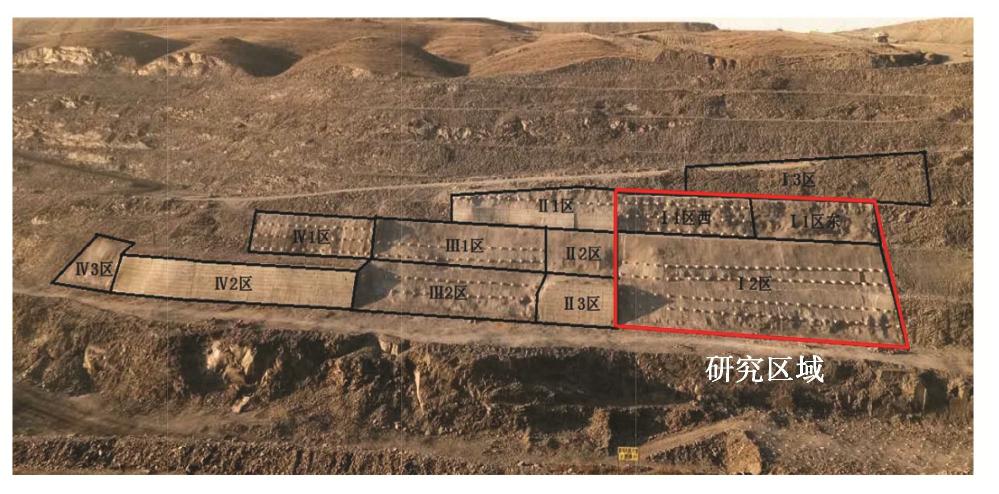
Anchorage effect of NPR cable based on second-order work criterion
-
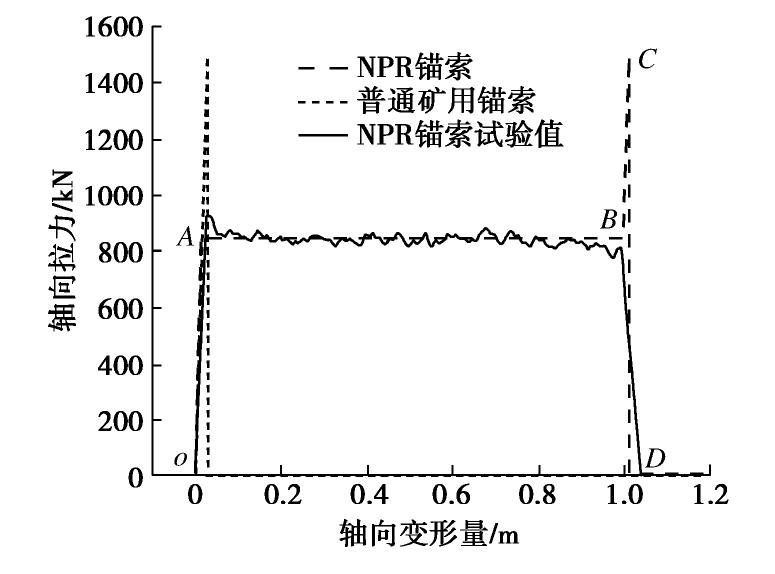
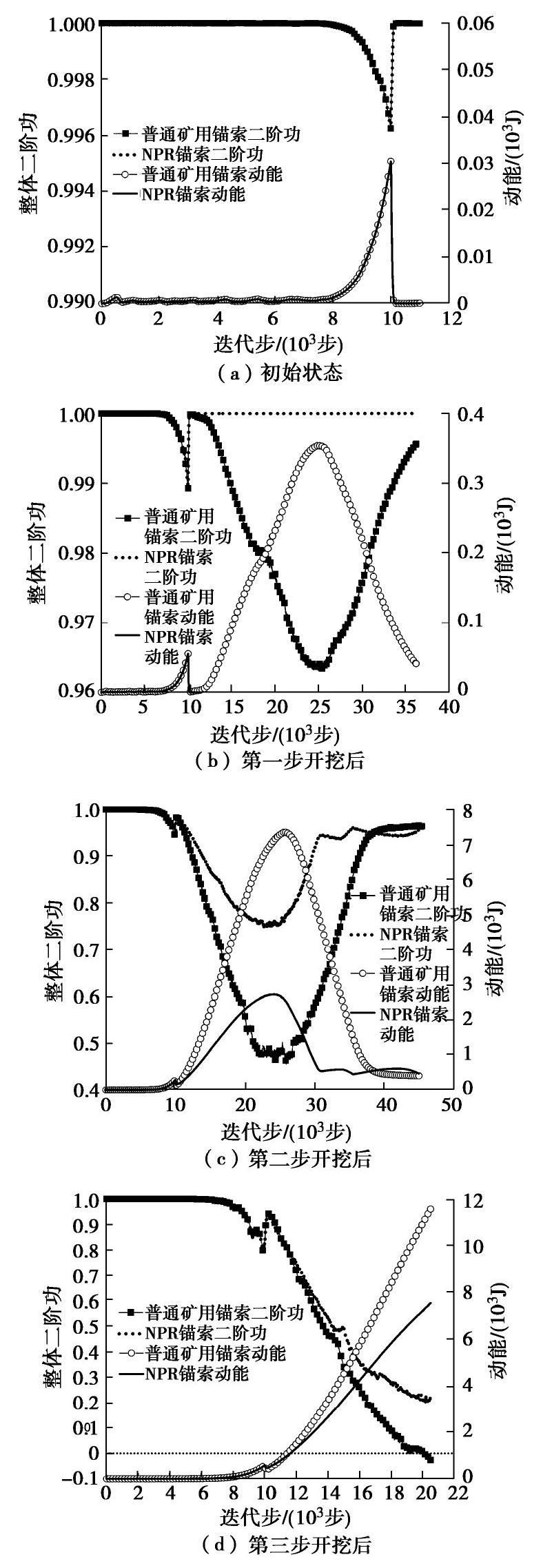
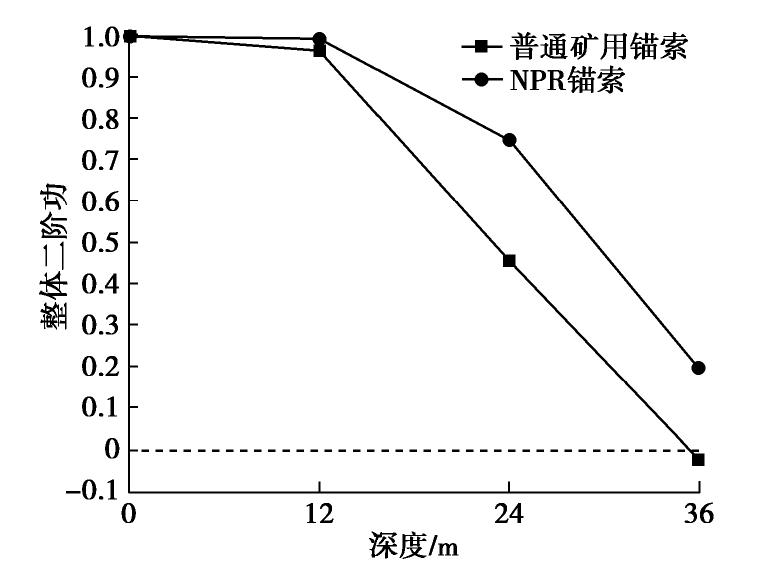
摘要: NPR锚索因其具有恒定工作阻力和较大变形量的特性,已广泛应用于巷道的加固和监测预警中。为了研究NPR锚索在露天矿山边坡中的支护效果,首先基于有限差分软件FLAC3D中的锚索单元开发出NPR锚索单元,并通过数值拉伸试验验证了NPR锚索比普通锚索具有更优异的吸能特性;之后引入二阶功作为边坡稳定性评价准则,并将其植入显式动力学算法中,详细讨论了其合理性和可靠性;最后,以浩尧尔忽洞金矿西采场北帮开挖诱发的滑坡为研究对象,对现有普通矿用锚索和NPR锚索支护体系下的边坡稳定性进行对比分析。根据数值模拟结果可知,NPR锚索支护体系下的边坡稳定性明显优于普通矿用锚索。Abstract: Due to the characteristics of constant working resistance and steady large deformation, the NPR cable has been widely applied in monitoring and reinforcement of a large number of roadways. In order to study the anchorage effect of NPR cables in open-pit slope, firstly, the NPR cable element is developed based on the cable element in the finite difference software FLAC3D, and it is proved by the tensile tests that the NPR cable has better energy absorbing capacity than the traditional one. Secondly, the second-order work criterion is then implemented, and the rationality and advantages of the second order work criterion as a safety factor in explicit numerical algorithm are discussed. Finally, the rock slope induced by the excavation at the north side of the west stope in Haoyaoerhudong Opencast Gold Ore is taken as the research object, and the stability of rock slope under the existing traditional mine cable support system and NPR cable support system is compared and analyzed. According to the numerical results, the global second-order work and kinetic energy of each loading step have the opposite variation tendency, and the slope stability of NPR cable support system is obviously better than that of the traditional mine cable.
-
Keywords:
- NPR cable /
- safety factor /
- stability of rockslope /
- second-order work /
- instability criterion
-
0. 引言
土的渗透特性是土重要的工程性质之一,影响着土木工程的施工。目前无黏性土渗透特性的试验研究,多是采用竖向圆柱体模型槽进行,试验中土体受到的水流的作用方向是由下至上的竖直方向,而对于土体承受水平向渗流时土体渗透特性的研究不多[1],渗流方向对土体渗流变形特性的研究还尚未给予足够重视。对土渗流的研究表明,实际施工中渗流的优势方向往往是水平方向,通常土体水平向的渗透性大于竖向,而抵抗水平向渗透破坏的能力低于抵抗竖向渗透破坏的能力[2-6]。
本文针对粉砂竖向和水平向渗透特性研究存有的不足,利用自主设计的实验装置,对粉砂开展竖向和水平向渗流试验,对比分析了两种不同方向渗流场下粉砂的渗透特性。基于室内模拟试验,建立三维离散元与计算流体力学耦合的细观力学模型,对粉砂在竖向和水平向的渗流情况进行分析和计算。通过数值计算结果,对竖向和水平向渗流作用下的粉砂内部接触力、渗流速度及流场的分布规律进行细观分析,将数值模拟与室内试验的结果进行分析、比较。
1. 不同渗流方向下粉砂渗透变形室内试验模拟
1.1 试验仪器和方法
(1)试验仪器
粉砂的竖向渗透变形试验借助实验室自主设计的圆柱形渗流试验仪进行,该装置示意图如图1所示。粉砂水平向渗流渗透变形特性的研究是在自主设计的水平渗流试验装置中进行的,见图2。模型由进水系统,装样区及排水系统3个主要部分组成。进水系统可以通过对进水水头高度的调节自由选择水头加载高度。
(2)试验方法及步骤
粉砂烘干并分层装样。称样烘干24 g取出装样,每10 cm分为一层进行装样;排气饱和。装样完成,分次提升水箱供水高度对试验土样进行饱和,最后一次使水头抬升至与试样顶端齐平,静置24 h;逐级调整水头进行试验。逐级抬升水头高度,对测压管水头高度读数并记录,同时量测渗流量大小,记录试验进程中的渗流现象,直至该级渗流稳定,转入下一级水头;当试验过程中,流量忽然增大,并出现明显的渗流通道,可以认定为试样发生渗透破坏,不再继续加大水头高度,试验完成。
1.2 粉砂竖向和水平向渗流试验结果分析
对粉砂在竖向渗流下的渗透流速受水力梯度影响下的变化规律进行研究,得到渗流速度随水力梯度变化的关系曲线,如图3所示。对粉砂在水平向渗流作用下的临界水力梯度进行研究,结果如图4所示。
由图3得到,在水力梯度
<0.787时,渗流速度随水力梯度呈近似线性的变化,此时土样处于渗流稳定阶段;当水力梯度为1.1时,渗流速度忽然增大,粉砂颗粒流失量也徒增,此时土体发生渗透变形。图4粉砂在水平向渗流下的变化规律显示:水力梯度小于0.45时,粉砂土渗透流速随着水力梯度的增大呈线性增长,水流清澈,粉砂流出较少。当水力梯度增至0.52时,试样整体的流速瞬间增大,粉砂流出量明显增多且呈持续流失状态,此时粉砂土样内部颗粒运移不再规律,试样开始发生渗透破坏。 表1给出粉砂在两种渗流方向下的渗透系数、临界坡降与破坏坡降。粉砂在竖向渗流时的临界水力梯度为0.787,破坏水力梯度为1.10;而水平向渗流中,所能承受的临界水力梯度为0.45。在影响因素诸如种类、级配、密度、孔隙大小等相同的前提下,粉砂竖向渗流的临界水力梯度比水平向高出近44%。由于土体在受到水平向渗流时,平均渗透系数取决于最透水土层的厚度和渗透性;而对于竖向渗流,其平均渗透系数取决于最不透水土层的渗透性。加之,竖向渗流中重力作用与渗流方向一致,会产生对土层的压密作用,使得该渗流方向下的渗透系数小于水平向,而土体能够承受的水头高于水平向的渗流。
表 1 不同渗流方向下粉砂渗透系数、临界坡降和破坏坡降Table 1. Datat of permeability coeffieient of silt, critical slope and failure slope under different seepage directions渗流方向 渗透系数/(10-4 cm·s-1) 临界水力梯度 破坏水力梯度 竖向 6.13 0.787 1.10 水平 6.25 0.450 0.52 2. 不同渗流方向下粉砂渗透变形颗粒流模拟
对于固相颗粒,通过求解运动和动量方程模拟颗粒运动,采用离散元的颗粒流理论进行模拟;对于液相介质,采用均一化流体计算技术模拟其在孔隙中的运动,也就是通过求解平均Navier-Stokes方程模拟孔隙中流体的运动[7-9]。
2.1 数值模型
对粉砂土不同向渗流形态的模拟中,边界条件的界定也略有不同。竖向渗流下,颗粒周边的边界为固壁边界条件,上下为压力边界条件。水平向渗流下,模型的前后和上下边界为固壁边界条件,左右设置为压力边界条件和自由边界条件。生成的土体模型如图5所示。
对于竖向的渗流,按照试验中模型,上覆为自由边界,没有压重。对于水平向的渗流,试样在重力和浮力作用下保持平衡,当作用渗流力后,土中小颗粒将从模型右侧流出,因此在试样右侧设置了相互交叉垂直的线墙,如图6所示。
2.2 数值计算流程
采用PFC3D对流固耦合问题进行计算流程如图7所示。
2.3 数值模拟结果
(1)粉砂土竖向和水平向渗流下渗透变形情况
a)粉砂竖向渗流下的渗透变形情况
图8给出了粉砂在竖向渗流作用下,土样随水力梯度的变化情况。
水力梯度从0.1,0.2,0.3,...,逐级增加,水力梯度施加至0.7时,粉砂几乎无变化;当水力梯度增至0.8时,土样出现从底部被整体抬升的趋势,发生少量细小颗粒流失的现象;水力梯度继续增至1.0时,土体发生了整体的抬升,土体表面颗粒簇发生整体迁移的现象。模拟结果表明,试样的临界水力梯度在0.8左右。
b)粉砂水平向渗流下的渗透变形情况
粉砂土的水平向渗流中水力梯度也是由0.1,0.2,0.3依次逐级抬升,图9给出了粉砂土在水平向渗流下试样随水力梯度变化的情况。
从图9中可以看出,当水力梯度增至0.3时,试样底部细小颗粒也开始发生迁移,水力梯度继续增大至0.4,此时试样发生颗粒成团的流失,土体发生了渗透变形。水力梯度加载至0.5时,土体颗粒发生了更加显著的整体性渗流破坏。根据模拟结果,得到粉砂土水平向渗流的临界水力梯度在0.4左右。
(2)粉砂土竖向和水平向渗流下配位数变化情况分析
土体的配位数表示了颗粒间的接触数,是表达土颗粒间接触情况的参数之一,总配位数是颗粒与颗粒之间以及颗粒与墙之间的平均接触数,反映出试样的压密程度;力学配位数为颗粒与颗粒之间接触数大于2时的颗粒接触数,反映额土骨架的压密程度。图10,11给出了粉砂土在竖向和水平向渗流作用下,配位数随水力梯度的变化情况。
图10,11可以看出,当竖向渗流的水力梯度为0.8,水平向渗流水力梯度为0.4时,土体的两个配位数都发生迅速的下降,说明此时的土体状态发生了较大的变化,即渗透变形发生。图中,总配位数和力学配位数都在随着水力梯度的增大而不断降低,总的配位数较力学配位数下降更快速,幅度也更大。这是由于水力梯度增大,颗粒发生了移动,颗粒的接触数减小,但在水力梯度增加至土体渗透变形前的整个过程中,总配位数下降幅度明显大于力学配位数,说明发生移动的多为小颗粒,小颗粒的运移使土体中接触数减少,随之小颗粒填充至骨架颗粒孔隙间,与大颗粒发生接触,保持了力学配位数的大小。
3. 结论
(1)粉砂在水平向能承受的渗流破坏作用一般低于竖向渗流。
(2)数值模拟结果与模拟试验过程中粉砂的渗流变化过程相符,数值方法所测得的临界水力梯度与试验测得的结果亦较为吻合。
(3)竖向和水平向渗流下,粉砂的总配位数和力学配位数均随着水力梯度的抬升而衰减,当土体发生渗透破坏,土体配位数出现迅速降低。
-
表 1 锚杆(索)物理力学参数
Table 1 Physical and mechanical parameters for bolts and cables
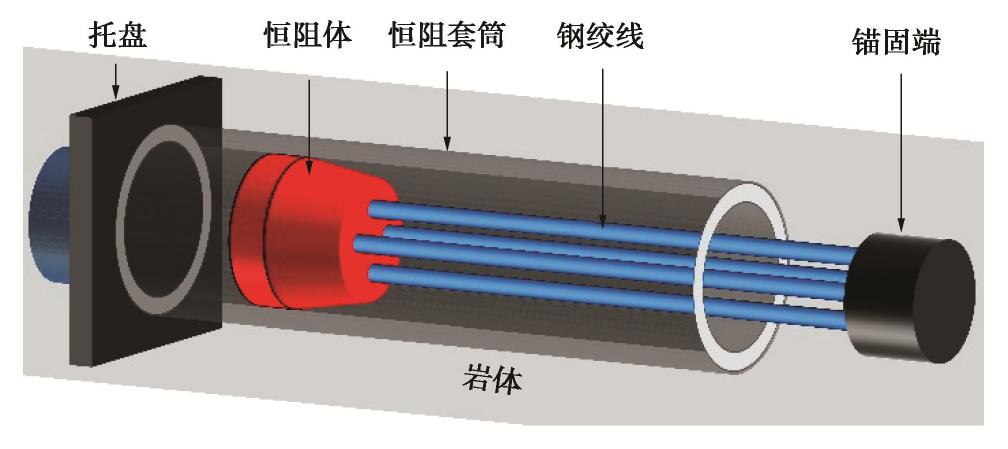
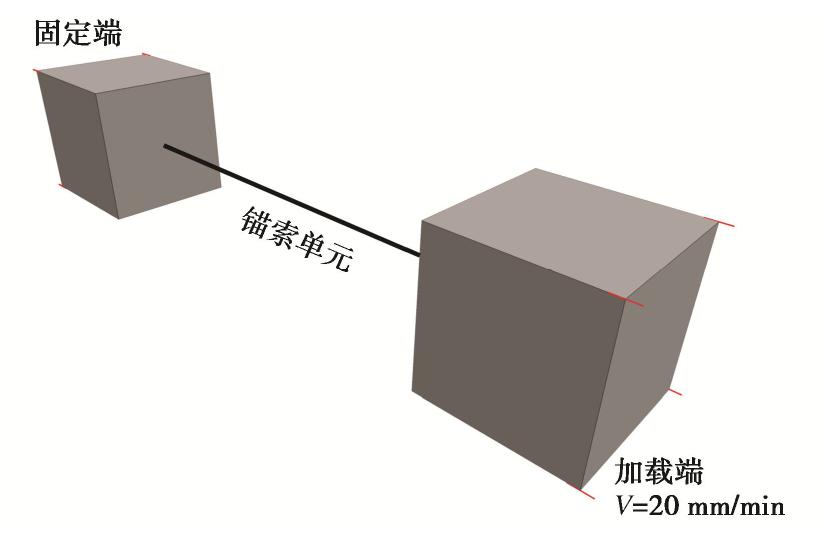
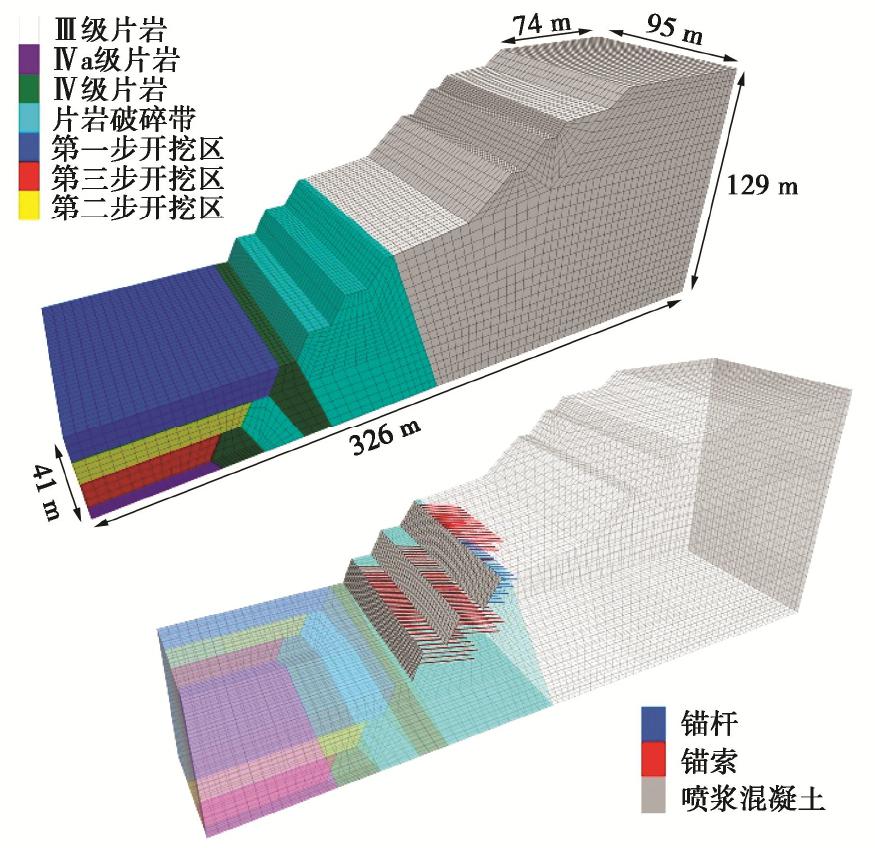
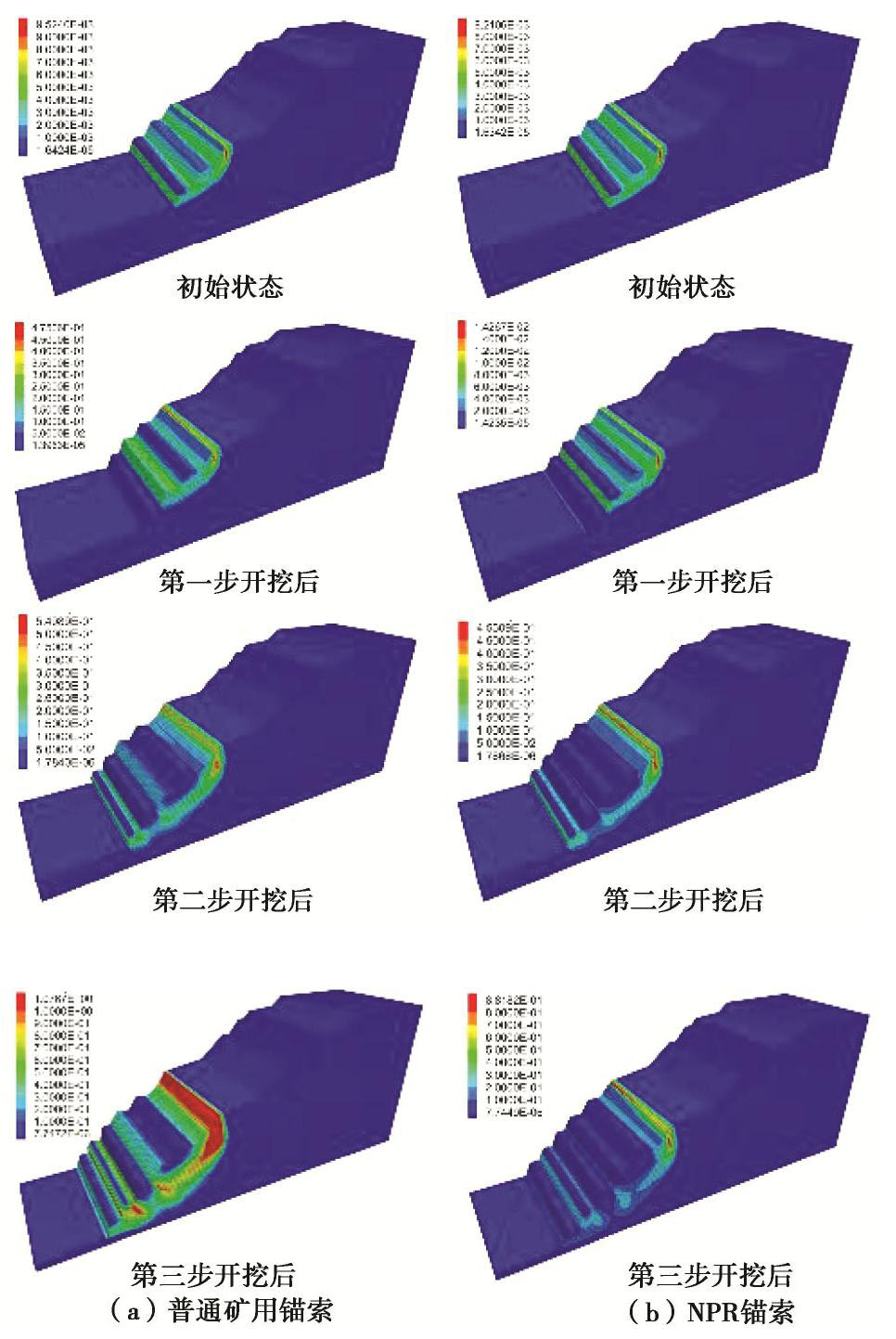
锚固类别 强度/kN 杨氏模量/GPa 长度/m 预应力/kN 横截面/m2 恒阻力/kN 变形量/mm NPR锚索 1500 205 27 750 0.2238 850 1000 矿用锚索 1500 205 27 750 0.2238 — — 矿用锚杆 800 205 8 0 0.373×10-3 — — 表 2 边坡岩体物理力学参数
Table 2 Physical and mechanical parameters of involved rockmass
类型 /(kg·cm-3) E/GPa c/MPa /(°) TS/MPa Ⅲ级片岩 2.7 4.54 0.25 0.40 35 0.12 Ⅳ级片岩 2.5 4.11 0.30 0.15 28 0.10 Ⅳa级片岩 2.5 4.11 0.30 0.15 28 0.10 片岩破碎带 2.4 2.50 0.35 0.02 18 0.10 开挖区 2.5 4.11 0.30 0.15 28 0.10 -
[1] 何满潮. 露天矿高边坡工程[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1991. HE Man-chao. High Slope Engineering in Open-Pit Mine[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House, 1991. (in Chinese)
[2] HE M C, GONG W L, WANG J, et al. Development of a novel energy-absorbing bolt with extraordinarily large elongation and constant resistance[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2014, 67: 29-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.01.007
[3] 吕谦, 陶志刚, 李兆华, 等. 恒阻大变形锚索弹塑性力学分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(4): 792-800. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201804002.htm LÜ Qian, TAO Zhi-gang, LI Zhao-hua, et al. Elasto-plastic analysis of large deformation cables[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018, 37(4): 792-800. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201804002.htm
[4] CAI Y, ESAKI T, JIANG Y. A rock bolt and rock mass interaction model[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(7): 1055-1067.
[5] LI C C. A new energy-absorbing bolt for rock support in high stress rock masses[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2010, 47(3): 396-404. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.01.005
[6] ORTLEPP W D, READ J J. Yieldable rock bolts for shock loading and grouted bolts for faster rock stabilization[J]. Mining Engineering, 1970, 60(3): 12-17.
[7] ST-PIERRE L, HASSANI F P, RADZISZEWSKI P H, et al. Development of a dynamic model for a cone bolt[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2009, 46(1): 107-114.
[8] CHARETTE F, PLOUFFE M. A new rock bolt concept for under ground excavations under high stress conditions[C]//Proceedings of the 6thInternational Symposium on Ground Support in Mining and Civil Engineering Construction, 2008, Johannesburg.
[9] LI C C. Field observations of rock bolts in high stress rock masses[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2010, 43(4): 491-496. doi: 10.1007/s00603-009-0067-8
[10] HE M, SOUSA L R E. Experiments on rock burst and its control[C]//Australasian Ground Control in Mining Conference, 2014, Sidney.
[11] 何满潮. 滑坡地质灾害远程监测预报系统及其工程应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(6): 1081-1090. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.06.001 HE Man-chao. Real-time remote monitoring and forecasting system for geological disasters of landslides and its engineering application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(6): 1081-1090. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.06.001
[12] HE M, TAO Z, ZHANG B. Application of remote monitoring technology in landslides in the Luoshan mining area[J]. Mining Science and Technology, 2009, 19(5): 609-614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2686.2009.05.011
[13] 何满潮, 李晨, 宫伟力, 等. NPR锚杆/索支护原理及大变形控制技术[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(8): 1513-1529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201608001.htm HE Man-chao, LI Chen, GONG Wei-li, et al. Support principles of NPR bolts/cables and control techniques of large deformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(8): 1513-1529. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201608001.htm
[14] 何满潮, 郭志飚. 恒阻大变形锚杆力学特性及其工程应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(7): 1297-1308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201407001.htm HE Man-chao, GUO Zhi-biao. Mechanical property and engineering application of anchor bolt with constant resistance and large deformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(7): 1297-1308. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201407001.htm
[15] SUN X M, ZHANG Y, WANG D, et al. Mechanical properties and supporting effect of CRLD bolts under static pull test conditions[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2017, 24(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1007/s12613-017-1372-y
[16] HE M, LI C, GONG W, et al. Dynamic tests for a Constant-Resistance-Large-Deformation bolt using a modified SHTB system[J]. Tunnelling & Underground Space Technology, 2017, 64(5): 103-116.
[17] Itasca . FLAC3D User Manual, Version 6.0[J]. Itasca Consulting Group Inc., USA2017.
[18] LI Z H, JIANG Y J, TAO Z G, et al. Monitoring prediction of a rockslide in an open-pit mine and numerical analysis using a material instability criterion[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78(3): 2041-2053. doi: 10.1007/s10064-017-1224-z
[19] 陶志刚, 李海鹏, 孙光林, 等. 基于恒阻大变形锚索的滑坡监测预警系统研发及应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(10): 3032-3040. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201510046.htm TAO Zhi-gang, LI Hai-peng, SUN Guang-lin, et al. Development of monitoring and early warning system for landslides based on constant resistance and large deformation anchor cable and its application[J]. Rock & Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(10): 3032-3040. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201510046.htm
[20] ADHIKARY D P, DYSKIN A V. Modelling of progressive and instantaneous failures of foliated rock slopes[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2007, 40(4): 349-362. doi: 10.1007/s00603-006-0085-8
[21] 杨有成, 李群, 陈新泽, 等. 对强度折减法若干问题的讨论[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(4): 1103-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.047 YANG You-cheng, LI Qun, CHEN Xin-ze, et al. Discussion on strength reduction using FLAC[J]. Rock & Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(4): 1103-1106. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.047
[22] PRUNIER F, CHOMETTE B, BRUN M, et al. Designing geotechnical structures with a proper stability criterion as a safety factor[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2016, 71(5): 98-114.
[23] HILL R. A general theory of uniqueness and stability in elastic-plastic solids[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1958, 6(3): 236-249. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(58)90029-2
[24] MERRIEN-SOUKATCHOFF V, DURIEZ J, GASC-BARBIER M, et al. Mechanical Stability Analyses of Fractured Rock Slopes[M]//Rockfall Engineering, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2013: 67-112.
[25] NICOT F, LERBET J, DARVE F. Second-order work criterion: from material point to boundary value problems[J]. Acta Mechanica, 2017, 228(7): 2483-2498. doi: 10.1007/s00707-017-1844-1
[26] NICOT F, SIBILLE L, DONZE F, et al. From microscopic to macroscopic second-order work in granular assemblies[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2007, 39(7): 664-684. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2006.10.003
[27] NICOT F, HADDA N, BOURRIER F, et al. Inertia effects as a possible missing link between micro and macro second-order work in granular media[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2012, 49(10): 1252-1258. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.02.005
[28] NICOT F, DARVE F, KHOA H D V. Bifurcation and second-order work in geomaterials[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2007, 31(8): 1007-1032.
[29] 黄茂松, 曲勰, 吕玺琳. 基于状态相关本构模型的松砂静态液化失稳数值分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(7): 1479-1487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201407021.htm HUANG Mao-song, QU Xie, LÜ Xi-lin. Instability and static liquefaction analysis of loose sands with a state-dependent constitutive model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics & Engineering, 2014, 33(7): 1479-1487. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201407021.htm
[30] 吕玺琳, 赖海波, 黄茂松. 饱和土体静态液化失稳理论预测[J]. 岩土力学, 2014(5): 1329-1333, 1339. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201405018.htm LÜ Xi-lin, LAI Hai-bo, HUANG Mao-song. Theoretically predicting instability of static liquefaction of saturated soils[J]. Rock & Soil Mechanics, 2014(5): 1329-1333, 1339. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201405018.htm
[31] 吕玺琳, 钱建固, 黄茂松. 不排水加载条件下K0固结饱和砂土失稳预测[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(6): 1010-1015. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201506007.htm LÜ Xi-lin, QIAN Jian-gu, HUANG Mao-song. Prediction of instability of K0-consolidated saturated sands under undrained loading conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(6): 1010-1015. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201506007.htm
[32] 刘洋, 樊猛, 晏洲毅. 常偏应力剪切条件下砂土失稳模式的离散元模拟[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(3): 467-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202003011.htm LIU Yang, FAN Meng, YAN Zhou-yi. DEM simulation of instability mode in sand under constant shear drained conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(3): 467-475. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202003011.htm
[33] LI Z, DUFOUR F, DARVE F. Hydro-elasto-plastic modelling with a solid/fluid transition[J]. Computers & Geotechnics, 2016, 75(2): 69-79.
[34] LI Z H, JIANG Y J, LV Q, et al. Consistent modeling of a catastrophic flowslide at the Shenzhen landfill using a hydro-elasto-plastic model with solid-fluid transition[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2018, 13(6): 1451-1466.
[35] 王立忠, 舒恒. Hill稳定条件在有限元法计算地基承载力中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(增刊1): 3122-3131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2010S1079.htm WANG Li-zhong, SHU Heng. Application of hill's stability condition to bearing capacity computation of foundation with finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics & Engineering, 2010, 29(7): 3122-3131. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2010S1079.htm
[36] NICOT F, DAOUADJI A, LAOUAFA F, et al. Second-order work, kinetic energy and diffuse failure in granular materials[J]. Granular Matter, 2011, 13(1): 19-28.
[37] NICOT F, DARVE F. Failure in rate-independent granular materials as a bifurcation toward a dynamic regime[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2012, 29(1): 136-154.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 应宏伟,陈雨,王阳扬,刘冠. 含碎石芯软黏土复合试样大三轴试验研究. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(11): 104-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邱俊峰,叶晨峰,陈峰,郑铖杰. 镍铁渣粉水泥固化砂土剪切强度与应力应变关系研究. 湖南文理学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 78-82+95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 殷天军,宁华宇,寇晓强. 深中通道沉管基础水下深层水泥搅拌桩应用全过程探讨. 中国港湾建设. 2022(07): 11-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张振,郑文强,叶观宝,陈勇. 循环荷载下水泥土桩复合单元体变形特性及其地基长期沉降计算方法. 中国公路学报. 2022(11): 21-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: