Multi-field coupling analysis of water-heat-salt in composite unsaturated soils
-
摘要: 研究了非饱和黏土上覆非饱和砂土组成的复合非饱和土中的水-热-盐多场耦合问题。基于多孔介质的质量守恒和能量守恒方程,选取温度、孔隙压力和含盐率以及它们的梯度作为状态变量,建立了非稳态条件下水热盐多场耦合问题的状态方程组。将状态方程组进行Laplace变换后,进而求解该强耦合的非线性变系数微分方程组的频域解,并通过反演法获得时域解。并将数值解与自主设计试验的试验结果进行了对比,验证了所建立数学模型的准确性。分析了复合非饱和土体在温度梯度下,底部非饱和砂土的厚度和饱和渗透系数等对整个非饱和土体中水分场和盐分场分布以及迁移规律的影响,继而对盐渍土的改良工作和工程土障的建设提供试验和理论依据。Abstract: The multi-field coupling problem of water, heat and salt in the composite unsaturated soils composed of unsaturated clay and unsaturated sand is studied. Based on the mass and energy conservation equations for porous media, the temperature, pore pressure, salt content and their gradients are selected as the state variables, and the state equations for the multi-field coupling problem of water, heat and salt under unsteady conditions are established. After the Laplace transformation of the state equations, the frequency-domain solution for the strongly coupled nonlinear variable coefficient differential equations is solved, and the time-domain solution is obtained by the inversion method. The numerical solution is compared with the experimental results of the self-designed tests, and the accuracy of the established mathematical model is verified. The influences of the thickness and saturated permeability coefficient of the unsaturated sand at the bottom of the composite unsaturated soils on the distribution and migration law of water and salt fields in the whole unsaturated soils under the temperature gradient are analyzed, and then the test and theoretical basis are provided for the improvement of saline soils and the construction of engineering soil barriers.
-
0. 引言
随着中国基础设施建设的快速发展,在非饱和盐渍土地区进行盐渍土的改良以及工程土障建设中,均涉及到水-热-气-传质等多物理场多相的耦合作用。Reshetin等[1]基于扩散定律和温度、湿度和蒸汽含量之间的函数关系,建立了关于温度场与湿度场的动力学数学模型,但数学模型中没有考虑非饱和土中水力梯度变化对耦合作用的影响。Jia等[2]在建立传热传质耦合模型时,考虑到水蒸汽对传热传质效应的影响。基于压力梯度和温度梯度等多种驱动因素建立了多种有关非饱和多孔介质的水-热耦合的数学模型,但忽略了非饱和多孔介质中水力梯度随时间和空间的变化规律且对气相的组分划分较为笼统[3-6],Mohammad等[7]考虑干燥气体与水蒸气的迁移对能量守恒的影响,但在在能量迁移的方式中忽略了对流作用影响。He等[8]在非饱和土水-热-力多场耦合的数学模型,没有考虑多场多相耦合作用中溶质的存在对多孔介质中水分场、温度场迁移规律的影响。
多孔介质中水-热-盐迁移现象是各影响因素相互耦合的过程,且迁移规律随时间和空间不断变化。Cleall等[9],HERNÁNDEZ-LÓPEZ等[10]通过试验孔隙的曲率因子和土体温度梯度的增强因子对水蒸汽通量有较大影响,Chen等[11]发现随着盐分在一端的大量聚集,溶液中的盐分会在盐分梯度作用下继续向该处迁移。周凤玺等[12-13]建立了完善热-湿-盐多物理场多相耦合的数学模型。但模型仅考虑均质非饱和多孔介质中的热湿盐多场耦合,并没有对复合非饱和土中的水-热-盐迁移规律进行进一步的研究且缺乏试验验证。
本文全面研究了复合非饱和土中的液态水、液相中的干燥气体和盐分以及孔隙中水蒸气等对水分场、盐分场和温度场随时间变化在空间上的分布规律的影响,并在能量守恒中考虑盐分、干燥气体以及各组分导热系数等分项对温度场的影响,建立了非稳态条件下复合非饱和土中多场多相耦合的状态方程。通过试验分单层验证了数学模型的准确性而后对复合非饱和土中水-盐-热的多场耦合问题进行参数分析。
1. 数学模型
1.1 质量守恒方程
∂(ϕπρπα)∂t+∇⋅(ϕπρπαvα)+∇⋅jπα=˙mπα,, (1) 式中,jπα为α组分在π相的非对流通量矢量,ϕπ为π相的体积分数,ρπα为α组分在π相的质量分数,vα为α组分的速度矢量[12-13]。
由式(1)可得水分平衡方程为
∂(nSlρlw)∂t+∂(nSgρgw)∂t+∇⋅(nSgρgwvg)+∇⋅jgw+∇⋅(nSlρlwvl)+∇⋅(ρlwql)+∇⋅(ρgwqg)=0 , (2) 式中,饱和度Sl为孔隙水压力Pl与孔隙气压力Pg的函数,存在表达式Pl + Pg = 1。液相、气相通量[12-13]存在表达式:
ql=−Kl(∇Pl+ρlwg), (3) qg=−Kg(∇Pg+ρgg), (4) 式中,Kl,Kg为水动力参数[12-13],g为重力加速度矢量。
非对流水通量遵循Philip等[14]所建立的模型,气相中水蒸汽非对流通量的变化可以归因于系统中水分的变化和系统中温度的变化:
jgw=jgvw+jgvT=−Dvw∇Pl+Dvw∇Pg−DvT∇T。 (5) 其中由温度和水分引起的分子扩散系数存在表达式[12-13]:
DvT=nSgρgwDatmvτfTv[4974.0T2+MwψRT2ρlw], (6) Dvw=nSgρgwDatmvτMwRTρlw, (7) 式中,Datm为水蒸汽分子的扩散系数,Datm = 2.16×10-5(T/273.15)1.8,τ为曲率因子[12-13]。
结合式(1)可得干燥气体的质量平衡方程为
∂(nHSlρla)∂t+∇⋅(ϕlρlavl)+∇⋅jla+∂(nSgρga)∂t+∇⋅(ϕgρgavg)+∇⋅jga=0 。 (8) 干燥气体在液相中不发生扩散,即jla=0。非对流项中的干燥气体的非对流通量与水蒸气的非对流通量存在表达式jga=−jgw,水中气体的密度存在[12-13]:
ρla≈ρga=ρa=MaRT(Pg−Pv), (9) 式中,Pv为水蒸气压力,Ma为干气摩尔质量,R为气体常数。
结合式(1)可以得出液相中盐分的质量守恒方程为
∂(ϕlρlp)∂t+∇⋅(ρlwωql)+∇⋅jlp=0。 (10) 由于研究土壤液相中盐分得浓度较低,不考虑溶质的溶解与析出。液相中溶质非对流通量jlp可以表示为
jlp=−nSlρlwτDp∇ω, (11) 1.2 能量平衡方程
系统中能量平衡的一般形式为[15]
∂Φh∂t+Q+∇⋅qh=0, (12) 式中,Φh为内能,Q为潜热,∇⋅qh表示热对流和传导。
考虑局部平衡以及不同组分温度相等的条件下,土壤的内能变化可表示为
∂Φh∂t=[(1−n)ρscs+nHSlρaca+nSgρaca+nSlρlwclw+nSgρgwcgw]∂T∂t 。 (13) 在非饱和土中由汽化和凝结引起的能量变化可表示为
Q=˙mgwHgw, (14) 式中,Hgw为液相中水分的汽化焓[16],Hgw=Lgw− (clw−cgw)(T−T0),˙mgw为蒸发率。
热流方程包括固相热传导、液相对流、气相对流,存在表达式[14]:
qh=qT+ρπαEπTαqα+EπTαjπα=−(λ1−nsλnSlwλnSpp)∇T+(ρaca+ρgwcgw)(T−T0)qg+(cgw−ca)(T−T0)jgw+c1pj1p(T−T0)+(ρacaH+ρ1wc1w)(T−T0)q1。 (15) 以往的研究忽略温度对溶液热容与导热系数的影响,溶液热容和导热系数与溶质的浓度有关[17]
c′w=β2cs+cw,λw=β3cs+λl,} (16) 式中,β2= -167,β3= 0.00493。
1.3 复合非饱和土非稳态问题求解
方程(2),(8),(10),(12)给出了复合非饱和土中水-气-盐-热多场耦合过程的控制方程,耦合方程是将孔隙水压力、孔隙气压力、温度、含盐率及其一阶偏导为未知量的封闭方程。将控制方程进行拉普拉斯变换后通过数值方法计算可得控制方程的频域解,而后基于Hausdoff矩问题将频域解u(x)转化为时域解qN(t)。
Hausdoff矩问题存在积分关系式
∫10xnu(x)dx=μn (n=0,1,2,⋅⋅⋅) 。 (17) Hausdorff矩问题是一个典型的不适定问题,u(x)的正则化近似解为
pN(x)=N∑i=0λiLi(x)。 (18) 最终Laplace逆变换的近似解为
qN(t)≡pN(e−t)=N∑i=0λiLi(e−t)。 (19) 基于式(19)Hausdoff矩问题的稳定化算法获得Laplace逆变换的解。
2. 试验验证
试验采用的土样是取自甘肃省兰州市的粉质黏土,该土样的颗粒相对质量密度为2.70 g/cm3,渗透系数约为2.89×10-6 m/s。将土样压制成高为280 mm、直径为200 mm,试验土柱的孔隙率n为0.3。初始时刻试验土柱的温度为25℃,顶板与底板的温度分别设为30,15℃。两端的孔隙气压力为101 kPa、初始质量含水率为10 %、初始含盐率为7%。
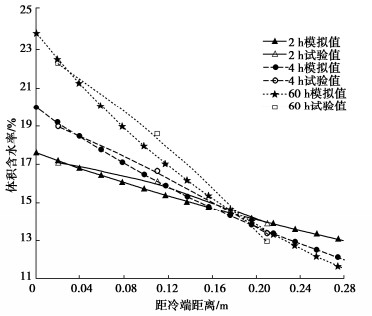
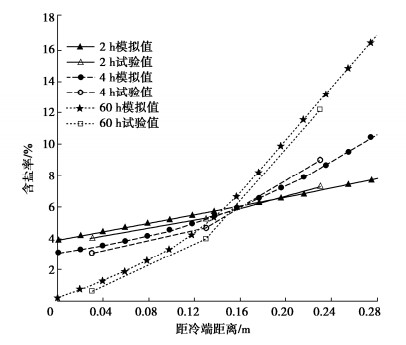
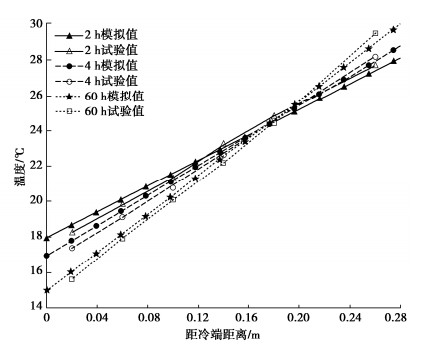
表 1,2分别给出了试验粉质黏土土样各物理成分的热力学参数和Van Genuchten(VG)模型[13,15]参数。经试验和计算可得粉质黏土土样在VG模型中所对应的拟合参数分别为nvg=1.69,mvg=0.0147。图 1~3分别给出了试样中水分,盐分和温度的分布规律,并与本文所提出的教学模型进行验证,两者吻合较好。
表 1 多孔介质中各物理成分的热力学参数Table 1. Thermodynamic parameters of physical components in porous media参数 数值 参数 数值 ca/(J·kg-1·K-1) 1000 Lgw/(J·kg-1) 2413000 clw/(J·kg-1·K-1) 4180 k0/(m·s-1) 2.89×10-6 cgw/(J·kg-1·K-1) 1900 g/(m·s-2) 9.8 clp/(J·kg-1·K-1) 3750 ρgw/(kg-1·m-3) 1000 λg/(W·m-1·K-1) 0.024 Ma/(kg-1·mol-1) 0.0288 λs/(W·m-1·K-1) 2.93 Mw/(kg-1·mol-1) 0.018016 λl/(W·m-1·K-1) 0.56 R/(J·mol-1·K-1) 8.3144 表 2 粉质黏土VG模型参数Table 2. VG model parameters of silty clay参数 数值 参数 数值 n 0.3 nvg 1.698 Slres 0.15 v 1.4 Slsat 0.85 fτv 1.2 mvg 0.411 Ps/kPa 68 3. 参数分析
表 2,3[18]分别给出了粉质黏土与砂土的VG模型参数。非饱和黏土上覆非饱和砂土的高度为300 mm保持不变,对砂土不同厚度、渗透系数等条件下复合非饱和土中的水分、盐分随时间变化的分布情况以及变化规律进行分析。砂土的孔隙率为0.5,上覆粉质黏土的孔隙率为0.3、土体上下边界的温度分别为27℃,3℃,上下边界的孔隙气压力均为102 kPa。复合非饱和土初始时刻的温度为15℃、初始时刻的孔隙气压力为102 kPa,为了让迁移规律更加明显砂土与黏土中初始的孔隙水压力设为-800 kPa、含盐率为0.12%。
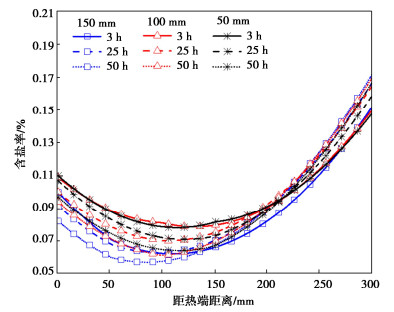
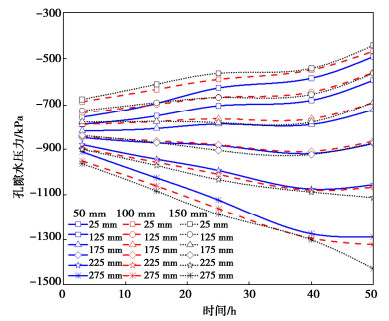
表 3 砂土的VG模型参数Table 3. VG model parameters of sand soil参数 数值 参数 数值 n 0.5 nvg 2.45 Slres 0.07 v 2 Slsat 0.93 fτv 1.4 mvg 0.59 Ps/kPa 32 图 4,5分别给出了在砂土厚度分别为50,100,150 mm,且复合非饱和土厚度始终为300 mm条件下,复合土体中孔压和溶质的分布情况。从图 4中可以明显地看出随着砂土厚度的增加,复合土体中砂土中的盐分是降低的。图 5给出了距热端25,75,125,75,225,275 mm位置处复合非饱和土孔隙水压力随时间的变化情况。随着砂土厚度增大,相同位置处复合非饱和土热端的孔隙水压力越小,继而含水率越小。当孔隙率为0.5的砂土厚度越大,砂土对复合非饱和土中盐分迁移和水分迁移阻碍能力就越大。
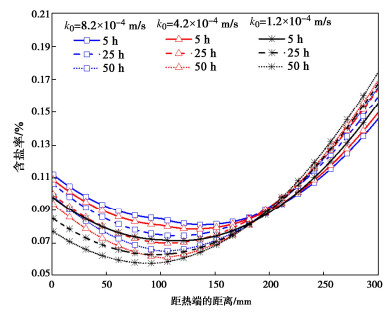
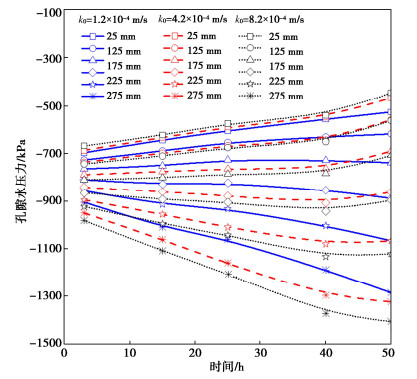
为了分析砂土渗透系数对复合非饱和土中水-热-盐耦合行为的影响,当砂土与粉质黏土的孔隙率以及复合非饱和土体的边界和初始条件保持不变。图 6绘出了砂土厚度为100 mm,复合非饱和土厚度为300 mm,砂土的渗透系数分别为1.2×10-4,4.2×10-4,8.2×10-4 m/s条件下,复合非饱和土体中盐分的变化情况。由图中曲线可以看出:随着砂土渗透系数的增大,复合非饱和土热端处溶液中的盐分浓度是增加。图 7给出了距低温端25,75,125,175,225,275 mm位置处孔隙水压力随时间的变化情况,随着砂土渗透系数增大,相同位置处复合非饱和土热端处的孔隙水压力越小,继而含水率越小。
4. 结论
文章建立了完善的双层非饱和多孔介质中水-热-盐耦合运移的数学模型,并进行相应的参数分析和试验研究。
(1)复合非饱和土中,盐分在温度梯度的作用下逐渐向热端聚集,水分在温度梯度的作用下逐渐向冷端聚集。
(2)随着砂土厚度的增大,复合非饱和土低温端聚集的水分是逐渐增加的,高温端的水分是逐渐减少的。高温端砂土中聚集的盐分会随着砂土厚度的增大而逐渐降低,低温端粉质黏土中的盐分随着砂土厚度的增大而增加。
(3)随着砂土渗透系数的增大,复合非饱和土低温端的水分降低。高温端砂土中聚集的盐分会随着砂土渗透系数的增大而逐渐增加,低温端粉质黏土中的盐分随着砂土渗透系数的增大而减小。
-
表 1 多孔介质中各物理成分的热力学参数
Table 1 Thermodynamic parameters of physical components in porous media
参数 数值 参数 数值 /(J·kg-1·K-1) 1000 /(J·kg-1) 2413000 /(J·kg-1·K-1) 4180 /(m·s-1) 2.89×10-6 /(J·kg-1·K-1) 1900 g/(m·s-2) 9.8 /(J·kg-1·K-1) 3750 /(kg-1·m-3) 1000 /(W·m-1·K-1) 0.024 /(kg-1·mol-1) 0.0288 /(W·m-1·K-1) 2.93 /(kg-1·mol-1) 0.018016 /(W·m-1·K-1) 0.56 /(J·mol-1·K-1) 8.3144 表 2 粉质黏土VG模型参数
Table 2 VG model parameters of silty clay
参数 数值 参数 数值 0.3 1.698 0.15 v 1.4 0.85 1.2 0.411 /kPa 68 表 3 砂土的VG模型参数
Table 3 VG model parameters of sand soil
参数 数值 参数 数值 n 0.5 2.45 0.07 v 2 0.93 1.4 0.59 /kPa 32 -
[1] RESHETIN O L, ORLOV S Y. Theory of heat and moisture transfer in a capillary-porous body[J]. Technical Physics, 1998, 43(2): 263–264. doi: 10.1134/1.1258982
[2] JIA Yong ying, WANG Zhi guo. The study of coupled transfer of heat, moisture and air in reservoir porous media[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012, 271/272: 1195–1200. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.271-272.1195
[3] 任荣. 非等温条件下土壤水热耦合迁移数值模拟研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2018. REN Rong. Numerical Simulation of Coupled Soil Water and Heat Transfer under Non-Isothermal Conditions[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese)
[4] DEB S K, SHUKLA M K, SHARMA P, et al. Coupled liquid water, water vapor, and heat transport simulations in an unsaturated zone of a sandy loam field[J]. Soil Science, 2011, 176(8): 387–398. doi: 10.1097/SS.0b013e318221f132
[5] 安然. 地下水流与气流、热流的典型耦合问题及解耦条件研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. AN Ran. Research on Typical Coupling Problems and the Decoupling Conditions for Groundwater Flow Linked with Air Flow and Thermal Flow[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2015. (in Chinese)
[6] 姜建梅. 基于滨海平原区浅层地下水对土壤水汽热耦合运移规律的影响研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2015. JIANG Jian-mei. The Effect of Shallow Groundwater on Coupled Soil Water Vapor and Heat Transport in Coastal Plain[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2015. (in Chinese)
[7] JAHANGIR M H, SADRNEJAD S A. A new coupled heat, moisture and air transfer model in unsaturated soil[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2012, 26(11): 3661–3672. doi: 10.1007/s12206-012-0839-z
[8] HE Z Y, ZHANG S, TENG J D, et al. A coupled model for liquid water-vapor-heat migration in freezing soils[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 148: 22–28. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.01.003
[9] CLEALL P J, SINGH R M, THOMAS H R. Vapour transfer in unsaturated compacted bentonite[J]. Géotechnique, 2013, 63(11): 957–964. doi: 10.1680/geot.12.P.147
[10] HERNÁNDEZ-LÓPEZ M F, GIRONÁS J, BRAUD I, et al. Assessment of evaporation and water fluxes in a column of dry saline soil subject to different water table levels[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2014, 28(10): 3655–3669. doi: 10.1002/hyp.9912
[11] CHEN Y P, SHI M H, LI X C. Experimental investigation on heat, moisture and salt transfer in soil[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2006, 33(9): 1122–1129. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2006.06.013
[12] 周凤玺, 高国耀. 非饱和土中热-湿-盐耦合作用的稳态分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(6): 2050–2058. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201906004.htm ZHOU Feng-xi, GAO Guo-yao. Steady-state analysis of the heat-moisture-salt coupling for unsaturated soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(6): 2050–2058. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201906004.htm
[13] 周凤玺, 高国耀. 非饱和土中热湿盐多场耦合过程分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(5): 813–820. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201905004.htm ZHOU Feng-xi, GAO Guo-yao. Multi-field coupling process of heat- moisture-salt in unsaturated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(5): 813–820. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201905004.htm
[14] PHILIP J R, DE VRIES D A. Moisture movement in porous materials under temperature gradients[J]. Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 1957, 38(2): 222. doi: 10.1029/TR038i002p00222
[15] WANG W Q, RUTQVIST J, GÖRKE U J, et al. Non-isothermal flow in low permeable porous media: a comparison of Richards' and two-phase flow approaches[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 62(6): 1197–1207. doi: 10.1007/s12665-010-0608-1
[16] NASSAR I, HORTON R. Heat, water, and solution transfer in unsaturated porous media: I: theory development and transport coefficient evaluation[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 1997, 27: 17–38. doi: 10.1023/A:1006583918576
[17] 肖泽岸, 赖远明, 尤哲敏. 单向冻结过程中NaCl盐渍土水盐运移及变形机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(11): 1992–2001. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201711006 XIAO Ze-an, LAI Yuan-ming, YOU Zhe-min. Water and salt migration and deformation mechanism of sodium chloridesoil during unidirectional freezing process[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(11): 1992–2001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201711006
[18] 陈世平, 李毅, 高金芳. 覆膜开孔入渗-蒸发条件下夹砂层土壤水、盐、热变化规律[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2011(11): 47-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNSD201111014.htm CHEN Shi-ping, LI Yi, GAO Jin-fang. The movement of soil water, solute and heat for saline-alkali soil with sand layers under infiltration and plastic film hole evaporation[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2011(11): 47–51. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNSD201111014.htm



 下载:
下载: