Damage evolution mechanism of coal rock under long-term soaking
-
摘要: 富水状态下煤岩力学性能的持续劣化是导致煤矿水害的重要原因,为探究长期浸润作用下煤岩的渐进损伤特征,以神木地区弱黏煤为研究对象,首先以无压力水浸泡的方式模拟煤岩的长期浸润(15,30,60,120,240 d);然后对干燥及浸润试样进行渐进破坏试验,辅以声发射(AE)监测,定量分析煤岩的软化特性;最后利用扫描电镜(SEM)和核磁共振(NMR)研究不同浸润时长下煤岩孔隙结构的劣化规律。研究表明:①煤岩饱和度随浸润时长的增加而增加,增加速度先快后慢,最后达到稳定。②随饱和度的增加,煤岩力学性能劣化;饱和后,随浸润时长的持续增加,煤岩力学性能仍持续劣化,表现为抗压强度、弹性模量的减小和累计振铃数的增加;③干燥处理后,原状煤岩表面干燥收缩,浸水后吸水膨胀,随着浸润时间的增加,小孔隙逐渐增多,孔隙结构趋于复杂。研究结果可为浸水煤岩失稳破坏问题提供有益参考。Abstract: The deterioration of the mechanical properties of water-rich coal rock is a predisposition to many mine geologic hazards. To explore the progressive damage characteristics of coal rock under long-term soaking, the weakly caking coal of the Shenmu region is selected as the research object. Firstly, the long-term soaking tests on coal rock are carried out without pressures for 15, 30, 60, 120 and 240 days. Then, the uniaxial compression tests with acoustic emission (AE) monitoring are carried out on the dry and then soaked coal rock to analyze its water-softening characteristics. Finally, the evolution of pore structure of coal rock under different soaking durations is studied using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The results show that: ①The water saturation of coal rock increases with the duration of soaking, and the increase rate continuously decreases, and tends to a constant. ②In the process of saturation, the mechanical properties of coal rock deteriorate, and those of saturated coal rock still deteriorate with the increase of the soaking duration, characterized by the decrease of the compressive strength and elastic modulus, and an increase in the cumulative AE ringing numbers. ③A surface shrink may occur after the drying process, and during the soaking tests, the small pores of samples gradually increase, and the pore structure becomes more complex with the increase of the soaking duration. The research results can provide useful prevention for the instability and failure of coal rock under water-rich conditions.
-
Keywords:
- coal rock /
- soaking duration /
- mechanical property /
- multi-scale /
- damage mechanism
-
0. 引言
煤炭是中国经济发展的重要能源基石[1-2],随着矿井建设走向深部,复杂水文地质条件下的煤矿水害防治成为亟待解决的难点问题[3-4],开展不同浸润时长作用下的煤岩损伤劣化机制研究对中国富水煤矿安全开采至关重要。
目前,众多学者开展了水对煤岩物理力学特性影响的研究,并取得了阶段性的成果。在宏观物理力学特性方面,明确了含水率对煤岩力学特性的影响,确立了煤岩的含水率与强度间呈现负相关的关系[5]。在此基础上,进一步分析了煤岩弹性模量,内摩擦角,泊松比等材料参数与含水率之间关系[6],且发现水会延缓受荷煤岩变形速率的增长[7]。对比煤岩浸润不同时间下的体积变化,发现了长期浸润煤岩体积会发生膨胀[8-10]。除宏观力学参数的劣化外,声发射技术也被用于损伤监测,如Meng等[11]基于声发射技术对煤岩应力应变曲线峰后的裂隙发育阶段进行了监测,得到了煤岩脆性越强,峰后的应力下降和声学特征越明显的规律。Vishal等[12]通过声发射和压力试验机,研究了不同含水率煤岩压缩过程的声发射特性,发现了饱水煤岩在高应力状态下声学特征明显。夏冬等[13-14]开展了不同浸水时长的岩石力学特性和声发射特征研究,探讨了浸水岩石损伤和声发射特征之间的内在关系。
为揭示煤岩浸水后力学性能的劣化机制,研究人员也开展了较为系统的微、细观研究。在微观尺度上,运用SEM对煤岩进行扫描,得到不同宏观组分的孔隙结构有明显差异[15],对孔隙按尺寸进行了分类[16],考虑水对煤岩的作用,观测了不同含水率煤岩的结构变化,并分析了孔隙细部结构的成因[17-18]。水浸润作用使煤岩细观结构会发生变化,导致煤岩产生损伤[19]。随着煤岩损伤程度的增大,煤岩的孔容、比表面积、平均孔径均呈增大趋势。各孔径段孔容以小孔占比最高,且比例逐渐升高[20]。
在细观尺度上,研究人员运用核磁共振分析了煤岩孔隙随浸润时间的变化规律,发现浸润煤岩内部孔隙随时间的增加会发生变化[21]。在不同围压及孔隙水压力条件下,煤岩内部的结构和水分布规律,揭示了围压和孔隙水压力对煤样结构和渗流特性的影响规律[22]。Jia等[23]基于核磁共振的T2谱划分了岩石孔隙类型。Xie等[24]对比了不同煤岩在干燥和浸水处理后的孔隙结构,发现浸润前后煤岩总孔隙体积、大孔比和渗透率都会增大。王龙飞等[25]通过煤层低压注水研究了水在煤岩中的运移规律,得到了水会由大孔隙逐渐进入微小孔隙的规律,且水对煤岩各孔径段的孔隙影响不同,为研究长期浸润煤岩内孔隙变化提供了参考。
综上,对于水-煤岩相互作用的研究已广泛开展,但多聚焦于含水率对煤岩宏观力学特性的影响,对于长期浸润和劣化机制的研究相对较少。因此,本课题在力学试验的基础上采用SEM和NMR监测煤岩浸润过程中的结构和孔隙变化,通过分析细、微观结构演化过程,揭示浸润作用下煤岩劣化机理,为富水地区煤矿灾害防治提供有益参考。
1. 浸润煤岩物理力学特性研究
1.1 试验方案
本文试样采集自神木矿区,按GB/T 23561—2009《煤和岩石物理力学性质测定方法》(后文简称《规范》)要求通过取芯、切割、打磨制备成标准试样140个,选取试样研磨至200目进行工业分析和元素分析,煤岩的工业分析和元素分析如表 1所示。
表 1 煤岩的工业分析和元素分析Table 1. Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of coal rock样品 工业分析/% 元素分析/(%daf) Mad Aad Vdaf C H O N S C/H H/O 煤岩 5.65 5.23 32.65 78.21 4.77 15.32 1.65 0.43 1.37 0.226 浸润煤岩试验详细流程如图 1所示,具体步骤如下:
(1)将制备的试样于105±5℃条件下进行恒温干燥,冷却至室温后称重,并运用超声波对煤岩进行筛选,选择超声波速接近的试样进行后续试验。
(2)按《规范》要求对干燥煤岩进行无压力水浸泡,浸泡时浸润液为蒸馏水,最长浸润时间为240 d。
(3)将干燥及浸水时长达到预设值(15,30,60,120,240 d)的试样取出,擦干表面水分后进行力学特性试验,试验过程中配合AE探头,对破坏过程的声发射特性进行监测。
(4)浸润物理特性组和力学试验组进行无压力水浸润,对浸润物理特性试验组试样饱和度持续进行测量,采用SEM和NMR装置对干燥、浸润15,30,60,120,240 d后的煤岩孔隙变化和细观结构进行测量。
1.2 浸润煤岩饱和度分析
由于试样质量间存在差异,相较于含水率,将饱和度作为浸润程度的定量指标更为合适。根据浸水过程中试样质量的变化规律,在浸水5~240 d阶段试样质量基本稳定,将此状态的试样视为浸水饱和状态(后文称饱和状态)。根据《规范》的规定,饱和度的定义为
S=(Mt−M0Mn−M0)×100% 。 (1) 式中:Mt为浸润t d的煤岩质量(g);M0为煤岩烘干后的质量(g);Mn为浸润煤岩的自然饱和状态质量(g)。
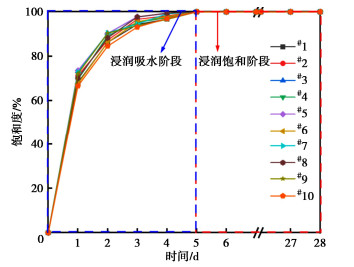
考虑煤岩离散性对试验结果的影响,选取10个试样研究煤岩饱和度与浸润时长的关系,试验结果如图 2所示。
从图 2可知,浸润煤岩可以分成浸润吸水阶段和浸润饱和阶段,浸润吸水阶段随浸润时间的增加,煤岩饱和度逐渐增加,增长速率先快后慢,最后达到饱和状态。浸水1 d后,煤岩的平均饱和度已达70.49%,随后饱和度增长速率逐渐降低,试样浸润第5天达到饱和状态,即饱和度为100%。煤岩浸润5 d之后进入浸润饱和阶段,饱和度维持在100%,即随时间增加饱和度不变。
1.3 浸润煤岩声发射与压缩试验及分析
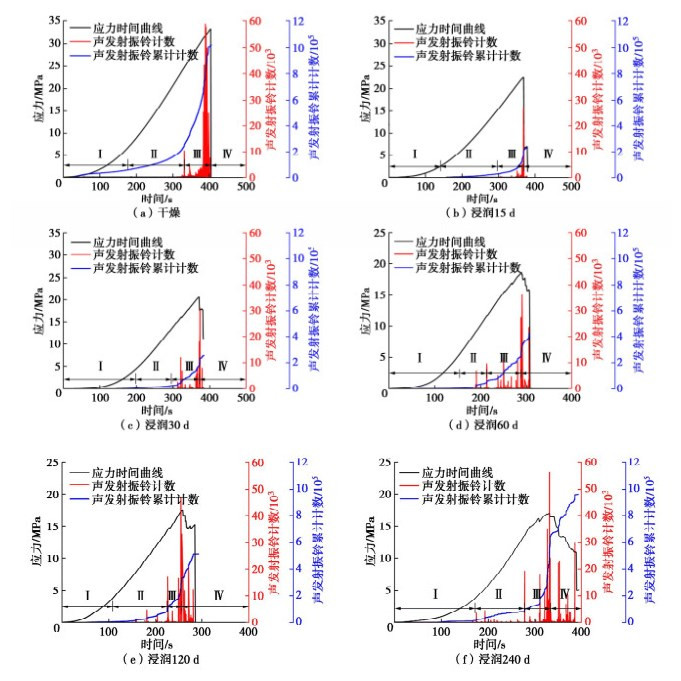
通过声发射及压缩系统对煤岩的声学特征及应力进行监测。声发射系统主放设定为40 dB,检测阈值为40 dB,探头谐振频率20~400 kHz。浸润煤岩的单轴压缩与声发射结果,如图 3所示。
由图 3可知,根据浸润煤岩声发射特征可划分为4个阶段(Ⅰ压密阶段、Ⅱ弹性阶段、Ⅲ裂纹稳定扩展阶段和Ⅳ裂纹不稳定扩展阶段)[26]。煤岩在压密阶段声学特征不明显,饱和后随着浸润时间增加弹性阶段、裂纹稳定扩展阶段和裂纹稳定扩展阶段的声发射活动发生的频率逐渐增加。
其中干燥状态和不同润时长下煤岩的声发射振铃计数及振铃累计数演化特征存在较大差异。煤岩干燥状态下振铃累积计数高达10.18×105,裂纹稳定扩展阶段持续时间为75 s,裂纹不稳定扩展持续时间接近0 s,呈现脆性。浸润30 d相对15 d煤岩声发射振铃累积计数增加了0.07×105,且裂纹不稳定扩展时间增加了0.9437 s,表征此时段煤岩内部结构逐渐变得松散且缺陷逐渐增多;浸润60,120,240 d相较浸润60 d之前的试样不仅出现声发射振铃计数最大值逐渐增大和累积计数范围逐渐扩大,而且裂纹不稳定扩展的持续时间逐渐增大,表征此阶段的煤岩不仅内部结构变得更加松散而且缺陷进一步增多。随浸润时间的增加,煤岩呈现由脆性向塑性转变。
1.4 浸润煤岩抗压强度特征
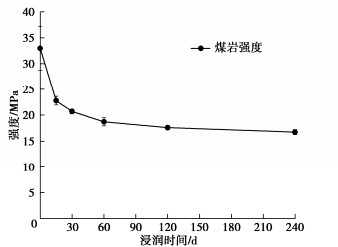
浸润煤岩压缩试验获得的强度-时间曲线如图 4所示。
从图 4可以看出,随着浸润时间的增加,煤岩单轴抗压强度均逐渐降低,由干燥煤岩的32.95 MPa到浸润240 d的16.75 MPa,降低了49.16%。浸润15 d后,煤岩内部缺陷演化,对应峰值强度快速降低;浸润60 d后,因长期浸润引起导水空间不断扩大,促使浸润损伤进一步积累,但强度变化较小,损伤累积速率趋于稳定;浸润240 d后,煤岩强度波动较小。
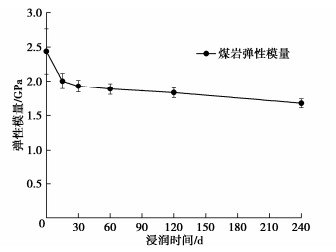
弹性模量与时间的关系如图 5所示,由干燥煤岩的2.44 GPa到浸润240 d的1.68 GPa,降低了31.15%。弹性模量的降低反映了煤岩抵抗变形能力减弱;同时受浸润时长影响,引起的变形特征也伴随着煤岩内部缺陷的发育,使得损伤加剧。结合图 3可知,随着浸润时间的增加,煤岩在相同应力下轴向应变逐渐增大,表面浸润时间越长,煤岩内部孔隙裂隙增多且扩展更加频繁,在相同应变下煤岩所能承受的荷载逐步降低。不同浸润时长下煤岩的应力应变特征与所划分的曲线孔隙裂隙压密阶段、弹性阶段、裂纹稳定扩展阶段和裂纹不稳定扩展阶段的特性对应,且煤岩随着浸润时间的增加损伤不断累积。
2. 浸润煤岩微观结构变化
不同浸润时长的煤岩SEM照片如图 6所示。
干燥煤岩微观结构如图 6(a)所示,干燥煤岩有明显的胶结结构,成岩矿物呈块状,矿物颗粒胶结在一起,形成较大的块状、板状结构,较大的颗粒由细小颗粒集结而成,片状、初始裂纹、孔隙较多,裂纹开度小,试样整体性较好。煤岩浸润饱和状态的微观结构,如图 6(b)所示,水充满了孔隙和裂隙,大量矿物吸水膨胀,颗粒相互挤压,颗粒之间的接触变得更加紧密。浸润120 d后,如图 6(c)所示,可以看出,浸润时长对煤岩微观结构存在较大影响。最初密实的煤岩由于受长期水浸润作用影响,逐渐变成疏松多孔的松散结构,矿物颗粒之间的连结变得较为松散;同时,矿物颗粒基本呈鳞片状或絮状结构分布,鳞片状和絮状结构在水和应力作用下相互挤压碰撞发生破坏,形成了许多孔隙和碎屑结构。煤岩长期浸润会导致矿物质结构发生变化,进而会影响其内部孔隙分布及宏观力学特性。此外,弱酸性会导致极少数碳酸盐矿物的溶解,加速试样的损伤。高岭石作为一种高渗透性的粒状材料,能迅速地将水吸附到孔隙裂隙中,高岭石的体积在水浸润下体积增大28%[18]。矿物的溶解和扩散对浸润过程中孔隙结构有重要影响。水合物会生成或吸水形成石膏,石膏体积会扩大61%[18]。通过观察也发现浸润煤岩存在膨胀,猜测其含水率会继续增加,可能是由于矿物溶蚀造成孔隙变化造成的,水继续进入结构。为了验证这个猜想,进行核磁共振试验。
3. 浸润煤岩细观结构分析
核磁共振分析仪采用由苏州纽迈科技有限公司生产的Macro MR12-150H-I型低场核磁共振设备,磁场强度(0.3±0.05)T,氢质子相应频率12.77 MHz,线圈的脉冲频率为1.499 MHz。在煤岩中,存在于不同类型孔洞的水,对应的弛豫时间也会不同,可以根据反演数据得到的T2谱来划分孔径分布[24]。T2与孔隙几何参数的关系为
1T2=ρ2(SpVp)=ρ2(FcRc)。 (2) 式中:ρ2为横向表面弛豫速率(μm/s),与岩石种类有关且为常数;Sp为孔隙表面积(μm2);Vp为孔隙体积(μm3);Fc为孔隙的几何形状因子;Rc为孔隙平均半径(μm)。
由式(2)可知:
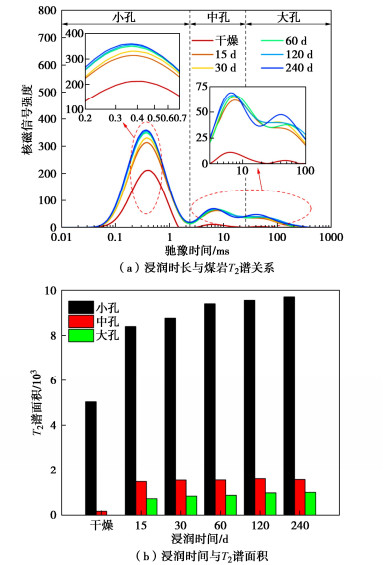
Rc=Fcρ2T2。 (3) 浸润煤岩通过核磁共振对干燥、浸润15,30,60,120,240 d的同一试样进行测试,计算得出不同浸润时长的煤岩T2谱,如图 7(a)所示。
T2谱图不同驰豫时间段对应的峰值,反映了不同大小的孔隙:0~3 ms对应小孔隙,3~33 ms对应中孔隙,33 ms以上对应大孔隙。T2谱图峰面积大小代表孔容的多少。面积越大,对应的孔隙容积越大。T2谱图中出现的峰值位置,反映了对应的孔径大小。峰值位置越大,对应的孔径越大。
煤岩中孔隙根据孔径大小可分为小孔隙、中孔隙和大孔隙3种类型。小孔隙对应孔径 < 0.1 μm,中孔隙对应0.1~1000 μm,大孔隙对应 > 1000 μm。根据核磁共振弛豫时间T2的不同,可以区分这3种尺度的孔隙:T2在0~3 ms内的脉冲响应对应小孔隙,3~33 ms对应中孔隙,33~10000 ms对应大孔隙[23]。此外,核磁共振T2谱峰面积与该峰下对应孔隙的容积成正比[24],峰面积越大,表示对应尺度孔隙的容积空间越大。则根据图 7(b)可知,干燥和不同浸润时长煤岩的大孔隙、中孔隙、小孔隙体积占比会发生变化。浸润饱和后,大孔隙和中孔隙体积分别占总孔隙体积的10%左右,而小孔隙体积占总孔隙体积达到78.67%以上,这说明浸润煤岩孔隙均以小孔隙为主。在浸润15 d时,小孔峰面积达到8398.57;在浸润240 d时,小孔峰面积达到9703.53;T2谱三峰的面积不断动态变化,表征煤岩随浸润时间增加,中孔数量动态变化,小孔、大孔在逐渐增多,其中小孔增加最为显著。反映浸润作用下煤岩的孔隙不是固定的,随时间的变化孔隙呈现动态变化,即使煤岩达到饱和状态,孔隙的数量仍然随浸润时间的增加而改变,验证了浸润煤岩含水率会增加的猜想。
4. 浸润煤岩损伤机制讨论
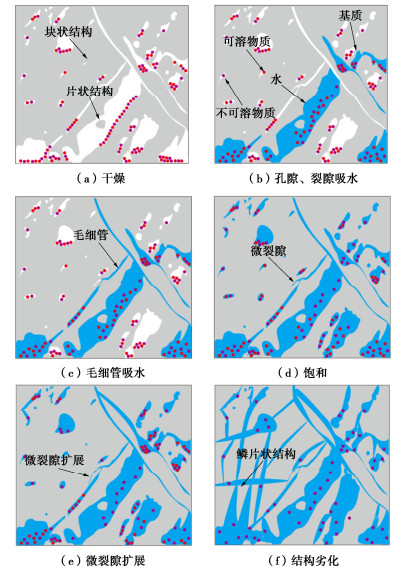
煤岩在浸水过程中存在结构的位移与形变、原生孔隙的发育与原生裂隙的扩展、水分的迁移与消散、局部密度的改变等[27-29]。综合上述试验结果,本课题从宏、细、微尺度对煤岩进行讨论,绘制浸润过程中煤岩损伤劣化机制图,如图 8所示。
4.1 宏观尺度分析讨论
如图 8(a)所示,干燥煤岩压缩过程中由于内部表面粗糙且相互间距离较大,孔洞中含有矿物质颗粒所以结构间的摩擦和局部应变变化剧烈,声发射振铃计数较多且主要集中在裂纹稳定扩展阶段,煤岩破坏模式以剪切为主,且强度及弹性模量较高。
如图 8(d)所示,饱和煤岩在压缩过程中块体间的摩擦由于水的润滑而减弱,声发射振铃计数减少但仍然主要集中在裂纹稳定扩展阶段,煤岩破坏模式以张拉为主,水楔和润滑作用降低了煤岩的强度及弹性模量。
浸润240 d煤岩压缩过程中由于溶蚀作用造成煤岩松散,使得声发射振铃计数分布范围逐渐扩大。部分矿物质被运移出煤岩内部,从而弱化煤岩基质和矿物质的内聚力和抗压能力,致使煤岩强度及弹性模量损失严重。因此,浸润时长改变了微观和细观结构,从而引起了宏观物理性能改变。
4.2 细观尺度分析讨论
干燥煤岩内部分布了许多孔隙、裂隙,如图 7(a)所示,核磁共振T2呈现三峰分布,可以分为小孔隙、中孔隙和大孔隙3种类型。其中,小孔隙含氢化物较多,中孔隙和大孔隙的氢化物含量较少。
浸润后,煤岩主要受到毛细作用和溶蚀两种作用的影响。毛细作用方面,由于压强差存在,水分进入孔隙中,如图 8(b)所示,孔隙裂隙水与煤岩内部毛细管产生毛细作用,促使水分进入煤岩内部,如图 8(c)所示,毛细力越大,水分通过流动通道涌入煤岩的速度越快。发达的毛细管促进水迁移至孔隙内,随着毛细管逐渐被水填满,毛细力不断减弱,水分迁移减缓,吸水减慢,从而使饱和度增长速率先快后慢,最后趋于稳定且煤岩达到饱和。溶蚀作用方面,如图 8(e)所示,煤岩饱和后,随着浸润时间的增加,小孔、中孔、大孔的核磁振幅、峰面积持续增大,原生裂隙间溶蚀,原生孔隙扩大,煤岩的骨架物质损失,且孔隙形状改变,孔隙内空间曲率、梯度突变的结构产生应力集中现象,孔隙进一步张开、断裂。原本多重弥散、随机分布的毛细管孔隙群扩展、贯通,劣化出超毛细管孔隙,使得内部通道发生不可逆扩展,导致了损伤的累加,促进原有裂隙延伸扩张形成宏观裂隙。复杂的空间分布形态形成结构相对简单的大孔径孔隙和连通孔隙,促进原有微裂隙和裂隙延伸扩张形成裂隙。
4.3 微观尺度讨论分析
煤岩干燥状态微观呈现块状和片状分布,如图 8(a)所示。由于干燥作用,水分几乎被烘干,块状、片状结构干燥密实,块体表面粗糙且含有微孔洞和微裂隙,基质和矿物质收缩且胶结紧密,但块体相互间距离较大。
浸润后,水分子与煤岩颗粒表面产生的范德华力相互吸引,并与表面极性基团形成氢键,水被带入原生微孔隙和微裂隙内部。水通过微裂隙进入块体和片体的内部,溶解可溶物质(部分有机物和无机物),形成新的微孔洞、微裂隙,不可溶解物质在水中流动。导致原生微孔隙、微裂隙的延伸、扩展以及次生微裂隙的形成,造成了微裂隙和微孔隙增多。而微孔隙、微裂隙空间的扩大进一步加强了煤岩对水的吸附作用,最终被水充满,如图 8(d)所示。虽然煤岩达到饱和,但随着浸润时间的持续增加,基质和矿物颗粒受到不同程度的水化作用而发生体积变形,由于膨胀系数的差异,相互之间产生非均匀应变,容易在其粘结位置产生较大的张拉应力,引起煤岩损伤范围的扩大表面、造成表面发育出次生孔隙。内部与水接触的基质和矿物质继续发生溶解、膨胀、挤压破坏。更多的基质和矿物质与水接触产生新的损伤,造成微孔隙增多并产生新的微裂纹,部分微裂纹劣化成裂纹。胶结物逐步稀释,溶解产生浓度梯度,形成传质推动力,使溶解的物质逐渐向外扩散,如图 8(e)所示。浸润240 d后结构呈现鳞片状结构,如图 8(f)所示,水充满了内部孔隙和堆积结构层间,水楔作用下游离的水分子形成水膜包裹各颗粒,层状结构间的游离水充当滚珠,促进加载过程中的滑移错动。
因此,浸润时间长对煤岩微观结构损伤效果明显,水分会随时间增加,使微观结构形态改变和微孔隙、微裂隙的延伸、扩展。总之,干燥状态煤岩含有微裂隙、孔隙、裂隙等,随着浸润时间的增长,通过在分子间的作用力下水与煤岩接触,毛细作用下水经过裂隙、毛细管、超毛细管运送到各处,引起基质和矿物质非均匀膨胀,减弱结构间摩擦,溶解部分有机物和排出无机物。基质和矿物质非均匀膨胀产生微裂隙,促进了煤岩微观损伤的积累。水浸润促进膨胀矿物继续膨胀,微裂纹发展、溶蚀作用和膨胀作用促进细观损伤积累。微观结构的损伤累积促进了细观结构的改变,细观结构的损伤累积引起了宏观上煤岩试样力学性能的劣化。这是一个循序渐进不断积累的过程。
5. 结论
以长期浸润煤岩为研究对象,利用压力试验机、声发射、核磁共振以及扫描电镜得到浸润煤岩的宏、细、微观物理力学特征,进行损伤机制分析,主要得到3点结论。
(1)饱和煤岩随浸润时间增长,荷载作用下裂隙不稳定扩展持续时间呈现逐渐增加,累积振铃计数逐渐增加,峰值强度和弹性模量逐渐降低,而峰值应变增加,最后强度趋向于稳定。60 d的饱水时间为煤岩力学强度趋于稳定的分界点。因而,可以认为,煤岩在浸润条件下,60 d前力学性质将发生较大的变化,煤岩由脆性向塑性转变,需要改变煤岩支护方式。
(2)长期浸润作用下煤岩微、细观结构劣化显著,表现为煤岩内部结构微膨胀,孔隙大小和数量不固定,即使煤岩达到饱和状态,孔隙的大小和数量仍然随浸润时间的增加而改变,浸润煤岩含水率会持续增加,结构间孔隙裂隙会动态变化,大、小孔隙数量均增加,且小孔隙数量增加最为显著。
(3)浸润作用对煤岩力学特性影响显著,浸润煤岩强度不仅和含水率有关,还受浸润时长的影响。干燥煤岩含有缺陷,随着浸润时间的增长,水与煤岩的分子间作用力、溶解作用、非均匀膨胀促进了煤岩微观损伤的积累;毛细作用、溶蚀作用和膨胀挤压促进了煤岩细观损伤积累。微观结构的损伤累积推动了细观结构改变,细观结构的损伤累积导致了煤岩宏观力学性能的劣化。
研究发现煤岩饱和后长期浸润强度会降低,富水的煤矿开采过程中需要注意,由于长期浸润煤岩问题的复杂性,研究的难度很大,有许多问题尚需进一步深化和细化。
-
表 1 煤岩的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of coal rock
样品 工业分析/% 元素分析/(%daf) Mad Aad Vdaf C H O N S C/H H/O 煤岩 5.65 5.23 32.65 78.21 4.77 15.32 1.65 0.43 1.37 0.226 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022. National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022. (in Chinese)
[2] ZHANG Anlin, XIE Heping, ZHANG Ru, et al. Mechanical properties and energy characteristics of coal at different depths under cyclic triaxial loading and unloading[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2023, 161(1): 105271.
[3] 张玉军. 控水采煤技术原理、关键技术及在砂岩含水层下综放开采实践[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(10): 3380-3388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202010002.htm ZHANG Yujun. Principle and key technologies of controlled water mining and practice of fully-mechanized mining under soft sandstone aquifer[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(10): 3380-3388. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202010002.htm
[4] 武强, 申建军, 王洋. "煤-水"双资源型矿井开采技术方法与工程应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(1): 8-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201701002.htm WU Qiang, SHEN Jianjun, WANG Yang. Mining techniques and engineering application for "Coal-Water" dual-resources mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(1): 8-16. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201701002.htm
[5] CHEN Tian, YAO Qiangling, WEI Fei. Effects of water intrusion and loading rate on mechanical properties of and crack propagation in coal–rock combinations [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(2): 183-191.
[6] YAO Qiangling, CHEN Tian, XIA Ze, et al. Mechanisms of failure in coal samples from underground water reservoir[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 267: 105494. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105494
[7] ZHONG Chunlin, ZHANG Zhenyu, RANJITH P G, et al. The role of pore water plays in coal under uniaxial cyclic loading[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 257: 105125. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.05.002
[8] WEN Guangcai, YANG Shuo, LIU Yanbao, et al. Influence of water soaking on swelling and microcharacteristics of coal[J]. Energy Science and Engineering, 2020, 8, 50-60. doi: 10.1002/ese3.508
[9] YANG Shuo, WEN Guangcai, YAN Fazhi, et al. Swelling characteristics and permeability evolution of anthracite coal containing expansive clay under water-saturated conditions [J]. Fuel, 2020, 279: 118501. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118501
[10] 刘驰, 刘晓丽, 张东, 等. 软岩软化的水岩界面动力学模型及其演化规律[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(12): 2280-2289. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202212015 LIU Chi, LIU Xiaoli, ZHANG Dong, et al. Dynamic model for water-rock interface of softening of soft rock and its evolution law[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(12): 2280-2289. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202212015
[11] MENG Fanzhen, ZHOU Hui, ZHANG Chuanqing, et al. Evaluation methodology of brittleness of rock based on post-peak stress-strain curves[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2015, 48(5): 1787-1805. doi: 10.1007/s00603-014-0694-6
[12] VISHAL V, RANJITH P G, SINGH T N. An experimental investigation on behaviour of coal under fluid saturation, using acoustic emission[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 22: 428-436. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2014.12.020
[13] 夏冬, 杨天鸿, 王培涛, 等. 干燥及饱和岩石循环加卸载过程中声发射特征试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(7): 1243-1247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201407008.htm XIA Dong, YANG Tianhong, WANG Peitao, et al. Experimental study of acoustic emission characteristics of dry and saturated rocks during cyclic loading and unloading process[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(7): 1243-1247. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201407008.htm
[14] 夏冬, 杨天鸿, 徐涛, 等. 浸水时间对饱水岩石损伤破坏过程中声发射特征影响的试验[J]. 煤炭学报, 2015, 40(增刊2): 337-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2015S2005.htm XIA Dong, YANG Tianhong, XU Tao, et al. Experimental study on AE properties during the damage process of water saturated rock specimens based on time effect[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(S2): 337-345. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2015S2005.htm
[15] ZHENG Chao, MA Dongmin, CHEN Yue, et al. Pore structure of different macroscopically distinguished components within low-rank coals and its methane desorption characteristics[J]. Fuel, 2021, 293: 120465. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120465
[16] 张慧, 李小彦. 扫描电子显微镜在煤岩学上的应用[J]. 电子显微学报, 2004, 23(4): 467. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2004.04.169 ZHANG Hui, LI Xiaoyan. Application of scanning electron microscope in coal petrology[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2004, 23(4): 467. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2004.04.169
[17] 张慧, 吴静, 袁立颖, 等. 煤中气孔的发育特征与影响因素浅析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2019, 47(1): 78-85, 91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.01.011 ZHANG Hui, WU Jing, YUAN Liying, et al. Analysis on the development characteristics and influencing factors of gas pores in coal[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2019, 47(1): 78-85, 91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.01.011
[18] XU Yong, CHEN Xuexi, ZHAO Wei, et al. Effect of water intrusion on the characteristics of surface morphology and pore fracture spaces in argillaceous meagre coal[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 81: 103404. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103404
[19] 张村, 贾胜, 王方田, 等. 水岩作用下煤体孔裂隙结构演化特征及驱动机制实验研究[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2023, 31(1): 185-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX202301014.htm ZHANG Cun, JIA Sheng, WANG Fangtian, et al. An experimental research on the pore and fracture evolution characteristics and its driving mechanism for coal samples under water-rock interaction[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2023, 31(1): 185-196. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX202301014.htm
[20] 常会珍, 李贵山, 张蒙, 等. 松软低渗区不同煤体结构煤的孔裂隙发育特征[J]. 煤炭技术, 2023, 42(1): 133-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS202301027.htm CHANG Huizhen, LI Guishan, ZHANG Meng, et al. Pore and fissure development characteristics of coal with different coal structure in soft and low permeability area[J]. Coal Technology, 2023, 42(1): 133-137. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS202301027.htm
[21] XU Hao, TANG Dazhen, CHEN Yanpeng, et al. Effective porosity in lignite using kerosene with low-field nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Fuel, 2018, 213: 158-163. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.10.112
[22] LIU Zhen, YANG He, WANG Wenyu, et al. Experimental Study on the pore structure fractals and seepage characteristics of a coal sample around a borehole in coal seam water infusion[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2018, 125(2): 1-21.
[23] JIA Hailiang, DING Shun, WANG Yan, et al. An NMR-based investigation of pore water freezing process in sandstone [J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2019, 168, 102893. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102893
[24] XIE Jingna, NI Guanhua, HAO Jian, et al. The pore characteristics of high temperature coal mine and the impact of invasive water on its development[J] Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2019, 12(21): 657. doi: 10.1007/s12517-019-4856-4
[25] 王龙飞, 蒋仲安, 陈举师, 等. 低压注水对煤体孔隙特征及渗透率的影响[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(6): 108-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201806017.htm WANG Longfei, JIANG Zhongan, CHEN Jushi, et al. Influence of low pressure water injection on pore characteristics and permeability of coal. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2018, 14(6): 108-113. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201806017.htm
[26] 荣腾龙, 刘克柳, 周宏伟, 等. 采动应力下深部煤体渗透率演化规律研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(6): 1106-1114. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202206015 RONG Tenglong, LIU Keliu, ZHOU Hongwei, et al. Permeability evolution of deep coal under mining stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 1106-1114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202206015
[27] 冯国瑞, 文晓泽, 郭军, 等. 含水率对煤样声发射特征和碎块分布特征影响的试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(8): 2910-2918. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202108035.htm FENG Gourui, WEN Xiaoze, GUO Jun, et al. Study on influence of moisture content on coal sample AE properties and fragment distribution characteristics[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(8): 2910-2918. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202108035.htm
[28] 张慧梅, 王云飞. 冻融红砂岩损伤演化多尺度分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(8): 2103-2114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202208006.htm ZHANG Huimei, WANG Yunfei. Multi-scale analysis of damage evolution of freezing-thawing red sandstones[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(8): 2103-2114. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202208006.htm
[29] 楚亚培, 张东明, 王满, 等. 基于核磁共振技术和压汞法的液氮冻融煤体孔隙结构损伤演化规律试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(9): 1820-1831. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202209005.htm CHU Yapei, ZHANG Dongming, WANG Man, et al. Experiment study on influence of liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw on pore structure of coal based on nuclear magnetic resonance technology and mercury intrusion methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(9): 1820-1831. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202209005.htm
-
其他相关附件
-
本文英文pdf
20240609-G23-0229英文发布稿 点击下载(4305KB)
-



 下载:
下载: