中整体位移。而传统注浆膨胀模拟主要通过对拟膨胀体施加应力膨胀或者施加位移膨胀,这两种方法无法较好的模拟囊体扩张过程。因此,本文基于热胀冷缩原理采用温度膨胀的方式模拟囊体扩张过程,对膨胀体预设膨胀系数和温度场,通过改变温度场使其膨胀达到预定体积,从而模拟现场试验中囊体扩张效果[19]。根据现场试验,模型中膨胀体设置为圆柱形,且圆柱边界不透水。膨胀体法向膨胀系数设置为0.01℃-1,切向膨胀系数为0℃-1,即囊体只在法向膨胀扩张,而无切向和高度方向变形,且预设温度场不影响囊体周围土体的性质。囊体扩张时间与现场试验注浆时间一致,在30 min内完成囊体膨胀模拟。在固结阶段前14 d通过减小温度场温度来实现囊体的收缩(1.2%)。桩基与土体和囊体与土体之间接触关系均采用面-面接触模拟,在法向上为硬接触,切向上为摩擦接触,桩-土接触面摩擦系数为0.3,囊-土接触面摩擦系数为0.1,接触面采用有限滑动。
(3)模型计算步骤
模型计算共需以下4个步骤:①激活初始边界和应力条件;②激活桩基并加桩顶约束;③激活囊体并修改温度场完成膨胀;④固结稳定。
2.2 模型计算结果验证
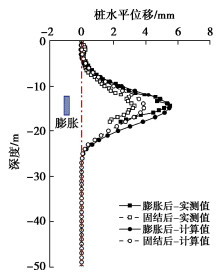
为验证数值模型结果的可靠性,将囊体扩张引起桩基变形的数值结果与现场试验结果进行对比,如图 4所示。数值计算的桩基变形曲线与实测变形曲线线形相似。实测结果表明在囊体中心(-14 m)左右位置,桩身最大水平变形为5.5 mm,固结后变形值为3.3 mm。且桩基变形深度范围与囊体扩张范围(-12~-16 m)对应良好,囊体扩张对桩基变形控制具有良好的靶向性。数值结果表明桩基在扩张后最大水平位移约为5.5 mm,孔隙水压力消散后最大水平位移为3.8 mm,控制效率为69.1%。固结后桩基水平位移计算值略大于实测结果,这可能是由于数值模型中将土体简化为均质连续介质,孔隙分布均匀,孔隙水压力消散过程完全理想,而现场试验中土壤的非均质性和结构性影响了超孔隙水压力的消散,从而造成固结后桩基水平变形计算值与实测值的差异。总体而言,计算结果与现场试验结果基本一致,表明本研究采用的本构模型和模型参数是合理的,可在本模型基础上开展进一步研究分析。
3. 数值结果与分析
3.1 囊体扩张引起变形特性分析
(1)土体位移分析
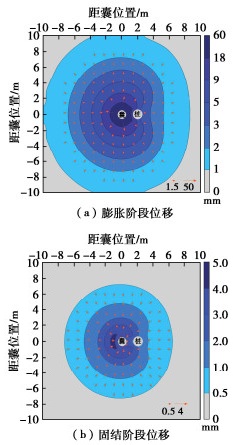
图 5为囊体扩张引起周围土体的水平位移。如图 5(a)所示,囊体扩张导致周围土体的形成了以囊体为中心的圆形土体位移等高线,土体位移随与囊体距离增大而迅速减小。由于桩基的遮拦效应,位移等高线在桩基附近明显凹陷,桩后土体位移明显小于其他距囊相同距离处土体。但是桩基的遮拦效应影响范围有限,随与桩距离增大,桩后土体受两侧土体位移影响,土体位移等高线又逐渐趋于平滑。
如图 5(b)所示,超孔隙水压力消散后,囊体周围土体出现了反向位移,土体以囊体为中心反向位移。这是由于在固结过程中,土体中的高压孔隙水被排出,囊体扩张引起的超孔隙水压力逐渐消散,且超孔隙水压力所承受的应力部分转化为土体有效应力,导致土体压缩和反向位移[16, 21]。土体反向位移作用于桩,导致桩基出现反向变形,从而降低了囊体扩张控制效率。此外,相较于超孔隙水压力消散的影响,浆液体积收缩对土体变形影响非常微弱,可忽略不计。囊体-土体-桩体之间的相互作用和应力转换是囊体扩张控制桩基变形的关键,有必要进一步探究。
(2)孔隙水压力分析
图 6为囊体扩张引起土体中孔隙水压力变化。以囊体为中心形成近似圆形的超孔隙水压力分布范围,囊体外侧最大超孔隙水压力约为225 kPa。随着与囊体之间距离的增大,超孔隙水压力迅速降低。囊体扩张会挤压周围的土体,土体颗粒空隙逐渐被压缩减小,土体中孔隙水无法及时排出而导致孔隙水压力急剧增加。3 m外孔隙水压力无明显变化,故扩张直径为0.5 m的囊体扩张对周围土体孔隙水压力的影响半径约为3 m。此外,由于桩的遮拦效应,桩前侧(靠近囊侧)与桩后侧(背离囊侧)孔隙水压力差异较大。囊体扩张直接挤压桩前土体,引起桩前孔隙水压力增大了47 kPa,即囊体扩张的挤压效应。但是桩后土体孔隙水压力仅增大5 kPa,甚至在桩后侧方出现了孔隙水压力减小现象,形成了负的超孔隙水压力。这是由于桩后两侧土被两侧邻近较大位移土体牵引而产生位移变形,即土体的牵引效应。然而此位置挤压效应弱而牵引效应强,因此孔隙水压力降低[19]。挤压效应指土体受压于周围土体而压缩位移变形,牵引效应指土体受拉于周围土体而拉伸位移变形。同理,在桩后土体的牵引效应和挤压效应强度相近,因此桩后孔隙水压力保持稳定。桩周围土体孔隙水压力取决于挤压效应和牵引效应相对强弱关系。在固结过程中,超孔隙水压力的消散会导致土体在附加应力下被压缩出现反向位移,这是导致囊体扩张控制效率降低的重要原因。
(3)桩侧土体法向应力分析
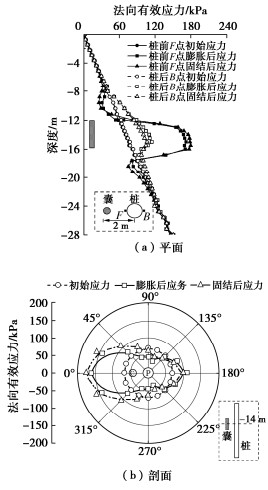
图 7为桩侧土体法向有效应力。囊体扩张后,在囊体对应的深度范围内(-12~-16 m),桩前(F点)的法向有效应力急剧增加至175.7 kPa,桩后(B点)有效应力增大至110.1 kPa。桩前土体受囊体扩张直接挤压导致有效应力增大幅度较大,而桩后土体是在囊体扩张推动桩基变形后,桩基再挤压作用于桩后土体,故有效应力增大幅度较小。此外,在囊体上方(-8~-11 m)和下方(-17~-20 m)桩前有效应力减小。膨胀不会直接挤压膨胀区上侧和下侧的土体,而上下侧的土体在桩变形后应力释放,导致有效应力降低。在桩后,由于桩变形对桩后侧土体的挤压(-8~-18 m),桩后土体的有效应力增加,这与桩前的有效应力相反。固结后,由于承受较大应力的超孔隙水压力消散,部分孔隙水压力转移到土体颗粒上,导致桩前土体的有效应力增加。但是由于桩后土体基本处于较小的负超孔隙水压力状态,固结后孔隙水压力承受更大的压力,土体有效应力降低。这与桩前孔隙水压力和有效应力之间的转换机制相反。
由图 7可知,囊体扩张引起土体有效应力增大,在桩前的影响范围约为90°,即315°~45°(顺时针方向),在桩后土的影响范围约为60°,即150°~210°。此外,在桩后两侧(90°~135°和225°~270°)土体发生应力释放,膨胀和固结后的土体有效应力均低于初始有效应力。桩前土体直接受囊体扩张挤压周围土体影响,故其法向挤压效应最强;桩后土体受桩基变形挤压作用,故其法向挤压效应次之;桩后两侧土体虽受桩基变形挤压但却不是法向方向作用,故其法向挤压效应最弱。此外,由于桩后两侧土体牵引效应较强。因此,桩后两侧土体法向有效应力减小。应力释放区与图 6中负的超孔隙水压力的位置一致,验证了桩基周围土体由牵引效应与挤压效应的共同作用。
3.2 囊体扩张变形控制参数分析
为进一步探究囊体扩张控制桩基水平位移的影响机制,在已验证数值模型(桩径1.2 m、扩张直径0.5 m、扩张距离2 m和⑥3粉砂层)基础上改变桩基直径(dp)、扩张直径(dc)、扩张距离(Dc-p)和土层性质开展数值分析。
(1)桩基直径影响
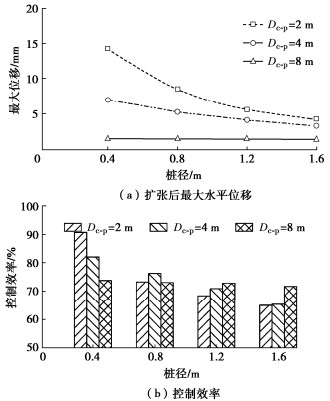
探究桩基直径对囊体扩张控制变形效果的影响,其中扩张直径保持不变为0.5 m,桩径为0.4~1.6 m。由图 8(a)可知,当扩张距离为2 m时,桩基的最大水平位移随桩径增大迅速减小了69.8%。而当扩张距离为8 m时,桩基最大水平位移随桩径增大而仅降低6.9%。因此,当扩张距离较小时,桩径对囊体扩张影响比较显著,桩径越大,囊体扩张可控制的最大水平位移越小。囊体扩张对桩径为0.4~1.6 m的桩均有一定的变形控制效果,尤其适用于小直径桩基的变形控制。此外,随桩径增大,囊体扩张的控制效率呈降低趋势。当扩张距离为2 m时,对0.4 m直径桩基的控制效率高达90.6%,而对1.6 m直径桩基的控制效率仅为65%。桩径大则桩遮拦效应会更显著,对孔隙水压力的影响可能也会较大,故导致控制效率的降低。当桩径为0.4 m时,控制效率随扩张距离的增大而显著降低。当桩径大于0.4 m时,控制效率变化幅度较小,并且当桩径大于0.8 m时,呈现随扩张距离增大而增大趋势。
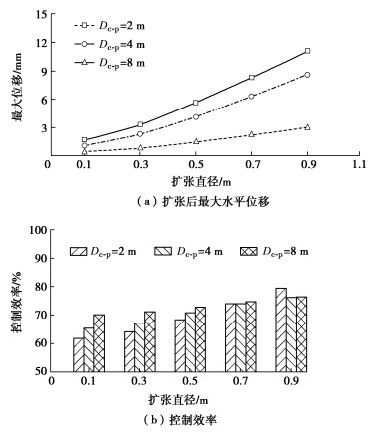
(2)囊体扩张直径影响
探究扩张直径对囊体扩张控制变形效果的影响,其中桩径保持不变为1.2 m,扩张直径为0.1~0.9 m。由图 9(a)可知,随扩张直径的增大,桩基的最大水平位移近乎呈线性增大。增大扩张直径可显著提高囊体扩张对桩基的水平变形控制效果。当扩张直径为0.9 m,扩张距离为2 m时,囊体扩张对直径为1.2 m桩的水平变形控制值高达11.1 mm。对于一些大直径桩基的水平变形控制,可通过增大扩张直径来达到预期控制效果。由图 9(b)可知,随着扩张直径增大,囊体扩张控制效率呈增大趋势,但扩张直径对控制效率影响幅度较小。当扩张直径为0.1 m时,控制效率随扩张距离增大而增大。这是可能由于囊体扩张对周围孔隙水压力影响直径有限,扩张距离越大,孔隙水压力受囊体扩张影响越小,故控制效率越高。例如扩张直径为0.5 m时,其影响直径约为3 m,而8 m处孔隙水压力固结前后变化小,因此控制效率较高。但是随扩张直径增大,不同扩张距离的控制效率的差异逐渐减小,甚至出现了相反的趋势。扩张直径增大,扩张对周围土体孔隙水压力影响范围较大,距离较远桩基仍处于影响较大区域,故控制效率差异减小。
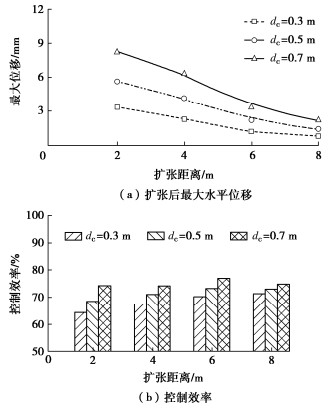
(3)囊体扩张距离影响
探究扩张距离对囊体扩张控制变形效果的影响,其中桩径保持不变为1.2 m,扩张距离为2~8 m。由图 10(a)可知,当扩张直径为0.5 m时,扩张距离从2 m增加到8 m,桩基最大水平位移减小了74.7%。桩基最大水平位移随扩张距离的增大而显著减小。扩张距离越大,由膨胀引起的桩前土体位移越小,故对桩的挤压推动效果越弱。扩张距离从2 m增大6 m,桩基最大水平位移减小速率较快,当扩张距离大于6 m时,减小速率降低。在囊体扩张控制桩基水平位移的实际应用中,应在满足结构安全前提下尽量将囊体扩张靠近待纠偏桩基结构。由图 10(b)可知,当扩张距离从2 m增大到8 m,控制效率大体上呈增大趋势,这是由于扩张距离越大,囊体扩张对孔隙水压力影响越小,故控制效率越高。增大扩张距离虽然会提高控制效率,但是对桩基水平变形的控制幅值较小,在实际应用中应该侧重于以控制水平变形为主。此外,由以上参数分析结果可知,囊体扩张对桩基的控制效率并非仅受单个因素独立影响,而是受多个影响因素耦合作用,表现出复杂的变化趋势,在实际应用中应综合考虑地质情况和囊体扩张参数以达到理想控制效果。
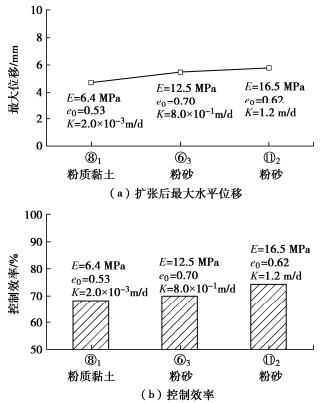
(4)土体性质影响
探究土层性质对囊体扩张控制变形效果的影响,将模型中-11.1~-16.3 m范围土体分别由⑥3粉砂土替换为⑧1粉质黏土和⑪2粉砂土,其余参数与现场试验一致。由图 11(a)可知,囊体扩张在3种性质土体中均有一定的变形控制效果,桩基最大水平变形都大于4.5 mm。当在⑧1粉质黏土和⑪2粉砂土中囊体扩张时,扩张后桩基最大水平位移分别为4.7,5.8 mm,相较于在⑥3粉砂土中扩张分别减小了14.5%和增大了5.5%。在高模量土体中囊体扩张效果较好,这是由于模量较高的土体整体性好,可更高效地将变形传递到被保护桩基,而低模量土体虽然在扩张作用下更易发生变形,但是土体易压缩并且土体变形可能在桩侧产生绕流现象,作用于桩侧的应力集中较小,导致控制效果较差。此外,从图 11(b)中可得囊体扩张在⑧1粉质黏土中控制效率略低于在粉砂土中,这是由于在粉砂土中土体渗透系数较大,囊体扩张产生的超孔隙水压力较小,并且粉砂土模量大不易压缩。因此,囊体扩张在不同性质土体中对桩基变形均有良好的控制效果,尤其适用于高模量、高渗透系数和低孔隙土体中变形控制。
(5)囊体扩张控制桩基变形策略
囊体扩张通过往囊袋中注入水泥基浆液实现囊袋膨胀扩张,浆液无法渗透通过囊袋而进入土体中,保证了膨胀体的体积稳定性,从而表现出较好的控制效果。此外,由于所采用的水泥基浆液收缩率较低(仅约1.2%),在固结阶段的收缩对土体和桩变形的影响可忽略不计。因此,注浆材料仅影响注浆施工过程,需满足较好的工作性能要求即可,即良好的流动性和较低的离析率。现场试验结果表明本文所提出的注浆材料配合比(水∶水泥∶膨润土∶粉煤灰=1∶1∶0.2∶0.3)具有良好的工作性能,可适用于常规囊体扩张控制桩基变形应用场景。
囊体扩张适用于粉质黏土和粉砂土中对桩基变形控制,具有良好的控制效果,尤其适用于模量较高的粉砂土层中的变形控制。这是由于土体模量高整体性强,可在桩侧形成更大的应力集中来引起桩基变形。此外,囊体扩张对强度低、含水率高、压缩性大、结构性强的淤泥质土也具有良好的控制效果[17],但是对于淤泥质土层中的桩基变形控制有待进一步试验研究。囊体扩张对不同直径桩基均有一定的控制效果,对小直径桩基(直径小于0.8 m)控制效果较好。对于大直径桩基可通过增大扩张直径或减小扩张距离来增强桩基水平变形控制效果,例如采用扩张直径为0.9 m,扩张距离为2 m的囊体扩张可对直径1.6 m桩产生最大9 mm的水平变形控制量。此外,考虑到实际工程中囊体扩张控制桩基变形可能邻近其他结构物,为了降低囊体扩张对非控制目标结构物的影响以及提高对目标保护桩基的控制效果,应尽量采用“短距离,小方量”控制策略,扩张距离不宜大于3 m,扩张直径不宜大于0.9 m。对于控制过大变形桩基可利用多排囊体扩张以提升桩基变形控制效果。
3.3 双排囊体扩张控制分析
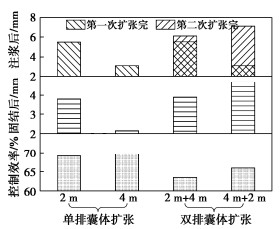
由于单排囊体扩张控制桩基变形效果有限,无论是调整扩张距离或是扩张直径都无法对一些过大变形桩基完全纠偏修复,故有必要布置多排囊体扩张以提高水平变形控制效果。基于已验证的数值模型,开展了双排囊体扩张控制桩基水平变形研究,为将来实际工程应用提供参考。双排囊体扩张位于桩基同侧,分别距离桩基2 m和4 m,囊体之间间距为2 m,囊体扩张直径均为0.5 m。两种囊体扩张方式分别为:①先2 m处扩张再4 m处扩张(2 m+4 m,先近后远);②先4 m处扩张再2 m处扩张(4 m+2 m,先远后近)。为了提高双排囊体扩张效果,实际工程通常采用具有速凝特性的双液浆(水泥浆+水玻璃)。因此,数值模型中第一排扩张完成后立即激活第二排扩张,且在开始第二排扩张时第一排扩张体已经形成强度(E=1 GPa),从而提高整体扩张效果。
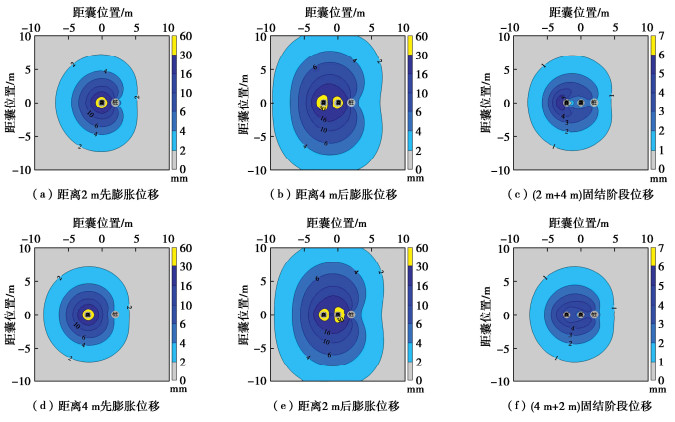
图 12为双排囊体扩张引起桩基变形和控制效率,其中2 m处和4 m处的单排囊体扩张作为对照组。当先2 m扩张再4 m处扩张时,扩张后桩基瞬时最大位移为6.1 mm,相较于2 m处单排扩张增大了11.5%,而在孔压消散稳定后,桩基最大位移为3.9 mm,仅增大了2.6%。由于2 m处囊体扩张后在地层中形成直径为0.5 m的圆柱体,类似于在4 m扩张体和桩基之前布置一道隔离桩,其会影响后排4 m囊体扩张时周围土体位移场,产生“遮拦效应”,削弱4 m处囊体扩张对桩基的控制效果。从图 13(b)中可以看出,当2 m处先扩张时,4 m处再扩张,土体位移已无法高效地向桩基方向传递,其在桩基侧的变形曲线面积明显小于先远后近扩张方式(图 13(e))。尤其是图 13(b)中黄色土体变形区明显呈现一种远离桩基趋势,2 m处扩张体不仅有“遮拦效应”,而且也会存在一种不利的“反力效应”,前排扩张体对后排囊体扩张形成一种“反力墙”,后排囊体被迫产生远离式扩张,不利于桩基变形控制。故先近后远式双排囊体扩张对桩基水平变形控制几乎无加强效果。
当先4 m处扩张再2 m处扩张时,扩张后桩基的最大水平位移为7.1 mm,比2 m处单排扩张增大了29.1%,固结稳定后桩基水平位移为4.7 mm,比2 m处单排扩张增大了23.7%。当远离桩基4 m处囊体先膨胀扩张,其对于前排2 m处扩张产生正面“反力墙”在有利“反力效应”作用下,2 m处膨胀扩张导致土体更多趋于朝向桩基位移。从图 13(e)可明显看出土体位移较大的黄色区域更多偏向于桩基方向,增强了桩基水平变形控制效果。同时,远处4 m处先扩张体对随后近处2 m处囊体扩张具有遮拦效应,这可减小囊体扩张对非控制侧结构物的影响。
此外,双排囊体扩张控制效率(约65%)低于单排囊体扩张控制效率(约69%),其原因可能是由于双排扩张对土体挤压更强而产生了更大的超孔隙水压力,而较大的超孔隙水压力消散会导致控制效率的降低。并且先远后近式双排扩张控制效率(65.9%)高于先近后远式双排扩张(63.5%),图 13(c)和(f)显示了同样的结果,即先远后近式双排扩张中土体在固结阶段的反向位移小于先近后远式双排扩张。
因此,先远后近式双排囊体扩张对桩基变形控制效果远大于先近后远双排囊体扩张方式。这一结果与常规袖阀管注浆对土体变形和隧道变形试验结果一致[22-23]。工程实践中,利用多排囊体扩张控制邻近桩基变形时,应遵循“先远后近”逐排扩张的原则,以提高对桩基变形的控制效果,同时可降低对非变形控侧土体及结构物的影响。
4. 结论
本文采用数值分析方法研究了囊体扩张对桩基水平变形控制机理,探究了囊体扩张引起桩基和土体变形特性,并开展了桩基变形控制参数分析。得到以下4点结论。
(1)囊体扩张对桩基水平变形控制效果显著,扩张直径0.5 m的囊体对直径1.2 m桩基的最大水平变形控制量为5.5 mm,固结后最大变形为3.3 mm,控制效率为60%。此外,囊体扩张引起距离2 m处土体的超孔隙水压力增大了40.5 kPa,孔压消散后桩基变形控制量减小。
(2)囊体扩张会显著影响周围土体位移,桩基对土体位移有一定的遮拦作用。囊体扩张(扩张直径0.5 m)将导致邻近土体较大的超孔隙水压力,其影响范围约为3 m。桩前后超孔隙水压力差异较大,桩后两侧出现了负超孔隙水压力。在囊体对应的深度范围内,桩前(F点)的法向有效应力显著增大。固结后,由于承受较大应力的超孔隙水压力消散,部分孔隙水压力转移到土体颗粒上,导致桩前土体的有效应力增加。囊体扩张引起的超孔隙水压力的消散会导致土体在附加应力下被压缩出现反向位移,这是桩基的控制效率降低的主要原因。
(3)当扩张距离较小时,桩径对囊体扩张影响显著。随桩径增大,囊体扩张的控制效率呈降低趋势。囊体扩张对桩径为0.4~1.6 m的桩均有一定的变形控制效果,尤其适用于小直径的桩基变形控制。随扩张直径的增大,桩基最大水平位移近乎呈线性增大。此外,桩基最大水平位移随扩张距离的增大而减小。当扩张距离从2 m增大到8 m,控制效率大体上呈增大趋势,这是由于扩张距离越大,囊体扩张对孔隙水压力影响越小,控制效率越高。囊体扩张在不同性质土体中对桩基变形均有较好的控制效果,尤其适用于高模量、高渗透系数和低孔隙土体。此外,为了降低囊体扩张对非控制目标结构物的影响以及提高对目标保护桩基的控制效果,应尽量采用“短距离,小方量”控制策略,扩张距离不宜大于3 m,扩张直径不宜大于0.9 m。
(4)双排囊体扩张中,先近后远(2 m+4 m)囊体扩张对桩基水平变形控制几乎没有提升效果,前排扩张体“遮拦效应”显著。先远后近(4 m+2 m)囊体扩张方式可显著提高桩基变形控制效果,后排扩张体对前排囊体扩张的“反力效应”明显加强了囊体扩张控制效果。工程实践中,利用多排囊体扩张控制既有桩基变形时,应遵循“先远后近、逐排扩张”的原则,以提高对桩基的变形控制效果,同时可降低对远离纠偏对象一侧土体及结构物的影响。
-
表 1 土层物理和力学参数
Table 1 Physical and mechanical parameters of soils
土层r 层厚/m γ/(kN·m-3) E/MPa μ e0 φ′/(°) c′/kPa k/(m·d-1) ①1填土 3.3 19.4 4.0 0.40 0.93 16.1 12.4 5.0×10-1 ④1粉质黏土 4.3 19.4 5.5 0.37 0.79 19.7 14.0 1.0×10-1 ⑥1粉质黏土 3.5 19.9 5.6 0.36 0.74 18.9 13.4 2.0×10-1 ⑥3粉砂 5.2 19.8 12.5 0.28 0.70 27.6 6.5 8.0×10-1 ⑦粉质黏土 4.6 20.8 5.9 0.35 0.59 17.5 13.0 5.0×10-3 ⑧1粉质黏土 5.5 20.2 6.4 0.34 0.53 19.3 12.0 2.0×10-3 ⑧2粉质黏土 4.7 19.8 12.7 0.28 0.70 27.7 11.0 5.0×10-3 ⑨1粉质黏土 5.5 20.6 7.7 0.34 0.60 18.4 12.5 3.0×10-3 ⑩1粉质黏土 3.6 20.4 4.6 0.37 0.66 16.5 15.0 5.0×10-4 ⑩2粉砂 6.5 21.1 11.9 0.30 0.55 32.1 6.0 1.3 ⑪1粉质黏土 4.3 19.6 5.9 0.35 0.66 24.2 15.0 5.0×10-4 ⑪2粉砂 5.0 20.3 16.5 0.26 0.62 32.6 5.0 1.2 ⑪4粉砂 4.7 20.0 12.9 0.27 0.59 32.8 6.5 1.3 ⑫1粉质黏土 4.2 19.9 7.3 0.34 0.70 22.3 20.5 4.0×10-4 ⑬1粉质黏土 12.1 19.6 6.6 0.35 0.75 22.0 26.0 3.0×10-4 -
[1] 郑刚, 朱合华, 刘新荣, 等. 基坑工程与地下工程安全及环境影响控制[J]. 土木工程学报, 2016, 49(6): 1-24. ZHENG Gang, ZHU Hehua, LIU Xinrong, et al. Control of safety of deep excavations and underground engineering and its impact on surrounding environment[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2016, 49(6): 1-24. (in Chinese)
[2] SHAKEEL M, NG C W W. Settlement and load transfer mechanism of a pile group adjacent to a deep excavation in soft clay[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 96: 55-72. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.10.010
[3] CHEN L T, POULOS H G, LOGANATHAN N. Pile responses caused by tunneling[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1999, 125(3): 207-215. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1999)125:3(207)
[4] 李进军, 王卫东, 邸国恩, 等. 基坑工程对邻近建筑物附加变形影响的分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(增刊1): 623-629. LI Jinjun, WANG Weidong, DI Guoen, et al. Analysis of the influence of excavation engineering on additional deformation of adjacent buildings[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(S1): 623-629. (in Chinese)
[5] 魏丽敏, 辛学忠, 何群, 等. 邻近开挖对桥梁桩基变形与内力影响分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2017, 34(5): 38-44. WEI Limin, XIN Xuezhong, HE Qun, et al. Effect of adjacent excavation on deformation and internal force of bridge pile foundation[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2017, 34(5): 38-44. (in Chinese)
[6] BRYSON L S, ZAPATA-MEDINA D G. Method for estimating system stiffness for excavation support walls[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2012, 138(9): 1104-1115. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000683
[7] FINNO R J, BRYSON S, CALVELLO M. Performance of a stiff support system in soft clay[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(8): 660-671. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2002)128:8(660)
[8] WEI G, QI Y J, CHEN C L, et al. Analysis of the protective effect of setting isolation piles outside the foundation pit on the underpass tunnel side[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2022, 35: 100791. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2022.100791
[9] WU T H, GAO Y T, ZHOU Y. Application of a novel grouting material for prereinforcement of shield tunnelling adjacent to existing piles in a soft soil area[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 128: 104646. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2022.104646
[10] XU Q W, ZHU H H, MA X F, et al. A case history of shield tunnel crossing through group pile foundation of a road bridge with pile underpinning technologies in Shanghai[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2015, 45: 20-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2014.09.002
[11] IWASAKI Y, WATANABE H, FUKUDA M, et al. Construction control for underpinning piles and their behaviour[J]. Géotechnique, 1994, 44(4): 681-689. doi: 10.1680/geot.1994.44.4.681
[12] 徐前卫, 朱合华, 马险峰, 等. 地铁盾构隧道穿越桥梁下方群桩基础的托换与除桩技术研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(7): 1217-1226. http://cge.nhri.cn/article/id/14629 XU Qianwei, ZHU Hehua, MA Xianfeng, et al. Pile underpinning and removing technology of shield tunnels crossing through group pile foundations of road bridges[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(7): 1217-1226. (in Chinese) http://cge.nhri.cn/article/id/14629
[13] 刘喆, 何平, 张安琪, 等. 盾构隧道施工过程及支护方式对高速铁路高架桥群桩基础影响分析[J]. 工程力学, 2016, 33(S1): 219-226. LIU Zhe, HE Ping, ZHANG Anqi, et al. Analysis of effects of shield tunnel construction process and supporting ways on pile groups of high-speed railway viaduct[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(S1): 219-226. (in Chinese)
[14] 郑刚, 杜一鸣, 刁钰. 隔离桩对基坑外既有隧道变形控制的优化分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(增刊1): 3499-3509. ZHENG Gang, DU Yiming, DIAO Yu. Optimization analysis of efficiency of isolation piles in controlling the deformation of existing tunnels adjacent to deep excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(S1): 3499-3509. (in Chinese)
[15] 寇晓强, 杨京方, 叶国良, 等. 盾构近距离穿越群桩旋喷加固效果分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2011, 28(11): 98-103. KOU Xiaoqiang, YANG Jingfang, YE Guoliang, et al. Study on reinforcement effect of shield tunnel adjacent to existing pile foundation with churning pile[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2011, 28(11): 98-103. (in Chinese)
[16] 郑刚. 软土地区基坑工程变形控制方法及工程应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(1): 1-36. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202201001 ZHENG Gang. Method and application of deformation control of excavations in soft ground[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 1-36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202201001
[17] 郑刚, 苏奕铭, 刁钰, 等. 基坑引起环境变形囊体扩张主动控制试验研究与工程应用[J]. 土木工程学报, 2022, 55(10): 80-92. ZHENG Gang, SU Yiming, DIAO Yu, et al. Field tests and application of capsuled expansion for active control of environmental deformation induced by excavation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2022, 55(10): 80-92. (in Chinese)
[18] ZHENG G, SU Y M, DIAO Y, et al. Field measurements and analysis of real-time capsule grouting to protect existing tunnel adjacent to excavation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 122: 104350.
[19] HUANG J Y, DIAO Y, ZHENG G, et al. Horizontal deformation efficiency of a pile controlled by the capsuled expansion technique: a field trial and numerical analysis[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2024, 24(1): 04023262.
[20] ZHENG G, HUANG J Y, DIAO Y, et al. Formulation and performance of slow-setting cement-based grouting paste (SCGP) for capsule grouting technology using orthogonal test[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 302: 124204.
[21] 李广信. 静孔隙水压力与超静孔隙水压力: 兼与陈愈炯先生讨论[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(5): 957-960. http://cge.nhri.cn/article/id/14591 LI Guangxin. Static pore water pressure and excess pore water pressure: a discussion with Mr. CHEN Yujiong[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(5): 957-960. (in Chinese) http://cge.nhri.cn/article/id/14591
[22] 郑刚, 潘军, 程雪松, 等. 基坑开挖引起隧道水平变形的被动与注浆主动控制研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(7): 1181-1190. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201907001 ZHENG Gang, PAN Jun, CHENG Xuesong, et al. Passive control and active grouting control of horizontal deformation of tunnels induced neighboring excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(7): 1181-1190. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201907001
[23] 郭景琢, 郑刚, 赵林嵩, 等. 多排孔注浆引起土体变形与孔压规律试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2023, 44(3): 896-907. GUO Jingzhuo, ZHENG Gang, ZHAO Linsong, et al. Experimental study of soil deformation and pore pressure caused by multi-row grouting[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(3): 896-907. (in Chinese)
-
其他相关附件



 下载:
下载: