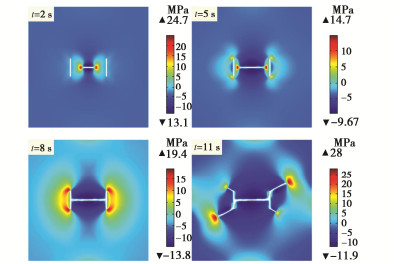
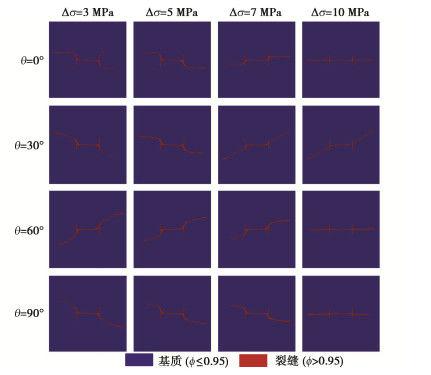
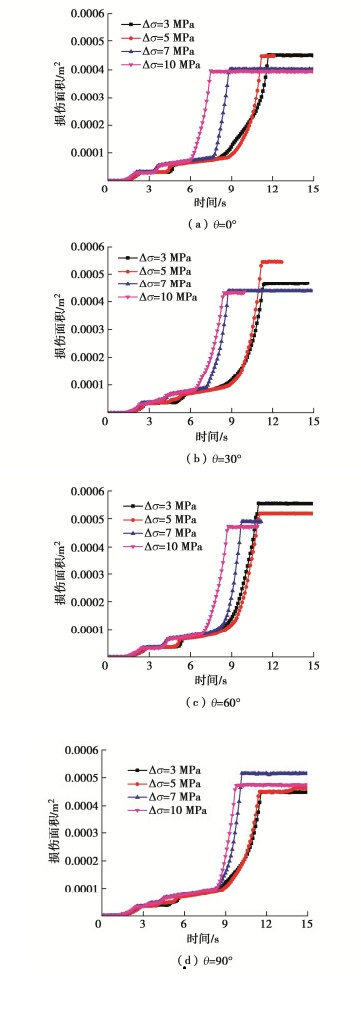
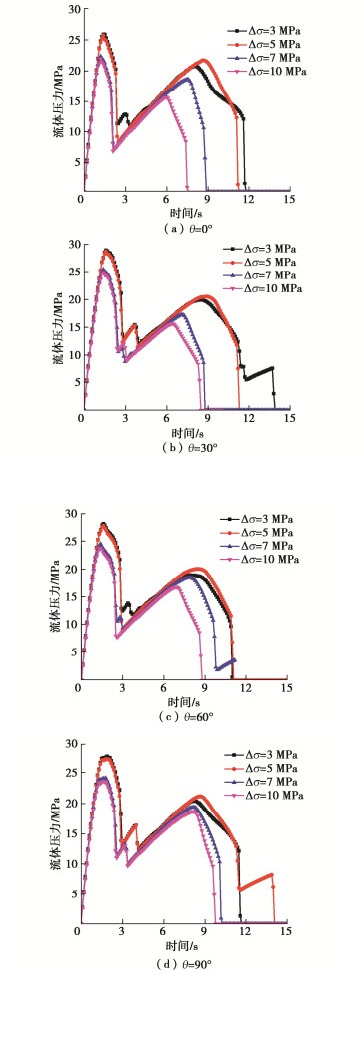
Propagation of hydraulic fractures in bedded shale based on phase-field method
-
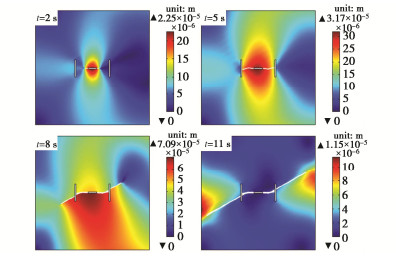
摘要: 准确预测层理页岩水力裂缝扩展路径对于页岩压裂方案优化与压裂效果评价至关重要。基于多孔弹性理论和能量最小化原理建立水力耦合的相场模型,采用交错策略的分离式耦合方法进行求解。通过压裂试验数据对比验证模型的可靠性,同时基于页岩三维水力压裂模拟分析,验证该方法对于模拟不同地应力条件下的水力裂纹扩展问题的适用性。基于该模型,利用插值函数表征页岩层理与基质的力学和渗流参数,研究不同层理角度与地应力差工况下,水力裂缝、天然裂隙以及层理面三者之间的交互作用。研究表明:页岩的层理面改变了水力裂缝预期的扩展路径,该作用效果取决于层理角度。随着地应力差的增大,水力裂缝的扩展路径以及与天然裂隙、层理面交互模式逐渐由地应力差所控制。相场法模拟多场耦合环境下的复杂裂纹扩展与交互等现象相对于其它数值方法具有显著优势。Abstract: Accurate prediction of the propagation path of hydraulic fractures in shale plays an important role in optimizing fracturing schemes and evaluating fracturing effects. Based on the theory of poroelasticity and the energy minimization principle, a hydro-mechanical coupling phase-field model is established. The segregated coupling method based on the staggered scheme is adopted to solve it numerically. The reliability of the model is verified by the existing experimental results. The simulation analysis of 3D hydraulic fracturing confirms the feasibility of the proposed method in capturing the propagation path of hydraulic fractures under different in-situ stress configurations. Based on the model, the mechanical and seepage parameters of bedding planes and matrix are characterized by the interpolation function. The interactions among hydraulic fractures, natural fractures and bedding planes are investigated under different bedding angles and in-situ stress configurations. The results show that the bedding planes of shale alter the expected propagation path of hydraulic fractures, which depends on the bedding angle. With the increase of in-situ stress difference, the propagation path of hydraulic fractures and the interaction mode are gradually controlled by the in-situ stress difference. Compared with other numerical methods, the phase-field method has a significant advantage in simulating complex crack propagation and interaction in coupled multiphysics environment.
-
Keywords:
- phase-field method /
- bedded shale /
- hydraulic fracture /
- natural fracture /
- in-situ stress
-
0. 引言
21世纪以来,随着中国地下空间的开发利用,地铁工程中不断涌现出大跨度、浅埋地下车站,根据以往的震害调查,在地震中这种类型的地下结构比较容易产生破坏。与地面交通工程相比,地下车站造价高昂且破坏后修复困难,同时中国地处环太平洋地震带上,地震频发,因此,越来越多的目光聚焦于地下公共设施的抗震安全问题[1]。
物理模型试验是研究地下结构抗震问题的有效手段[2],常见的地下结构抗震试验方法主要分为两大类:动力试验和静力试验。动力试验包括普通振动台试验和离心机振动台试验[3-4],而静力试验包括地下结构整体静力试验和地下结构局部构件静力试验。动力试验可以主动控制输入的地震动,能够考虑地震动特性对试验的影响,但受振动台面和模型箱尺寸限制,地下结构模型通常较小,难以满足复杂的相似关系,而且动力试验资源消耗大,数据采集条件要求高(动态传感器必须具有高稳定性和采样频率,往往这类精密仪器在振动过程中又极易损坏)。静力试验可按照特定的水平加载模式,荷载逐级递增,实现破坏性试验,可分析试验体在全试验过程中的力学特性和破坏模式,此外,静力试验相比动力试验对传感器的要求低,普通传感器可以满足试验测试要求。
Liu等[5]采用低周循环加载试验对比了预制拼装和现浇两种工艺对地下车站梁板柱节点抗震性能的影响;孔令俊[6]分析了5组大型箱涵结构在往复荷载下的塑性发展顺序、滞回曲线和节点损伤情况;禹海涛等[7]设计了几何比尺为1∶10的沉管隧道管节接头拟静力试验,研究了隧道接头和管节本体相对刚度比随着接头轴向压力变化的规律;程新俊等[8]使用橡胶垫对沉管隧道最薄弱的接头位置进行填充,采用拟静力试验研究了剪力键的荷载–位移滞回曲线和抗剪承载力;陈之毅等[9]对上海某多层地铁车站模型开展了单向Pushover静力推覆试验,分析了地下结构破坏模式以及3个变形阶段分别对应的层间位移角;魏奇科等[10]针对叠合装配、整体现浇两种地下综合管廊结构的边节点和中节点抗震性能展开了10组静力试验,给出了节点配置箍筋间距和纵筋锚固长度的建议。上述静力试验研究均以地下结构局部或整体为试验对象,忽略了土层条件的影响。
研究表明周边土层变形是控制地下结构地震响应的关键因素[11],土层变形作为控制条件下土–地下结构整体模型响应、破坏模式及土–结构相互作用关系,亟待开展相关试验研究。土–地下结构系统在垂直向上传播的横波作用下,反应以一阶振型为主,且结构侧墙产生最大侧向变形时呈现为规律的倒三角形变形[12],因此可以借鉴地面结构推覆分析中常用的倒三角形分布模式进行加载。综上所述,本文以可用于土–地下结构整体模型的岩土综合试验模型箱为试验平台,采用控制土层位移的方式施加水平单向推覆作用,研究了不同加载水平下整体模型的变形模式,详细阐述了推覆试验全过程中土和地下结构之间的相互作用机制。
1. 试验设计
1.1 试验设备
要开展土–地下结构整体模型试验,须有配套模型箱,由于对整体式推覆试验的研究相对滞后,现有模型箱多是针对动力试验而设计的,鲜有静力试验箱相关介绍。仇文革等[13]在国内率先设计了一种动静耦合剪切模型箱,并通过振动台试验和静力试验对比探索了土–地下结构整体模型试验的可靠性,但是该模型箱左右转动板的变形受前后板约束。
本次试验采用课题组自行研制的大型静力推覆模型箱[14],该模型箱由自平衡式反力框架和试验舱两部分构成,试验舱内左右侧分别加装了两块可绕底部转动的滑板,其中一块滑板与悬挂在反力框架上的两个作动器通过滑轨连接,加载时作动器等比例施加水平位移,从而让该滑板沿深度按倒三角形位移模式转动,另一块滑板通过弹簧与试验舱端板连接,并设置了限制底部位移的凸阻块。试验舱内部净尺寸为3 m×2 m×2 m,滑板尺寸为0.15 m×2 m×2 m,装上两块滑板后实际净尺寸为2 m×2 m×2 m,前后安装了钢化夹胶玻璃能减小摩擦力且便于观察,同时在试验舱底部设置了可用透水石覆盖的排水孔,模型箱如图 1所示。
1.2 试验材料和模型制作
本次试验以1995年日本阪神地震中,破坏较为轻微的大开车站单层双跨运营隧道断面作为原型结构[15],由于试验主要考虑土层–结构之间的相互影响,故将原型横断面中柱取消简化为一个中空矩形,试验模型如图 2所示。
车站模型采用立方体抗压强度为11.52 MPa,弹性模量为8.75 GPa的微粒混凝土制作[16],微粒混凝土配比为m水泥∶m细砂∶m粗砂∶m水=1∶2.68∶4.56∶0.82,结构内部布置双层镀锌铁丝网,配筋率与原型一致,均为1.1%。模型结构几何缩尺为1/10,横截面宽为0.9 m,高为0.636 m,模型壁厚为0.04 m,沿纵向取1 m。试验以结构几何尺寸、弹性模量和密度相似比作为基本量,进一步推导出其余参量的相似比,如表 1所示。
表 1 主要参量相似比Table 1. Similarity ratios of key parameters类型 物理量 量纲 数值 几何
特性长度L L 1/10 面积S L2 1/100 惯性矩I L4 1/10000 材料
特性密度ρ ρ 1 弹性模量E E 1/4 质量m ρL3 1/1000 抗弯刚度EI EL4 1/40000 反应
特性应变ε 1 1 应力σ E 1/4 力F EL2 1/400 弯矩M EL3 1/4000 试验用土采用常见中粗砂,颗粒级配曲线如图 3所示,参数为:平均粒径D50为0.505 mm,不均匀系数Cu为2.687,土粒相对质量密度Gs为2.627,最大干密度ρdmax为1.966 g/cm3,最小干密度ρdmin为1.384 g/cm3,含水率w为6.2%,相对密实度Dr为0.464,内摩擦角为34.931°。填土过程中分层夯实,通过环刀取样控制土体密度为1.70 g/cm3从而保证土体均匀性,受试验条件所限,不考虑土体相似比。
1.3 传感器布置
为监测试验中砂土场地、地下结构的响应规律及其相互作用,本次试验所采用的传感器包含应变片、阵列式位移计SAA(shape acceleration array)、顶杆位移计和土压力计,传感器布置如图 4所示。图 4中以地下结构中间作为A—A主观测断面,结构旁边250 mm处的横断面作为B—B辅助观测面。
TP为粘贴在结构左右侧壁的水平土压力计,共8个;T为土体内水平土压力计,主观测面8个,辅助观测面内对应结构侧壁位置4个;阵列式位移计SAA共3条,紧贴地下结构左右侧壁分别布置了一条,辅助观测面内布置了一条;IY与OY分别对应着地下结构同一测点内外侧对称布置的应变片,10个测点绕结构周身顺时针布置;D为顶杆位移计,共5个,其中D1至D3监测挡板的转动,D4和D5监测结构侧壁顶底相对位移。
1.4 试验步骤及加载工况
(1)试验开始前通过控制台调整作动器,使滑板处于竖直状态。
(2)将SAA与钢筋绑扎在一起,使其笔直地竖立在预留位置,SAA底端与固定在模型箱底部的磁性表座绑扎在一起。
(3)采用分层夯实、控制密度的方法填土,砂土填筑的同时,在预定的位置埋入各传感器及结构,隧道端头覆盖两块1 mm厚PVC塑料布,并用环氧树脂进行密封,土体总高度1.8 m。
(4)填土完毕后拔出与SAA绑在一起的钢筋,并连接数据采集系统。
(5)将两个水平作动器运动模式设置为等比例伸长,令推覆板按倒三角形位移模式转动。
(6)推覆板转动过程中通过距离板底1.8 m高的顶杆位移计D1实时监测,从而保证每次加载能够达到预先设定的转动角度。
(7)每级荷载施加完毕后让作动器稳定一段时间,待传感器示数恒定后再进一步加载。转动至预定的最大角度后加载结束,挖除砂土,拆除试样。
董正方等[17]通过统计分析给出了矩形地下结构在大震下层间位移角限值为1/70,为了实现破坏,将推覆板转角限值设为1/60,加载工况见表 2。韩润波等[18]通过数值模拟验证了静力推覆模型的土体宽度取为结构外宽的2~3倍较为合理,而本试验土体宽度与结构宽度比值为2.22,基本符合要求。
表 2 加载工况Table 2. Loading conditions of testsΔD1/mm 推覆板转角 ΔD1/mm 推覆板转角 0.9 1/2000 12.0 1/150 1.8 1/1000 15.0 1/120 3.6 1/500 18.0 1/100 5.0 1/360 20.0 1/90 6.0 1/300 25.0 1/72 9.0 1/200 30.0 1/60 10.0 1/180 2. 试验结论及分析
2.1 被动端滑板位移
顶杆位移计D3实时监测了被动端滑板与土表齐平处的水平位移,如图 5所示,对比推覆端和被动端滑板在相同高度的水平位移可知,由于两块滑板运动彼此独立,推覆端ΔD1达到30 mm时,被动端ΔD3仅为0.632 mm,被动端滑板位移很小。
2.2 结构应变反应及破坏模式
本次试验沿着结构周身顺时针布置了10个应变测点,为消除加载前初始变形的影响,对试验加载阶段的所有数据进行了清零处理。为了方便比较,记同一测点位置内外侧应变片的应变差为εM,以定性表征结构的弯曲变形,结构外侧受拉时εM为正,受压时为负。
图 6给出了推覆过程中部分测点内外侧应变差的变化曲线,从图 6中可以看出:ΔD1为15 mm时(即推覆板转角为1/120),推覆端各测点处弯曲应变同时出现峰值拐点,此时推覆端侧壁中部、上部和顶部的附加弯曲应变最大值分别为-439.7με,-293.7με,-357.9με,其中测点#4的外侧应变片在试验后期发生破坏,导致了数值突然增大;ΔD1为12 mm时(即推覆板转角为1/150),被动端侧壁下部和底部的附加弯曲应变最大值为-284.8 με,-121.9 με,其中测点#7附加弯曲应变在试验过程中持续增大,最大为-455.1 με。
可见在推覆过程中结构侧壁中部的应变测点#2、#7会产生较大的弯曲变形,是结构破坏最可能产生的位置;同时峰值拐点的出现则表明结构模型产生了破坏,在结构破坏后多数测点的弯曲应变逐渐减小;结构角部测点#3、#4和#8、#9的弯曲应变均为负值,表明监测的这两个角部都是内侧受拉。产生这些现象的原因为:①随着到推覆板距离的增大,土体内水平应力传递存在衰减现象(土体内T4、T5的最大值分别为72.8,38.4 kPa),导致被动板转角远小于主动板,当主动板转角不断增大时,便会对地下结构模型产生水平挤压作用,导致结构侧壁中部产生较大弯曲变形,甚至产生破坏;②由于主动板绕底部转动形成倒三角形水平变形模式,该变形通过土体传递到结构上便形成了剪切变形,因此两个角部内侧受拉。两种变形的耦合作用如图 7所示。
试验结束后挖出模型结构,模型结构宏观破坏现象如图 8所示,结构两侧壁内部出现明显的贯通裂缝,通过卷尺测量发现推覆端裂缝距离模型底板38 cm,由侧壁中部向上偏移了约6 cm;而被动端裂缝起伏较大,最低点距离模型底板仅21 cm,即由侧壁中部向下偏移了约11 cm。分析可知,结构内侧壁贯通裂缝主要是由挤压变形导致的,而剪切变形的加入使得裂缝在两侧壁的位置发生了一定的偏移。
2.3 结构位移反应
长度为1.8 m的SAA上间隔200 mm均匀分布了9个测点监测土体和地下结构位移情况,见图 4(c),由低至高分别命名为L1~L9:其中L3和L6与结构的底板、顶板平齐,L3~L6四个测点经过结构埋深位置,与图 4(d)中土压力计TP1~TP4高度相对应。
结构两侧壁在试验过程中的水平位移如图 9所示,从图 9中可以看到地下结构两侧壁水平位移随推覆板转角的增大而增大,而且在同一时刻高度越大水平位移越大,总体呈现出倒三角形位移模式,说明剪切变形主导着结构整体的变形模式。但是当ΔD1为20 mm时,SAA1上L5测点处水平位移赶上了L6,之后更是进一步反超;ΔD1达到18 mm之后,SAA2上L4测点处水平位移比L3更小。由于结构侧壁破坏主要是挤压变形导致的,而SAA1上L5测点处和SAA2上的L4测点处正好是裂缝产生的地方,这两处在结构开裂后迅速向结构内部凹陷,才造成了上述特征。
2.4 结构侧壁土压力反应
图 10为试验过程中地下结构推覆端和被动端侧壁外表面的水平土压力增量,从整体趋势上来看由于推覆板的转动,模型箱内土体被不断压实,模型结构四周土压力逐渐增加。
加载初期ΔD1为9 mm时,TP1和TP8的值分别为23.9,48.0 kPa,TP3和TP6的值分别为39.9,29.2 kPa,可见加载初期结构中部以上推覆端侧壁产生的土压力较大,而中部以下则是被动端侧壁产生的土压力较大,因此结构产生了剪切变形;加载中期ΔD1为15 mm时推覆端侧壁中上部TP3达到最大值65.5 kPa,ΔD1为12 mm时被动端侧壁中下部TP7达到最大值34.4 kPa,随后结构破坏导致这两个部位丧失承载力;加载后期ΔD1达到最大30 mm时,推覆端和被动端侧壁顶部土压力最大分别为216.1,213.4 kPa,底部最大值分别为104.4,109.9 kPa,两侧应力水平相当,挤压效应明显。从受力角度阐明了图 7结构产生“剪切+挤压”效果的原因。
2.5 土–结构相互作用分析
图 11给出了ΔD1分别为15 mm(临界破坏点)、30 mm时SAA1和SAA3沿深度各测点的水平位移,其中SAA1紧贴结构侧壁,与之平行埋置的SAA3偏离结构250 mm,视其所在的B—B剖面为不受结构影响的自由场。从图 11中可见,当ΔD1为15 mm时SAA1测得结构侧壁顶底水平相对位移为1.51 mm,而辅助观测面内SAA3测得土体在对应高度间的水平相对位移为3.42 mm,当ΔD1为30 mm时两者分别为6.34,8.44 mm,导致两者变形不一致的原因为结构的整体刚度比相同截面尺寸的等代土体大,结构抵抗变形的能力更强。
参考相互作用系数法[19-20],计算模型如图 12所示。结构的层间位移ΔSTR可以用自由场土体相应的层间位移ΔS乘以土–结构相互作用系数β来表示:
ΔSTR=βΔS, (1) 式中,β取值的大小与土–结构相对刚度有关,当结构刚度比土体大时β取值小于1,反之则大于1。
本试验两个工况下β可分别取为0.44和0.75,β值增大是因为结构产生破坏后整体刚度退化。同时可以发现SAA3上各点变化较为均匀平缓,而SAA1测得结构顶板上方土体水平位移会突然增大,原因在于结构顶板和土间的刚度突变,变形不协调可能导致该分界面上产生了水平滑移。
对于浅埋结构,相互作用系数法建议在结构侧壁施加倒三角形荷载进行计算。图 13给出了辅助观测面内对应结构侧壁位置的土体水平应力,从图中可知随着推覆板转角增大土体水平应力整体上涨,且上涨幅度随高度的增加而增加,水平应力沿深度呈倒三角形分布。为简化分析,以顶底板处水平荷载的差值来表征倒三角形荷载P,即结构所受倒三角形荷载的峰值PT为TP4与TP1的差值(TP4与TP1见图 9);相同截面等代土体所受倒三角形荷载峰值PS为T12与T9的差值。
图 14给出了PS与PT的比值关系。从图 14中可知:ΔD1为5 mm时比值从0.24下降到0.10,此时土体塑性发展导致刚度下降;ΔD1处于5 mm至15 mm时,土体完全进入塑性,比值在0.10附近波动;ΔD1超过15 mm后,结构破坏引起刚度退化,比值持续上升至0.32,超过初始比值。
由此可见:土–地下结构整体模型主要经历了土体变形引起的土体塑性发展阶段,土体进入塑性后以结构受荷为主的稳定阶段,和结构开裂破坏导致的结构刚度退化阶段,土–结构状态变化对整体模型进入各受力阶段的时效性存在重要影响。
2.6 水平基床系数
反应位移法是中国地下结构抗震设计规范普遍推荐的简化设计方法,该方法通过在地下结构周边布置集中地基弹簧以反映周边土层和结构的相互作用。弹簧刚度等于基床系数乘以作用面积,目前基床系数的试验方法包括:K30荷载板试验、三轴试验和固结试验,但是3种方法都没有考虑实际地下结构的存在,且忽略了基床系数随加载水平的变化。
本次试验采用SAA1和SAA3分别监测了结构侧壁和辅助观测面内对应位置处土体的水平位移δ,在位移测点处布置了相应的土压力计以获取水平应力q,从而计算结构侧壁和土体的水平基床系数K(K= q/δ)。辅助观测面内土体水平基床系数如图 15所示,T12~T9对应埋深为600~1200 mm。从图 15中可以发现:随着推覆水平增加,各测点基床系数值逐渐减小,且随埋深的减小而减小。整体来看土体水平基床系数值在3.8~44.6 MN/m3间变化,《城市轨道交通岩土工程勘察规范》[21]规定了土体水平基床系数经验值的变化范围(3~60 MN/m3),表明试验测得基床系数值在规范规定的范围内,具有一定的参考价值。
图 16给出了地下结构推覆端侧壁上各测点处水平基床系数值,TP4~TP1对应埋深为600~1200 mm。从图 16可以发现:在结构破坏之前,随着推覆水平增加,各测点水平基床系数逐渐减小,除了埋深1200 mm的侧壁底部测点TP1外(角部应力集中导致),埋深越浅处基床系数值越大;结构破坏之后侧壁中间偏上位置TP3处作为开裂点,承载力丧失导致基床系数值迅速下降,且破坏后的应力重分布导致侧壁底部TP1处水平基床系数发生反向增长。整体来看结构侧壁水平基床系数值在0.06~102.0 MN/m3变化,最小值是侧壁开裂破坏、丧失承载力引起的,而最大值是由于土体和结构挤压,且侧壁上角部应力集中造成的。
图 17给出了侧壁破坏前,埋深800,1000 mm处土体水平基床系数KS和结构侧壁水平基床系数KT之比(侧壁中间的两个测点)。从图 17可以发现,KS与KT的比值在试验开始时约为0.5,随着加载水平增加,其比值骤降至0.28左右,且比值基本在0.25~0.28波动,直至结构破坏。
由此可见:针对无结构的土体所获得的基床系数与结构侧壁上实测基床系数之间存在较大差异,差异的来源包括结构的破坏失效和结构角部可能存在的应力集中;而对于非角点位置,在稳定阶段土体和结构水平基床系数之间存在一定的比例关系,本次试验中该比值在0.25~0.28波动。
3. 结论
为探究水平推覆作用下土–地下结构的反应规律,开展了大型推覆试验,分别从土层、结构及土结相互作用3个层面开展了分析讨论,得到以下4点结论。
(1)相较于动力模型试验,静力模型试验可较好地反映土层和结构的变形,便于揭示最不利荷载条件下土–地下结构整体模型的破坏模式。
(2)在土–地下结构整体模型试验中,通过水平作动器控制推覆板转动给土体边界施加倒三角形变形,由于土层的非均匀变形(主因)和边界效应(模型箱左右滑板独立运动,次因),地下结构受到剪切变形和挤压变形的耦合作用。
(3)通过设置辅助观测面对土–结构相互作用展开研究,针对变形和受力两方面进行对比发现:结构推覆端侧壁顶底水平相对变形小于相同截面尺寸的等代土体,侧壁破坏刚度退化后结构与土体变形比值由0.44上升至0.75;而土体和结构所受倒三角形水平荷载的比值会经历土体塑性发展引起的下降阶段、稳定阶段和结构破坏后的上升阶段。说明土–结构相互作用并不恒定,会随着土、结构状态变化而改变,具有显著时效性。
(4)土体水平基床系数随推覆水平增加而减小,且埋深越浅基床系数值越小,试验值在3.8~44.6 MN/m3变化,与规范规定的经验值相符。而结构侧壁水平基床系数受到结构破坏、角部应力集中的影响,其波动范围较大。稳定阶段土体和结构非角点位置处水平基床系数具有较为稳定的比例关系,试验测得比值在0.25~0.28波动。
-
表 1 相关模拟参数
Table 1 Parameters used in simulations
参数 E ν αBm αBf Gc l0 值 30 0.3 0.1 1 200 2 单位 GPa — — — N/m mm 参数 c1 c2 ϕsm ϕsf cmf Km 值 0.4 1 0.04 1 10-8 10-19 单位 — — — 1/Pa m2 参数 ρm/f μm/f Kf δ B 值 1000 0.001 10-8 10-9 1000 单位 kg/m3 Pa·s m2 — — 表 2 数值模拟方案
Table 2 Schemes of numerical simulation
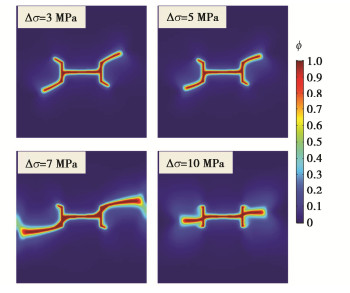
模拟方案 σmax/MPa σmin/MPa Δσ/MPa 1 8 5 3 2 10 5 5 3 10 3 7 4 13 3 10 -
[1] 赵凯凯, 张镇, 李文洲, 等. 基于XSite的钻孔起裂水力裂缝三维扩展研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(8): 1483–1491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202108015.htm ZHAO Kai-kai, ZHANG Zhen, LI Wen-zhou, et al. Three-dimensional simulation of hydraulic fracture from a borehole using XSite[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(8): 1483–1491. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202108015.htm
[2] 刘武, 过申磊, 陆倩, 等. 基于TOUGHREACT的岩石水力损伤耦合数值模型研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(7): 1306–1314, 1380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202107021.htm LIU Wu, GUO Shen-lei, LU Qian, et al. Numerical model for hydro-mechanical- damage coupling of rocks based on TOUGHREACT[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(7): 1306–1314, 1380. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202107021.htm
[3] FRANCFORT G A, MARIGO J J. Revisiting brittle fracture as an energy minimization problem[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1998, 46(8): 1319–1342. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5096(98)00034-9
[4] BOURDIN B, FRANCFORT G A, MARIGO J J. Numerical experiments in revisited brittle fracture[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2000, 48(4): 797–826. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5096(99)00028-9
[5] MIEHE C, WELSCHINGER F, HOFACKER M. Thermodynamically consistent phase-field models of fracture: Variational principles and multi-field FE implementations[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 83(10): 1273–1311. doi: 10.1002/nme.2861
[6] AMBATI M, GERASIMOV T, LORENZIS L. A review on phase-field models of brittle fracture and a new fast hybrid formulation[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2015, 55(2): 383–405. doi: 10.1007/s00466-014-1109-y
[7] AMOR H, MARIGO J J, MAURINI C. Regularized formulation of the variational brittle fracture with unilateral contact: numerical experiments[J]. J Mech Phys Solids, 2009, 57: 1209–1229. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2009.04.011
[8] ZHOU S W, ZHUANG X Y, ZHU H H, et al. Phase field modelling of crack propagation, branching and coalescence in rocks[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2018, 96: 174–192. doi: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2018.04.011
[9] 张豪, 于继东, 裴晓阳, 等. 相场断裂方法发展概况[J]. 高压物理学报, 2019, 33(3): 128–139. ZHANG Hao, YU Ji-dong, PEI Xiao-yang, et al. An overview of phase field approach to fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2019, 33(3): 128–139. (in Chinese)
[10] 吴建营. 固体结构损伤破坏统一相场理论、算法和应用[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(2): 301–329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB202102001.htm WU Jian-ying. On the theoretical and numerical aspects of the unified phase-field theory for damage and failure in solids and structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(2): 301–329. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB202102001.htm
[11] NGUYEN T T, WALDMANN D, BUI T Q. Computational chemo-thermo-mechanical coupling phase-field model for complex fracture induced by early-age shrinkage and hydration heat in cement-based materials[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 348: 1–28. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2019.01.012
[12] ZHUANG X Y, ZHOU S W. An experimental and numerical study on the influence of filling materials on double-crack propagation[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2020, 53(12): 5571–5591. doi: 10.1007/s00603-020-02220-1
[13] LIU J, XUE Y, CHEN W, et al. Variational phase-field model based on lower-dimensional interfacial element in FEM framework for investigating fracture behavior in layered rocks[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 255: 107962. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.107962
[14] ZHANG P, YAO W, HU X, et al. 3D micromechanical progressive failure simulation for fiber-reinforced composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 249: 112534. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112534
[15] MIEHE C, MAUTHE S. Phase field modeling of fracture in multi-physics problems: part III crack driving forces in hydro-poro-elasticity and hydraulic fracturing of fluid-saturated porous media[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 304: 619–655. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2015.09.021
[16] SANTILLÁN D, JUANES R, CUETO-FELGUEROSO L. Phase field model of hydraulic fracturing in poroelastic media: fracture propagation, arrest, and branching under fluid injection and extraction[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123(3): 2127–2155. doi: 10.1002/2017JB014740
[17] 易良平, 胡滨, 李小刚, 等. 基于相场法的煤砂互层水力裂缝纵向延伸计算模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(增刊2): 706–716. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2020S2017.htm YI Liang-ping, HU Bin, LI Xiao-gang, et al. Calculation model of hydraulic crack vertical propagation in coal-sand interbedded formation based on the phase field method[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(S2): 706–716. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2020S2017.htm
[18] 张飞. 基于自适应移动网格及相场逼近的水力裂缝延伸模拟[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018. ZHANG Fei. A Study on Adaptive Finite Element Solution of Phase-Field Models for Hydraulic Fracturing[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2018. (in Chinese)
[19] YI L, WAISMAN H, YANG Z, et al. A consistent phase field model for hydraulic fracture propagation in poroelastic media[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 372: 113396. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113396
[20] 班宇鑫, 傅翔, 谢强, 等. 页岩巴西劈裂裂缝形态评价及功率谱特征分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(12): 2307–2315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201912023.htm BAN Yu-xin, FU Xiang, XIE Qiang, et al. Evaluation of fracture morphology of shale in Brazilian tests and analysis of power spectral characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(12): 2307–2315. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201912023.htm
[21] 侯冰, 陈勉, 张保卫, 等. 裂缝性页岩储层多级水力裂缝扩展规律研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(6): 1041–1046. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201506011.htm HOU Bing, CHEN Mian, ZHANG Bao-wei, et al. Propagation of multiple hydraulic fractures in fractured shale reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(6): 1041–1046. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201506011.htm
[22] 侯冰, 武安安, 常智, 等. 页岩油储层多甜点压裂裂缝垂向扩展试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(7): 1322–1330. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202107024.htm HOU Bing, WU An-an, CHANG Zhi, et al. Experimental study on vertical propagation of fractures of multi-sweet of spots shale oil reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(7): 1322–1330. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202107024.htm
[23] MIEHE C, HOFACKER M, WELSCHINGER F. A phase field model for rate-independent crack propagation: Robust algorithmic implementation based on operator splits[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 199(45-48): 2765–2778. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2010.04.011
[24] ZHOU S W, ZHUANG X Y, RABCZUK T. A phase-field modeling approach of fracture propagation in poroelastic media[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 240: 189–203. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.04.008
[25] LEE S, WHEELER M F, WICK T. Pressure and fluid-driven fracture propagation in porous media using an adaptive finite element phase field model[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 305: 111–132. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2016.02.037
[26] BORDEN M J, VERHOOSEL C V, SCOTT M A, et al. A phase-field description of dynamic brittle fracture[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 217~220: 77–95.
[27] JIAO Y Y, ZHANG H Q, ZHANG X L, et al. A two-dimensional coupled hydromechanical discontinuum model for simulating rock hydraulic fracturing[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2015, 39(5): 457–481. doi: 10.1002/nag.2314
[28] LI K C, ZHOU S W. Numerical investigation of multizone hydraulic fracture propagation in porous media: new insights from a phase field method[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 66: 42–59.
[29] ZHANG Q, ZHANG X, JI P. Numerical study of interaction between a hydraulic fracture and a weak plane using the bonded-particle model based on moment tensors[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2019, 105: 79–93.
[30] 侯鹏, 高峰, 杨玉贵, 等. 黑色页岩巴西劈裂破坏的层理效应研究及能量分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(5): 930–937. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201605020.htm HOU Peng, GAO Feng, YANG Yu-gui, et al. Effect of bedding orientation on failure of black shale under Brazilian tests and energy analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(5): 930–937. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201605020.htm
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 许成顺,韩润波,杜修力,许紫刚. 考虑土-结构相互作用的弹簧-地下结构体系静力推覆试验技术及其试验研究. 建筑结构学报. 2023(01): 248-258 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 卢钦武,关振长,林林,吴淑婧,宋德杰. 基于静力推覆试验的山岭隧道衬砌-地层相互作用机制研究. 岩土力学. 2023(08): 2318-2326 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: