Uplift behaviour of shaft foundations in loess
-
摘要: 基于黄土抗拔基础现场试验成果,阐述了黄土平地和斜坡条件下等截面直柱基础和直柱扩底基础抗拔荷载位移特征及其承载机理。结果表明,黄土平地等截面直柱基础和直柱扩底基础抗拔荷载-位移曲线均呈“缓变型”变化规律,L1-L2两点法可较好反映黄土抗拔基础荷载-位移曲线的初始弹性直线段、弹塑性曲线过渡段和直线破坏段3阶段变化特征。等截面直柱基础抗拔承载力由直柱与周围土体间摩擦阻力提供,直柱扩底基础呈扩大端土体压缩挤密发生弹性变形—基础周围土体塑性区形成、发展、贯通—土体整体剪切破坏的渐进过程,抗拔极限承载力由基础自重、滑动面剪切阻力及滑动面范围内土体重量组成,并可分浅基础和深基础2种破坏模式。上拔荷载作用下,黄土斜坡地形等截面直柱基础和直柱扩底基础下坡侧的柱顶及柱侧周围土体位移均大于上坡侧,抗拔土体的破坏滑裂面形态具有不对称性,地表裂缝主要分布在基础下坡侧。基础顶面均产生沿上拔荷载作用方向的微小偏转,且转角随荷载增加而增加。扩底和增加埋深均可提高黄土斜坡基础抗拔承载性能。
-
关键词:
- 黄土 /
- 抗拔 /
- 斜坡 /
- 归一化荷载-位移曲线 /
- 失效准则
Abstract: Based on the field uplift load test results of the shaft foundations in loess, the uplift load-displacement behaviour and mechanism of the straight-sided and belled shaft foundations in flat and sloped loess ground is presented. In general, their load-displacement curves approximately exhibit the same three-region "slow change" characteristics. The L1-L2 method can be successfully used to interpret the uplift resistances and may reflect the sectors of an initial linear, a curvilinear transition, and a final linear region of the load-displacement curves. The uplift resistance of the straight-sided shaft foundation is provided by the friction resistance between the shaft and the surrounding soil. However, the belled shaft foundation presents the gradual process of the soil of the enlarged bottom being compressed and compacted with the subsequent elastic deformation, the formation, development and penetration of the plastic zone of the soil around the bell, and the finally overall shear failure of the soil. The ultimate uplift resistance is composed of the self-weight of the foundation, the shear resistance of the sliding surface and the weight of the soil within the sliding surface. There are two failure modes of shallow and deep foundations for the belled shaft foundations in horizontal loess ground. The vertical displacements of the shaft head and sloping ground surface on the lower slope side is greater than those of the upper one for both straight-sided and belled shaft foundations in sloped loess ground. The failure surface is not symmetric and developed mainly on the lower slope side. The shaft head rotates slightly in the loading direction when the shaft foundation is axially uplift-loaded. The enlarged base and additional embedment can be used to increase the uplift bearing capacity of foundations in sloped loess.-
Keywords:
- loess /
- uplift /
- slope /
- normalized load-displacement curve /
- failure criterion
-
0. 引言
黄土在中国分布广泛,是一类典型特殊土地基[1]。随着中国“一带一路”倡议和西部大开发战略实施,黄土地区工程建设急剧增加,越来越多工程建设面临基础抗拔问题,如输电线路杆塔和通信塔基础抗拔稳定性往往是其设计控制条件,抗拔基础承载性能已成为黄土地区工程建设的热点问题[2]。此外,黄土地区工程建设中,常因路径或场地条件限制,不得不将抗拔基埋置于斜坡地形的坡面。黄土斜坡边界条件使得抗拔基础低坡侧和高坡侧土体厚度不同,上拔荷载作用下,基础周围的上坡侧和下坡侧土体抗力有差异,黄土斜坡抗拔基础承载能力显著降低[3-4]。目前对黄土斜坡抗拔基础承载性能承载特性的研究相对薄弱。
国内外工程实践中,抗拔基础主要分为2大类:截面不随深度变化的直柱等截面基础和底部设计成扩大端的直柱扩底基础。本文基于黄土地区抗拔基础现场试验成果,阐述黄土平地直柱等截面基础和直柱扩底基础荷载-位移曲线特征、基础抗拔极限承载力确定准则、基础抗拔承载机理,并进一步对比分析黄土斜坡基础抗拔承载性能,可供工程设计参考。
1. 黄土平地抗拔基础荷载位移特征
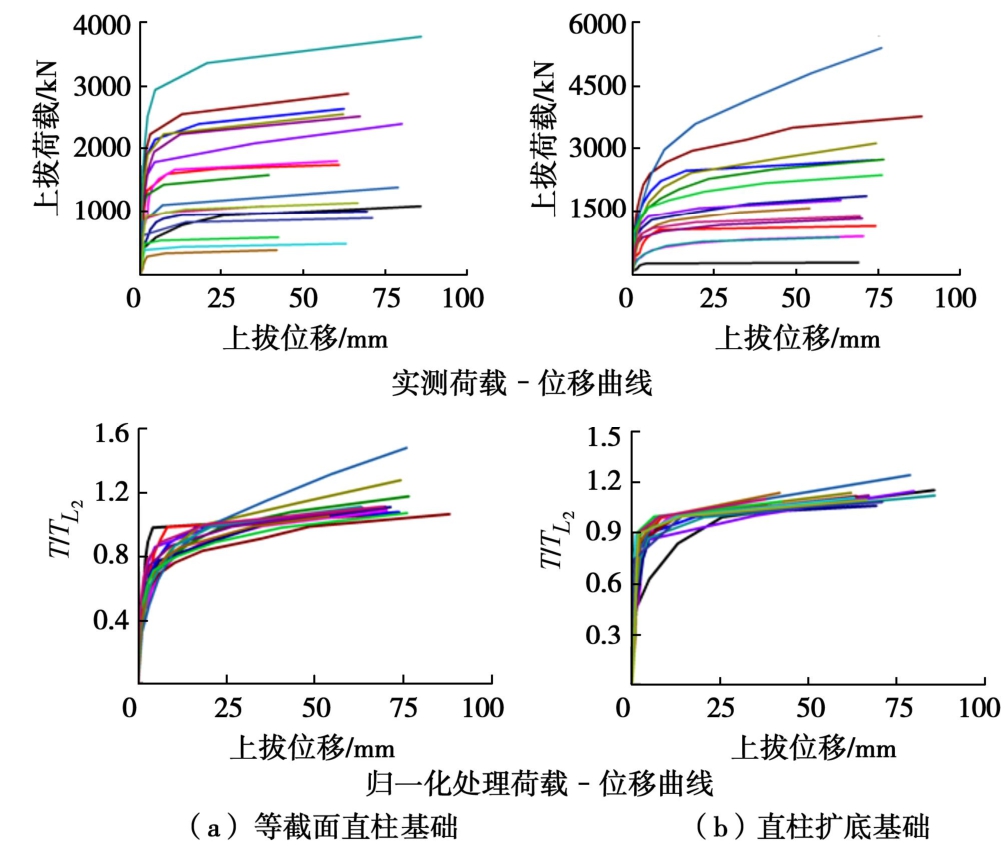
在甘肃天水、定西和榆中3个黄土试验场地开展了18个直柱等截面基础和15个直柱扩底基础抗拔静载荷试验[5]。立柱直径0.9~1.5 m,扩底直径1.2~2.7 m,埋深1.8~10.0 m。所有试验均采用慢速维持荷载法,实测荷载-位移曲线如图1所示。
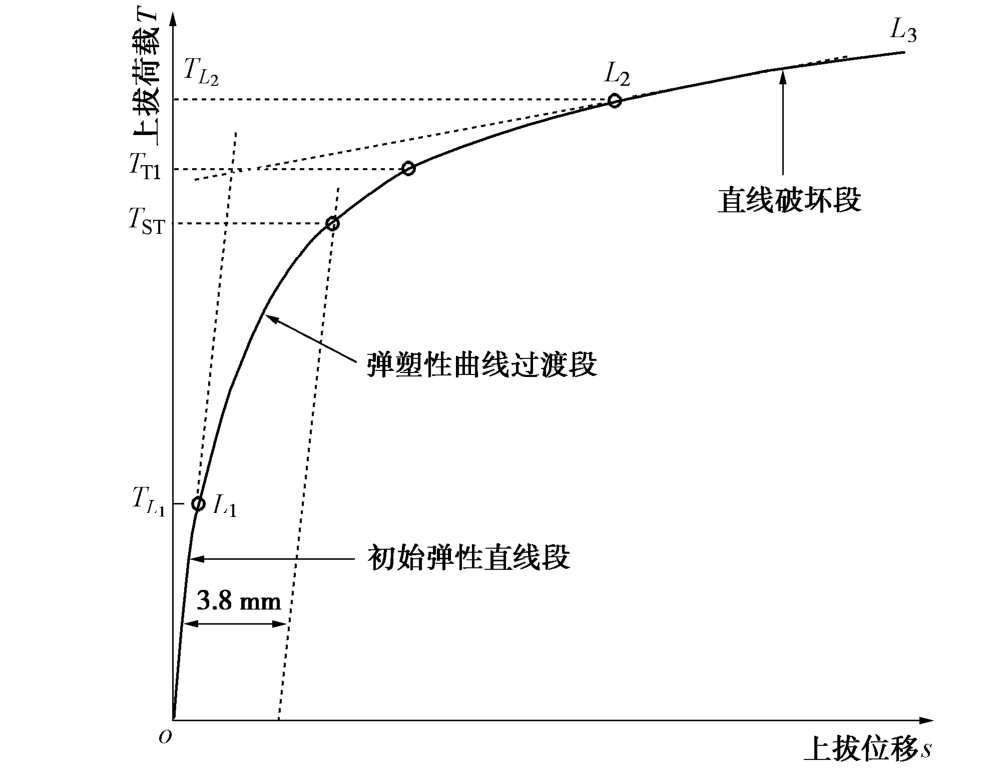
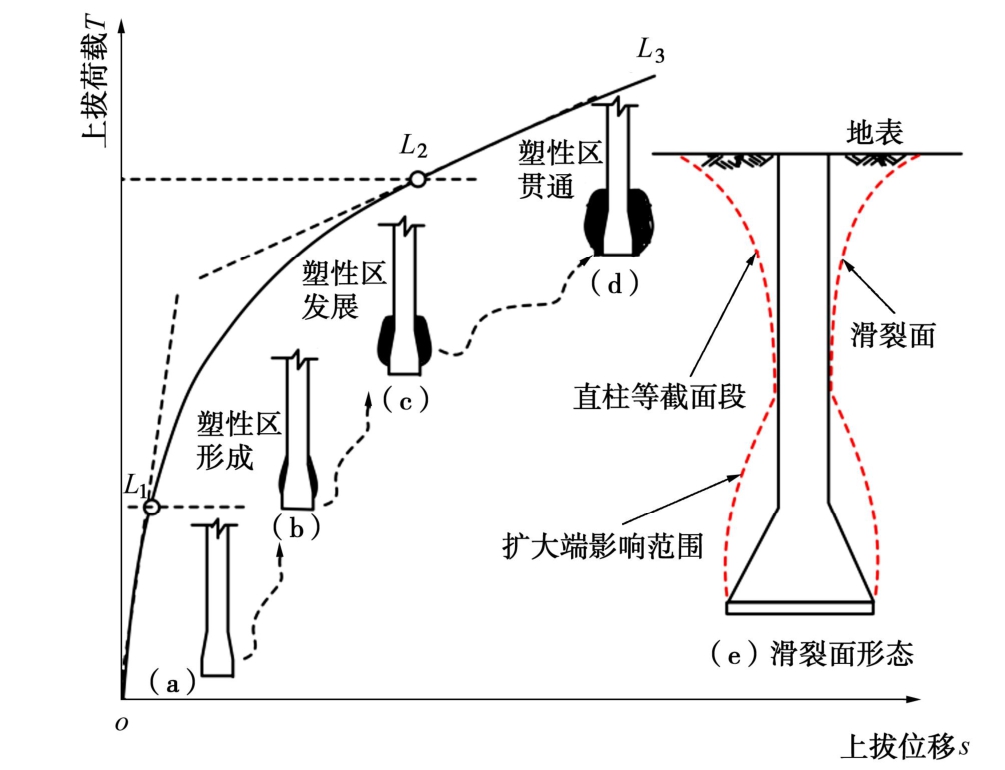
从图1可以看出,等截面直柱基础和直柱扩底基础抗拔荷载-位移曲线均呈图2所示“缓变型”变化规律,可划分为3个特征阶段:初始弹性直线段、弹塑性曲线过渡段和直线破坏段。在初始弹性直线段OL1,荷载-位移曲线呈线性变化,抗拔土体以弹性变形为主。在弹塑性曲线过渡段L1L2,基础上拔位移随荷载增加呈非线性增加,位移变化速率增大。在直线破坏段L2L3,随上拔荷载持续增加,基础变形急剧增大,较小的荷载增量即产生较大的位移增量,直至基础抗拔承载能力丧失而破坏。
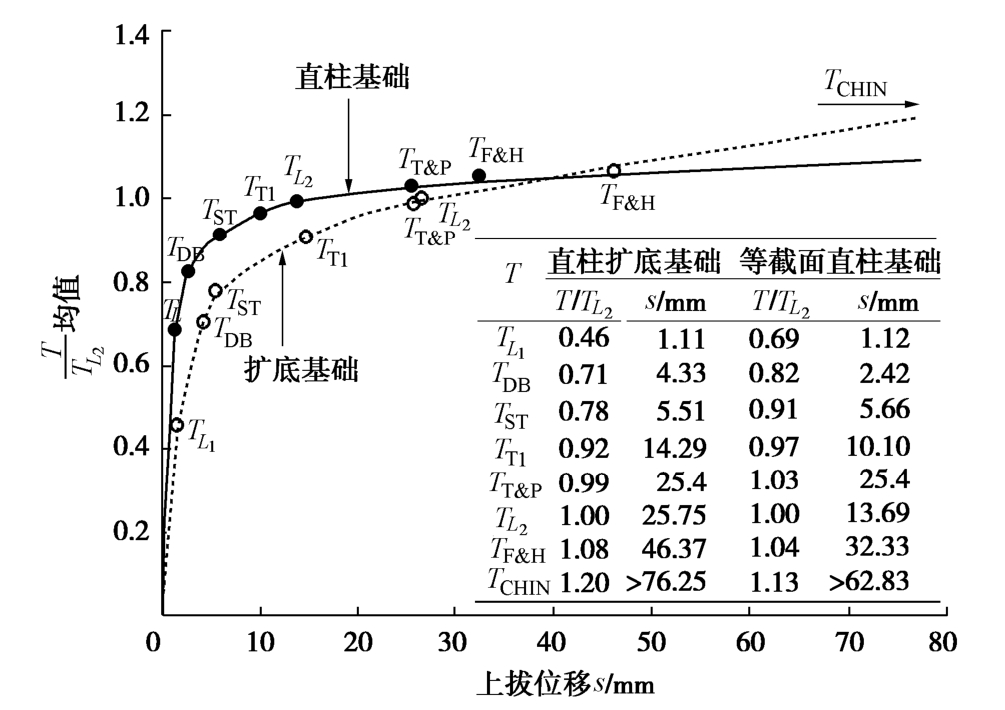
表1给出了针对抗拔基础呈“缓变型”荷载-位移曲线的几种典型承载力确定准则(如图2所示)。为便于比较,以L1-L2两点法确定的极限承载力2LT作为基准,将试验过程中每一级试验荷载T除以2LT,从而对试验荷载进行归一化处理,并以T/2LT为y轴,相应试验荷载对应的位移为x轴,得到直柱等截面基础和直柱扩底基础抗拔归一化荷载-位移曲线对比如图1所示。结果表明,归一化荷载-位移曲线离散性明显小于实测数据[15]。
表 1 几种典型的拔极基础限承载力确定准则Table 1. Definitions of representative uplift interpretation criteria名称 类别 极限承载力定义 Chin双曲线法[6] 数学法 将实测荷载-位移曲线按照直线型方程s/T=ms+c拟合,T为上拔荷载,s为上拔位移,m为直线斜率,c为截距。取直线斜率的倒数倒数1/m为极限承载力,记为TCHIN Terzaghi和Peck法[7] 位移法 取上拔位移25.4 mm所对应荷载为极限承载力,记为TT&P Fuller和Hoy法[8] 位移法 取位移变化速率为0.14 mm/kN所对应的最小荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TF&H DeBeer法[9] 位移法 将荷载实测荷载-位移曲线转化为双对数坐标轴的荷载-位移曲线,取双对数坐标轴的荷载-位移曲线斜率变化点对应荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TDB 初始斜率法[10] 图解法 取与初始直线段斜率相同且平移3.8 mm后的直线与实测荷载-位移曲线交点所对应的荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TST 双切线交点法[11-12] 图解法 取过初始弹性段和直线破坏段直线交点的水平线与实测荷载-位移曲线交点所对应荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TTI L1-L2两点法[13-14] 图解法 根据图2所示荷载-位移曲线3阶段特征,取初始弹性直线段终点L1对应的荷载为弹性极限荷载,取破坏直线线段起点L2对应的荷载为基础极限承载力,分别记为TL1和TL2 进一步地,取按照图2和表1所示不同失效准确定的基础极限承载力除以2LT,以T/2LT均值为y轴,相应失效准则确定的极限承载力所对应位移的均值为x轴,得到直柱等截面基础和直柱扩底基础抗拔归一化荷载-位移特征曲线对比如图3所示。
图3表明,不同失效准则所确定的基础极限承载力和位移值不同,从小到大顺序依次为:DeBeer法[9]、初始斜率法[10]、双切线交点法[11-12]、L1-L2两点法[13-14]、Terzaghi和Peck法[7]、Fuller和Hoy法[8],Chin双曲线法[6]最大,其过高估计了基础抗拔承载力。总体上看,L1-L2两点法取基础抗拔荷载-位移曲线初始弹直线性段终点荷载为弹性极限荷载,取破坏直线段起点荷载为基础塑性极限承载力,可较好地符合黄土抗拔基础荷载-位移曲线形态特征。
按L1-L2两点法,黄土直柱扩底和等直径直柱基础弹性极限荷载TL1对应位移1Ls均值分别为1.12,1.11 mm,二者较为接近,且对应1Ls/2Ls均值分别仅为0.04和0.08,抗拔弹性变形非常小。相应塑性极限荷载位移2Ls均值分别为25.75 mm和13.69 mm,基本满足一般结构物位移25 mm要求[16]。按L1-L2两点法确定的直柱扩底基础和等截面直柱基础弹性极限荷载1LT与塑性极限荷载2LT的比值分别为0.46和0.69。当试验中因加载能力限制而不能获得完整荷载-位移曲线时,可采用L1-L2两点法确定的弹性极限荷载1LT进行不同失效准则下基础抗拔极限承载力预估。对直柱等截面基础TST=1.371LT,TTI=1.471LT,2LT=1.521LT和TCHIN=1.721LT,对直柱扩底基础TST=1.721LT,TTI=2.021LT,2LT=2.211LT和TCHIN= 2.611LT。由此表明,在工程设计中如取黄土抗拔基础安全系数为2.5,则设计荷载下,黄土抗拔基础将均处于弹性承载状态。
2. 黄土平地基础抗拔承载机理
2.1 等截面直柱基础
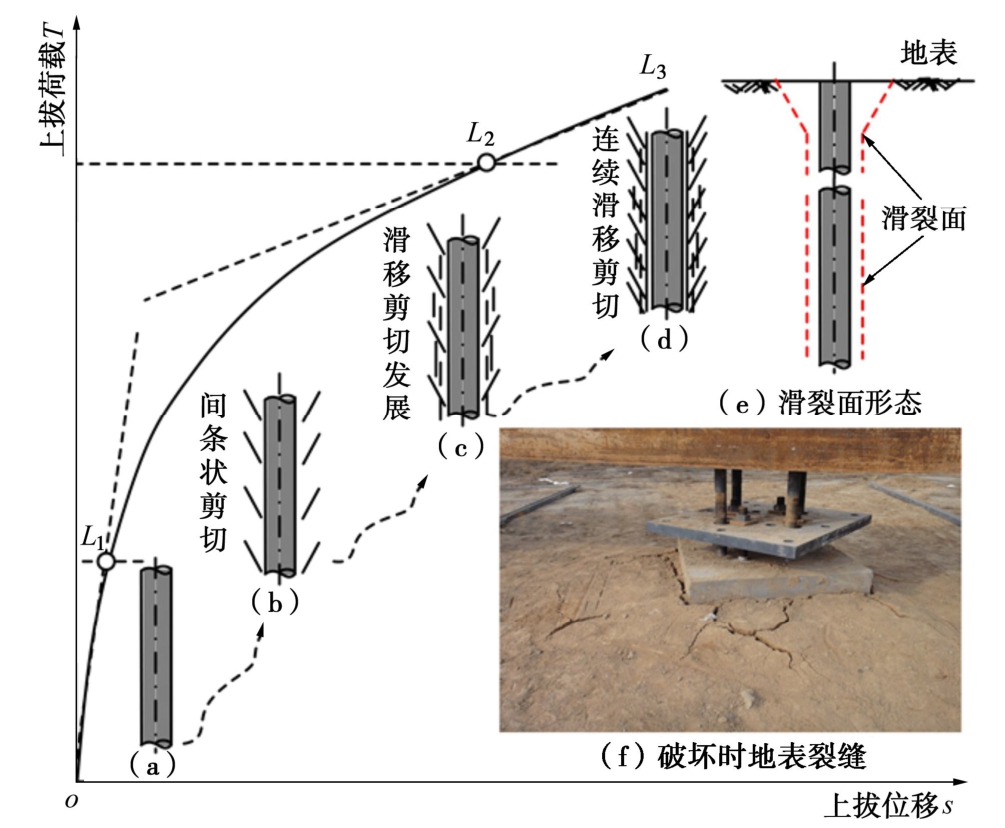
黄土等截面直柱基础埋深一般较大,抗拔承载力主要由基础直柱与其周围土体间摩擦阻力提供,其抗拔承载过程如图4所示。
当上拔荷载超过基础弹性极限承载力达到荷载-位移曲线L1点时,立柱接触面周围满足莫尔-库仑强度准则条件区域土体中出现间条状剪切面(图4(b)),并在空间上呈倒锥型斜面,基础沿接触面产生滑移较小。随上拔荷载继续增加,立柱周围土体中出现大致与界面平行的滑裂面(图4(c)),且随荷载增加而迅速发展、连续滑移,直至形成间条状剪切破坏面(图4(d)),荷载位移-曲线发展到L2点,达到抗拔基础极限承载力,基础立柱和黄土界面位移滑移值一般为13 mm左右,这与Kulhawy等[17]关于桩土界面圆柱形剪切破坏所需滑极限移值研究结果一致。当接近破坏时,荷载增加较小,位移迅速增大,下部呈圆柱形滑移而抽出破坏,靠近地表呈倒锥形破裂面(图4(e),(f))。
2.2 直柱扩底基础
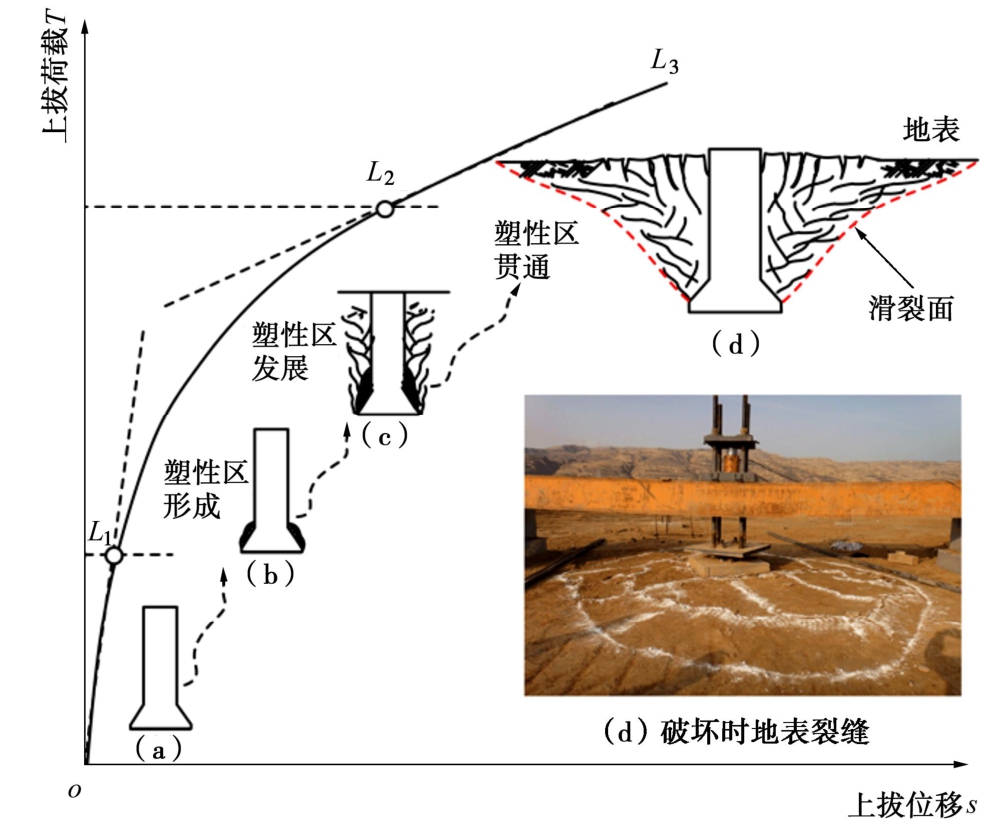
试验结果表明,直柱扩底基础极限抗拔承载力随深度变化存在临界深度hc。当基础抗拔埋深小于hc时呈浅基础破坏模式,抗拔土体滑动面一直延伸到地表,基础抗拔极限承载力随埋深增加而增加。当超过临界深度hc后,基础抗拔极限承载力随深度增加而提高的速率明显减小,临界埋深以上抗拔土体滑动面可延伸到地面,而在临界埋深以下,抗拔土体滑动面呈柱状。总体上看,黄土直柱扩底基础临界深度hc一般为扩底直径的3~4倍,呈扩大端土体压缩挤密产生弹性变形~基础周围土体塑性区形成、发展、贯通—土体整体剪切破坏的渐进过程,基础抗拔承载力主要由基础自重、滑动面剪切阻力及滑动面范围内土体重量组成。
图5为浅基础抗拔承载过程与破坏模式。初始加载阶段,荷载主要由基础自重和立柱周围土体侧摩阻力承担。随上拔荷载增加,立柱段摩阻力充分发挥并下移至扩大端,扩大端上方土体开始被压密而承载,荷载—位移曲线发展至L1点。上拔荷载持续增加,位移随荷载增加呈非线性变化且位移增加速率明显加大,扩大端周围土体由弹性状态转为塑性状态(图5(b)),并发生剪切变形,土体塑性区逐渐扩展(图5(c)),直至完全贯通(图5(d)),地表出现微裂缝并不断增大,抗拔土体滑裂面形成并延伸至地面,破坏时在地表产生环状和纵向裂缝(图5(e))。
图6为深基础抗拔承载过程与破坏模式。与浅基础抗拔承载过程相同,当等截面段侧阻力发挥至弹性极限值后,扩大端周围土体压缩挤密,直至局部进入塑性状态。随上拔荷载持续增长,位移继续增大,等截面直柱段侧摩力逐渐发挥至极限值,相应地在上拔过程中扩大端周边土体继续受挤压,塑性区范围进一步发展扩大,直至贯通而发生受压破坏,基础抗拔承载力达到极限值。但与浅基础抗拔承载过程不同,抗拔承载力极限状态时,基础底部扩大头段形成椭圆状局部破坏,而等截面段形成一曲线破裂面并延伸至地面的较小范围,如图6(e)所示。
3. 黄土斜坡基础抗拔承载性能
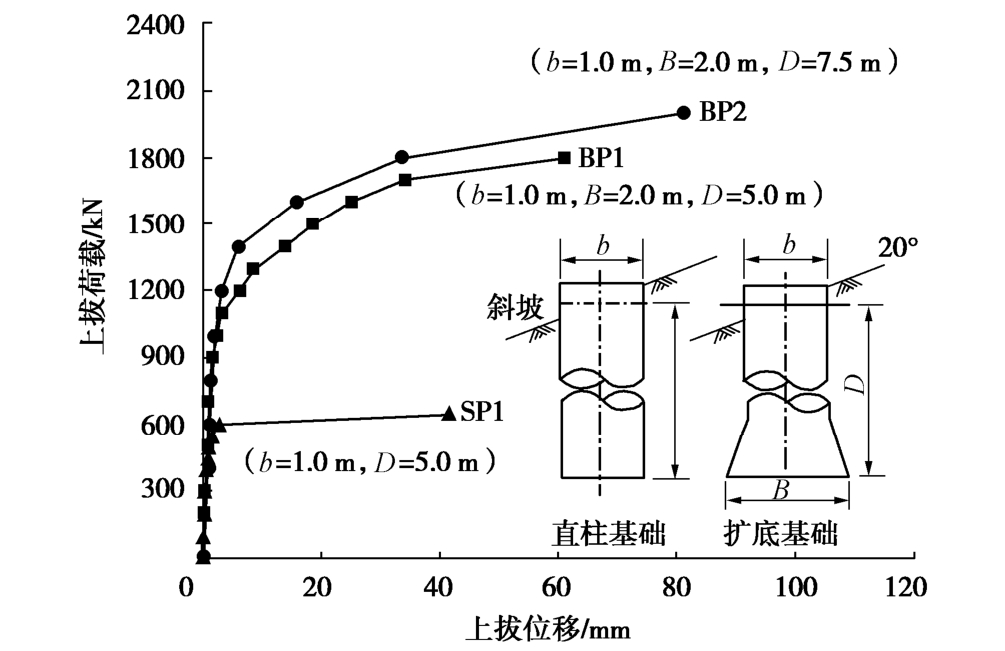
以甘肃定西市某黄土斜坡抗拔基础为例[3-4],试验场地坡度20°,共3个试验基础,其中等截面直柱基础SP1,直柱扩底基础BP1和BP2,基础结构尺寸及基顶位移均值随上拔荷载变化如图7所示。
图7表明,黄土斜坡等截面直柱基础抗拔荷载-位移曲线呈“陡降型”变化,陡降起始点极限上拔承载力600 kN,对应位移为2.82 mm。基础立柱侧壁与周围土体界面滑移而抽出破坏。然而,直柱扩底基础与黄土平地基础抗拔荷载-位移曲线变化规律相同,也呈图2所示的“缓变型”3阶段变化规律。采用L1-L2两点法确定BP1、BP2基础弹性极限荷载1LT分别为830,1040 kN,相应塑性极限荷载2LT分别为1700,1800 kN。因此,扩底和增加埋深均可显著黄土斜坡基础抗拔性能。
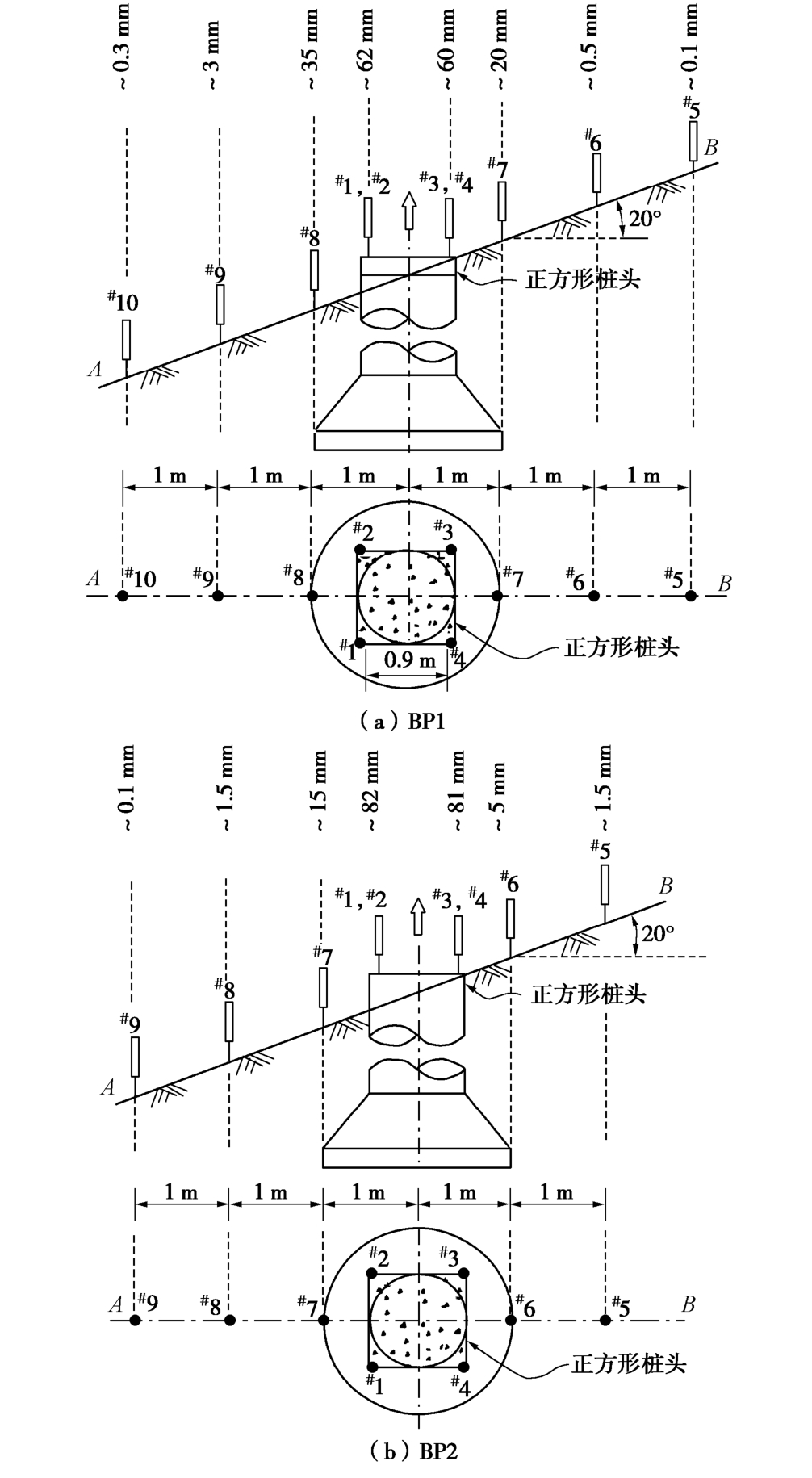
试验前,在斜坡地基下坡侧和上坡侧地表以及基础顶部布置了电子位移传感器,监测相应测点位移变化。图8以斜坡基础BP1和BP2为例,给出了极限荷载下地表不同测点和基顶测点位移大小。
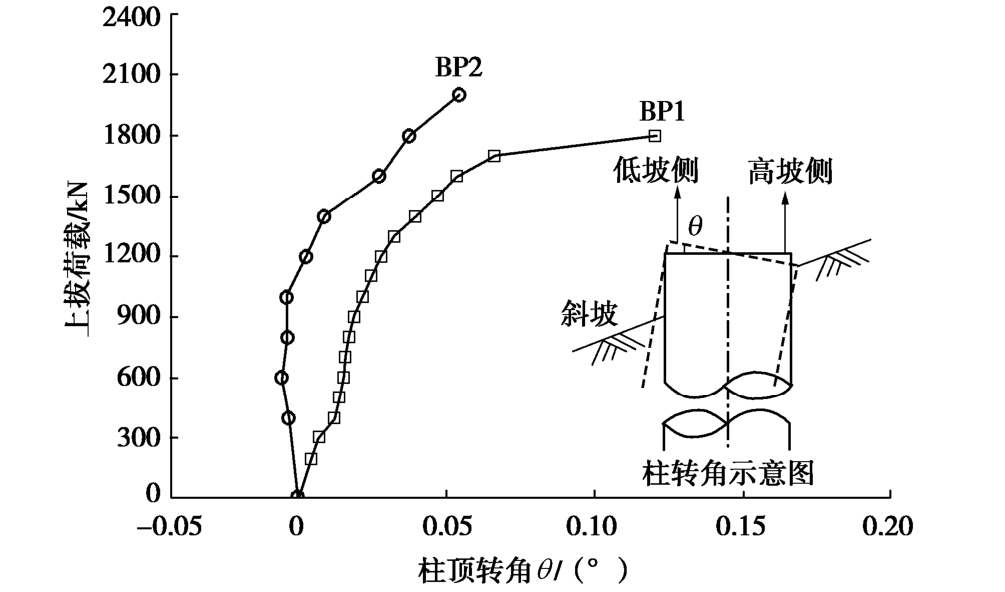
图8中基础顶部下坡侧位移传感器#1和#2均值要大于上坡侧传感器#3和#4的均值,因此每级上拔荷载作用下,基础顶部将产生竖向微小偏转,转角随荷载变化规律如图9所示。
由于基础BP2埋深大于BP1,相同上拔荷载作用下,BP2基顶转角要小于BP1。此外,图8中斜坡基础下坡侧黄土地表位移也明显大于上坡侧土体,抗拔土体破坏滑裂面形态及地表裂缝分布具有不对称性,如图10所示。
图10(a)中BP1呈浅基础破坏模式,基础破坏时地表裂缝延伸至地表呈环向和径向分布,并延伸向下坡侧较大范围,而上坡侧相对较小。相比较而言,BP2基础破坏时土体滑裂面延伸至地面,破裂面范围要远小于BP1基础,呈深基础破坏模式。因此,增加扩底基础埋深可有效提高黄土斜坡基础抗拔性能。
4. 结论
(1)黄土平地等截面直柱基础和直柱扩底基础抗拔荷载-位移曲线均呈3阶段变化规律:初始弹性直线段、弹塑性曲线过渡段和直线破坏段,L1-L2两点法可较好反映荷载-位移曲线变化特征。以L1-L2两点法确定的基础塑性极限荷载2LT为基准,对实测荷载-位移曲线进行归一化处理结果表明:直柱扩底和等截面直柱基础弹性极限荷载1LT对应位移均值分别为1.12,1.11 mm,塑性极限荷载2LT对应位移均值分别为25.75,13.69 mm。黄土抗拔基础设计安全系数取2.5,可使设计荷载作用下的黄土抗拔基础处于弹性承载状态。
(2)黄土等截面直柱基础和直柱扩底基础抗拔承载性能差异源于其承载机理的不同。前者抗拔承载力主要由基础直柱与周围土体间滑移而产生的侧阻力来提供,而后者呈扩大端土体压缩挤密发生弹性变形—塑性区形成、发展、贯通至土体整体剪切破坏的渐进过程,并可分为浅基础和深基础2种破坏模式,抗拔承载力主要由基础自重、滑动面剪切阻力及滑动面范围内土体重量组成。
(3)上拔荷载作用下,黄土斜坡地形等截面直柱基础和直柱扩底基础顶面沿上拔力方向均产生转角,下坡侧地表土体位移大于上坡侧,抗拔土体滑裂面及地表裂缝形成和发展具有不对称性。扩底和增加埋深可提高黄土斜坡基础抗拔承载性能。
-
表 1 几种典型的拔极基础限承载力确定准则
Table 1 Definitions of representative uplift interpretation criteria
名称 类别 极限承载力定义 Chin双曲线法[6] 数学法 将实测荷载-位移曲线按照直线型方程s/T=ms+c拟合,T为上拔荷载,s为上拔位移,m为直线斜率,c为截距。取直线斜率的倒数倒数1/m为极限承载力,记为TCHIN Terzaghi和Peck法[7] 位移法 取上拔位移25.4 mm所对应荷载为极限承载力,记为TT&P Fuller和Hoy法[8] 位移法 取位移变化速率为0.14 mm/kN所对应的最小荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TF&H DeBeer法[9] 位移法 将荷载实测荷载-位移曲线转化为双对数坐标轴的荷载-位移曲线,取双对数坐标轴的荷载-位移曲线斜率变化点对应荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TDB 初始斜率法[10] 图解法 取与初始直线段斜率相同且平移3.8 mm后的直线与实测荷载-位移曲线交点所对应的荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TST 双切线交点法[11-12] 图解法 取过初始弹性段和直线破坏段直线交点的水平线与实测荷载-位移曲线交点所对应荷载为基础极限承载力,记为TTI L1-L2两点法[13-14] 图解法 根据图2所示荷载-位移曲线3阶段特征,取初始弹性直线段终点L1对应的荷载为弹性极限荷载,取破坏直线线段起点L2对应的荷载为基础极限承载力,分别记为TL1和TL2 -
[1] 陈正汉, 郭楠. 非饱和土与特殊土力学及工程应用研究的新进展[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(1): 1-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901002.htm CHEN Zheng-han, GUO Nan. New developments of mechanics and application for unsaturated soils and special soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 1-54. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201901002.htm
[2] 鲁先龙, 乾增珍, 崔强. 黄土地基掏挖扩底基础抗拔试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(3): 647-652. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201403007.htm LU Xian-long, QIAN Zeng-zhen, CUI Qiang. Experimental investigation on uplift behavior of belled piers in loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(3): 647-652. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201403007.htm
[3] LU X L, QIAN Z Z, YANG W Z. Axial uplift behavior of belled piers in sloping ground[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2017, 40(4): 579-590.
[4] 杨文智, 崔强, 满银. 斜坡地基中基础抗拔承载特性的试验研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2016, 12(增刊2): 557-563. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE2016S2023.htm YANG Wen-zhi, CUI Qiang, MAN Yin. Test investigation upon uplift resistance characteristics of dig foundation in slope soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2016, 12(S2): 557-563. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE2016S2023.htm
[5] QIAN Z Z, LU X L, YANG W Z, et al. Comparative field tests on uplift behavior of straight-sided and belled shafts in loess under an arid environment[J]. Geomechanics & Engineering, 2016, 11(1): 141-160.
[6] CHIN F K. Estimation of the ultimate load of piles not carried to failure[C]//Proceedings of 2nd Southeast Asian Conference on Soil Engineering, 1970, Singapore.
[7] TERZAGHI K, PECK R B. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley, 1967.
[8] FULLER F M, HOY H E. Pile Load Tests Including Quick Load Test Method, Conventional Methods, and Interpretations[R]. Washington D C: Highway Research Board, 1970.
[9] DEBEER E E. Experimental determination of the shape factors and the bearing capacity factors of sand[J]. Géotechnique, 1970, 20(4): 387-411.
[10] O’ROURKE T D, KULHAWY F H. Observations on load tests on drilled shafts[C]//Drilled Piers and Caissons II. New York: ASCE, 1985: 113-128.
[11] HOUSEL W S. Pile load capacity: estimates and test results[J]. Journal of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Division, 1966, 92(SM4): 1-30.
[12] TOMLINSON M J. Pile design and construction practice (a viewpoint publication)[M]. London: Cement & Concrete Association of Great Britain, 1977.
[13] HIRANY A, KULHAWY F H. Conduct and Interpretation of Load Tests on Drilled Shaft Foundations: Detailed Guidelines[R]. California: Electric Power Research Institute U S A, 1988.
[14] HIRANY A, KULHAWY F H. On the interpretation of drilled foundation load tests results[C]//Deep Foundation 2002(GSP 116), 2002, Reston.
[15] LU X L, QIAN Z Z, ZHENG W F, et al. Characterization and uncertainty of uplift load-displacement behaviour of belled piers[J]. Geomechanics & Engineering. 2016, 11(2): 211-234.
[16] DITHINDE M, PHOON K K, WET M D, et al. Characterization of model uncertainty in the static pile design formula[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2011, 137(1): 70-85.
[17] KULHAWY F H, TRAUTMANN C H, BEECH J F, et al. Transmission line structure foundations for upliftcompression loading[R]. New York: Electric Power Research Institute, 1983.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 梁绍敏,冯云田,赵婷婷,王志华. 颗粒材料破碎行为数值分析方法研究综述. 力学学报. 2024(01): 1-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 丁林楠,李国英. 基于分形级配方程的堆石料颗粒破碎SBG模型. 岩土工程学报. 2022(02): 264-270 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 吴二鲁,朱俊高,陆阳洋,钱彬. 基于颗粒破碎耗能的粗粒料剪胀方程研究. 岩土工程学报. 2022(05): 898-906 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: